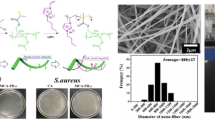
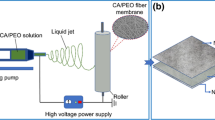
Abstract
Electret fiber filtration materials prepared by electrostatic spinning and corona polarization have drawn significant interest in treating radioactive aerosols. In this study, a three-dimensional biomass-based electret nanofiber aerogel material with high dust capacity, high filtration efficiency and low-pressure drop was created by pore structure regulation. The results showed that aerogels with good charge capture and storage ability were obtained by regulating the concentration of tert-butanol and ethylcellulose fiber suspension, and the pre-freezing temperature. The initial surface potential and stable surface potential increased from 0.85 and 0.05 kV to 1.37 and 0.15 kV respectively. Furthermore, the purification time was reduced from 44 to 15 min.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams S, Odonkor S (2021) Status, opportunities, and challenges of nuclear power development in Sub-Saharan Africa: the case of Ghana. Prog Nucl Energy 138:103816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2021.103816
Kim SI, Lee HY, Jung WC, Song JS (2021) Evaluation OF internal exposure to radioactive aerosol generated from plasma melting system using the bidas code. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 194:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncab061
Lee HY, Yang KT, An JY et al (2022) Evaluation of workers’ internal exposure because of inhalation of radioactive aerosols in a plasma melting facility by using IMBA and TAURUS codes. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 331:4397–4404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08512-w
Lee RE (1972) The size of suspended particulate matter in air: size distributions of ambient aerosols must be studied in order to determine their effects on the environment. Science 178:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.178.4061.567
Zosky GR (2023) Air pollution and respiratory health—Do we really need more evidence. Respirology 28:513–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.14490
Bayram H, Rastgeldi Dogan T, Şahin ÜA, Akdis CA (2023) Environmental and health hazards by massive earthquakes. Allergy 78:2081–2084. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.15736
Shukla SD, O’Toole RF (2020) Exposure to bushfire and biomass smoke and the risk of bacterial and viral lung infection. Respirology 25:1121–1122. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.13908
Li S, Guo Y (2018) Hazardous haze in Asia and breathing problems: editorial. Respirology 23:883–884. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.13336
Levy JI, Biton L, Hopke PK et al (2017) A cost-benefit analysis of a pellet boiler with electrostatic precipitator versus conventional biomass technology: a case study of an institutional boiler in Syracuse, New York. Environ Res 156:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.03.052
Xie B, Li S, Jin H et al (2018) Analysis of the performance of a novel dust collector combining cyclone separator and cartridge filter. Powder Technol 339:695–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.07.103
De Castro BJC, Sartim R, Guerra VG, Aguiar ML (2020) Hybrid air filters: a review of the main equipment configurations and results. Process Saf Environ Prot 144:193–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.07.025
Jaworek A, Sobczyk AT, Krupa A et al (2019) Hybrid electrostatic filtration systems for fly ash particles emission control. A Rev Separat Purifi Technol 213:283–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.12.011
Lee SE, Hutter B, Goldsmith S (1994) Comparisons of mechanical melt-blown filters and electrostatically enhanced split-fiber filters for cabin air filtration applications. Part Sci Technol 12:399–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726359408906665
Chen J-P, Chen S-C, Wu X-Q et al (2021) Multilevel structured TPU/PS/PA-6 composite membrane for high-efficiency airborne particles capture: preparation, performance evaluation and mechanism insights. J Membr Sci 633:119392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119392
Lee J, Kim J (2020) Material properties influencing the charge decay of electret filters and their impact on filtration performance. Polymers 12:721. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030721
Shu H, Xiangchao C, Peng L, Hui G (2017) Study on electret technology of air filtration material. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 100:012110. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/100/1/012110
Yuan Y, Zhao J, Dong C et al (2019) Improved Electret Properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/lithium niobate nanocomposites for applications in air filters. Macromol Mater Eng 304:1900003. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201900003
Owkis B, Motyl E (2001) Electret properties of polypropylene fabrics. J Electrostat 51–52:232–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3886(01)00053-5
Lee K-S, Hasolli N, Lee J-R et al (2020) Dust loading performance of a non-electret HVAC filter module in the presence of an external electric field. Sep Purif Technol 250:117204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117204
Zong D, Zhang X, Yin X et al (2022) Electrospun fibrous sponges: principle, fabrication, and applications. Adv Fiber Mater 4:1434–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00202-2
Pang C, You H, Liang L et al (2023) Bamboo pulp-based electret fiber aerogel with enhanced electret performance by P-phenylenediamine modification for simulated radioactive aerosol purification in confined spaces. Colloids Surf A 658:130502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130502
Deuber F, Mousavi S, Federer L et al (2018) Exploration of ultralight nanofiber aerogels as particle filters: capacity and efficiency. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:9069–9076. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b00455
Sambaer W, Zatloukal M, Kimmer D (2012) 3D air filtration modeling for nanofiber based filters in the ultrafine particle size range. Chem Eng Sci 82:299–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2012.07.031
Maury-Ramirez A, Nikkanen J-P, Honkanen M et al (2014) TiO2 coatings synthesized by liquid flame spray and low temperature sol–gel technologies on autoclaved aerated concrete for air-purifying purposes. Mater Charact 87:74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2013.10.025
