Abstract
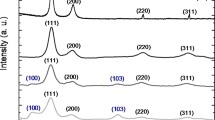
Alumina–titania mixed oxide nanocatalysts with molar ratios = 1:0.5, 1:1, 1:2, 1:5 have been synthesized by adopting a hybrid sol–gel route using boehmite sol as the precursor for alumina and titanium isopropoxide as the precursor for titania. The thermal properties, XRD phase analysis, specific surface area, adsorption isotherms and pore size details along with temperature programmed desorption of ammonia are presented. A specific surface area as high as 291 m2/g is observed for 1:5 Al2O3/TiO2 composition calcined at 400 °C, but the same composition when calcined at 1,000 °C, resulted in a surface area of 4 m2/g, while 1:0.5 composition shows a specific surface area of 41 m2/g at 1,000 °C. Temperature programmed desorption (of ammonia) results show more acidic nature for the titania rich mixed oxide compositions. Transmission electron microscopy of low and high titania content samples calcined at 400 °C, shows homogeneous distribution of phases in the nano range. In the mixed oxide, the particle size ranges between 10–20 nm depending on titania content. The detailed porosity data analysis contributes very much in designing alumina–titania mixed oxide nanocatalysts.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colomban P (1987) Rev. Phys Appliquee 22:719. doi:10.1051/rphysap:01987002208071900
Phachecomalagon G, Garucaborquez A, Costeer D, Sklyaroew A, Petit S, Fripiat JJ (1995) J Mater Res 10(5):1264. doi:10.1557/JMR.1995.1264
Kumar KNP, Keizer K, Burggraaf AJ (1993) J Mater Chem 3(9):917. doi:10.1039/jm9930300917
Kumar KNP (1994) Appl. Catal. A. Gen 119(1):163. doi:10.1016/0926-860X(94)85032-1
Ramirez J, Alejandre AG (1997) J Catal 170:108. doi:10.1006/jcat.1997.1713
Linacero R, Cervantes MLR, De L, Lopez-Gonzalez D (2000) J Mater Sci 35:3269. doi:10.1023/A:1004875322935
Lee HL, Lee HS (1994) J Mater Sci Lett 13:316. doi:10.1007/BF00420784
Toba M, Mizukami F, Niwa S, Kiyozumi Y, Maeda K, Annila A, Komppa V (1994) J Mater Chem 4(4):585. doi:10.1039/jm9940400585
Montoya JA, Delangel P, Viveros T (2001) J Mater Chem 11(3):944. doi:10.1039/b008161m
Mani TV, Pillai PK, Damodaran AD, Warrier KGK (1994) Mater Lett 19:237. doi:10.1016/0167-577X(94)90163-5
Lowel S, Shields JE (1984) Powder surface area and porosity, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, London
Padmaja P, Krishna Pillai P, Warrier KGK, Padmanabhan M (2004) J Porous Mater 11:147. doi:10.1023/B:JOPO.0000038010.54859.2f
Padmaja P, Warrier KGK, Padmanabhan M, Wunderlich W, Berry FJ, Mortimer M, Creamer NJ (2006) Mater Chem Phys 95:56. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.05.044
Acknowledgment
P. Padmaja acknowledges the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for a Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padmaja, P., Warrier, K.G.K., Padmanabhan, M. et al. High surface area sol–gel alumina–titania nanocatalyst. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 52, 88–96 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-009-1998-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-009-1998-y