Liang J, Cai Z, Li L et al (2014) Scalable and facile preparation of graphene aerogel for air purification. RSC Adv 4:4843. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra45147j
Qian H, Fang Y, Wu K et al (2021) Air filtration improvement of konjac glucomannan-based aerogel air filters through physical structure design. Int J Low Carbon Technol 16:867–872. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijlct/ctab011
Sun J, Zhou Y, Zhou J, Yang H (2023) Filtration capacity and radiation cooling of cellulose aerogel derived from natural regenerated cellulose fibers. J Nat Fibers 20:2181276. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2023.2181276
Qiao S, Yan J, Wang Z et al (2023) Tough and lightweight polyimide/cellulose nanofiber aerogels with hierarchical porous structures as an efficient air purifier. Sep Purif Technol 325:124668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124668
Zhou L, Zhai S, Chen Y, Xu Z (2019) Anisotropic cellulose nanofibers/polyvinyl alcohol/graphene aerogels fabricated by directional freeze-drying as effective oil adsorbents. Polymers 11:712. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040712
Huang Y, Zhou T, He S et al (2019) Flame-retardant polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanofibers hybrid carbon aerogel by freeze drying with ultra-low phosphorus. Appl Surf Sci 497:143775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143775
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Wang X et al (2018) Characterization of the nano-cellulose aerogel from mixing CNF and CNC with different ratio. Mater Lett 229:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.06.101
Jiménez-Saelices C, Seantier B, Cathala B, Grohens Y (2017) Spray freeze-dried nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels with thermal superinsulating properties. Carbohyd Polym 157:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.09.068
Wu P, Zhang B, Yu Z et al (2019) Anisotropic polyimide aerogels fabricated by directional freezing. J Appl Polym Sci 136:47179. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47179
Zhang G, Chen H, Yang S et al (2018) Frozen slurry-based laminated object manufacturing to fabricate porous ceramic with oriented lamellar structure. J Eur Ceram Soc 38:4014–4019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.04.032
Ni X, Ke F, Xiao M et al (2016) The control of ice crystal growth and effect on porous structure of konjac glucomannan-based aerogels. Int J Biol Macromol 92:1130–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.08.020
Zhang M, Li M, Xu Q, et al (2022) Nanocellulose-based aerogels with devisable structure and tunable properties via ice-template induced self-assembly. Industrial crops and products 179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114701
Wang X, Zhang Y, Jiang H et al (2017) Tert-butyl alcohol used to fabricate nano-cellulose aerogels via freeze-drying technology. Mater Res Exp 4:065006. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa72bc
Kasraian K, Deluca PP (1995) Thermal analysis of the tertiary butyl alcohol-water system and its implications on freeze-drying. Pharm Res 12:484–490. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1016233408831
Deogekar S, Islam MR, Picu RC (2019) Parameters controlling the strength of stochastic fibrous materials. Int J Solids Struct 168:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2019.03.033
Pang C, Wang H, Lin X (2021) Ultralight ethyl cellulose-based electret fiber membrane for low-resistance and high-efficient capture of PM2.5. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Aspects 630:127643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127643
Ke S-C, Wang T-C, Wong M-S, Gopal NO (2006) Low Temperature kinetics and energetics of the electron and hole traps in irradiated TiO 2 nanoparticles as revealed by EPR spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 110:11628–11634. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0612578
Chelbi S, Djouadi D, Chelouche A et al (2020) Effects of Ti-precursor concentration and annealing temperature on structural and morphological properties of TiO2 nano-aerogels synthesized in supercritical ethanol. SN Appl Sci 2:872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2633-3
Linn B, Tuukka N, Deeptanshu S et al (2021) Seaweed-derived alginate-cellulose nanofiber aerogel for insulation applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:34899–34909. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c07954
Liu C, Wan L, Li Q et al (2021) Ice-templated anisotropic flame-resistant boron nitride aerogels enhanced through surface modification and cellulose nanofibrils. ACS Appl Polym Mater 3:1358–1367. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.0c01219
Lasalle A, Guizard C, Leloup J et al (2012) Ice-templating of alumina suspensions: effect of supercooling and crystal growth during the initial freezing regime. J Am Ceram Soc 95:799–804. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2011.04993.x
Habib J, Annika S, Tomasz J et al (2012) Ice templating soft matter: fundamental principles and fabrication approaches to tailor pore structure and morphology and their biomedical applications. Adv Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202100091
Huiming X, Gangjin C, Xumin C, Zhi C (2017) A flexible electret membrane with persistent electrostatic effect and resistance to harsh environment for energy harvesting. Sci Rep 7:8443. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07747-y
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the financial support from State Key Laboratory of NBC Protection for Civilian, China (SKLNBC2021-21), and Engineering Research Center of Biomass Materials, Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review and editing. CP: Review and editing. SL: Investigation and Validation. XL: Writing-review and editing. YZ: Writing-review, Funding acquisition and Project administration. ZL: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Pang, C., Lei, S. et al. Preparation of 3D ethylcellulose-based electret fiber aerogel for simulated radioactive aerosol purification. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 333, 481–493 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09227-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09227-2