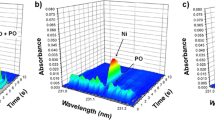
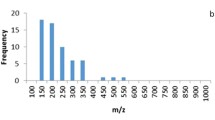
Abstract
An instrumental neutron activation analysis method in conjunction with Compton suppression spectrometry was developed for the simultaneous determination of nanogram levels of Cl, Br and I in salmon muscle and skin. Several non-chlorinated solvent systems were evaluated for the extraction of lipids containing organohalogens and an acetone-hexane (1:1) system was selected because it gave the highest extraction efficiency with least contamination. An extensive quality assurance program was designed. Lipid fractionation procedures were developed using size exclusion, solid phase extraction and thin layer chromatography followed by characterization using 1H, 13C and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry. Results show that both muscle and skin had high levels of triacylglycerols.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this manuscript are available in the MSc thesis of one of the coauthors (Najat H.O. Bahroun).
References
Bright DA, Dushenko WT, Grundy SL, Reimer KJ (1995) Effects of local and distant contaminant sources: polychlorinated biphenyls and other organochlorines in bottom-dwelling animals from an Arctic estuary. Sci Total Environ 160:265–283
Mizukawa HK, Nomiyama S, Nakatsu H, Iwata JY, Kubota A, Yamamoto M, Ishizuka M, Ikenaka Y, Nakayama SMM, Kunisue T, Tanabe S (2016) Organohalogen compounds in pet dog and cat: Do pets biotransform natural brominated products in food to harmful hydroxlated substances? Environ Sci Technol 50:444–452
Sonne C (2010) Health effects from long-range transported contaminants in Arctic top predators: an integrated review based on studies of polar bears and relevant model species. Environ Int 36:461–491
Kiceniuk JW, Holzbecher J, Chatt A (1997) Extractable organohalogens in tissues of beluga whales from the Canadian Arctic and the St. Lawrence Estuary. Environ Pollut 97:205–211
Cohen M (2007) Environmental toxins and health—the health impact of pesticides. Aust Fam Physician 36:1002–1004
Helmfrid I, Berglund M, Lofman O, Wingren G (2012) Health effects and exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and metals in a contaminated community. Environ Int 44:53–58
Gribble GW (2015) A recent survey of naturally occurring organohalogen compounds. Environ Chem 12:396–405
Rao P, Kodavanti S, Loganathan BG (2017) Organohalogen pollutants and human health. In: International encyclopedia of public health, 2nd edn, pp 359–366
Hites RA, Foran JA, Carpenter DO, Hamilton MC, Knuth BA, Schwager SJ (2004) Global assessment of organic contaminants in farmed salmon. Science 303:226–229
Hites RA, Foran JA, Carpenter DO, Hamilton MC, Knuth BA, Schwager SJ (2004) Farmed salmon contains high levels of organochlorine carcinogens: implication for public health. Neurotoxicology 25:691–692
Hites RA, Foran JA, Schwager SJ, Knuth BA, Hamilton MC, Carpenter DO (2004) Global assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in farmed and wild salmon. Environ Sci Technol 38:4945–4949
Hamilton MC, Hites RA, Schwager SJ, Foran JA, Knuth BA, Carpenter DO (2005) Lipid composition and contaminants in farmed and wild salmon. Environ Sci Technol 39:8622–8629
Mu HL, Ewald G, Nilsson E, Sundin P, Wesen C (2004) Fate of chlorinated fatty acids in migrating sockeye salmon and their transfer to arctic grayling. Environ Sci Technol 38:5548–5554
King MD, Rea LD, Kennish JM (2006) Chlorinated fatty acids in lipid class fractions from cardiac and skeletal muscle of Chinook salmon. Lipids 41:1133–1140
Bahroun NHO (2007) Studies of extractable organohalogens in salmon by neutron activation analysis and other techniques. MSc Thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
Shaw SD, Berger ML, Brenner D, Carpenter DO, Tao L, Hong C-S, Kannan K (2008) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in farmed and wild salmon marketed in the Northeastern United States. Chemosphere 71:1422–1431
Shaw SD, Brenner D, Berger ML, Carpenter DO, Hong C-S, Kannan K (2007) PCBs, PCDD/Fs, and organochlorine pesticides in farmed Atlantic salmon from Maine, Eastern Canada, and Norway, and wild salmon from Alaska. Environ Sci Technol 41:4180–4180
Svendsen TC, Vorkamp K, Ronsholdt B, Frier J-O (2008) Retrospective determination of primary feeding areas of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) using fingerprinting of chlorinated organic contaminants. ICES J Mar Sci 65:921–929
Easton MDL, Luszniak D, Von der Geest E (2002) Preliminary examination of contaminant loadings in farmed salmon, wild salmon and commercial salmon feed. Chemosphere 46:1053–1074
Da Costa Filho BM, Duarte AC, Rocha-Santos TAP (2022) Environmental monitoring approaches for the detection of organic contaminants in marine environments: a critical review. Trends Environ Anal Chem 33:e00154
Lunde G, Steinnes E (1975) Presence of lipid-soluble chlorinated hydrocarbons in marine oils. Environ Sci Technol 9:155–157
Lunde G, Gether J, Steinnes E (1976) Determination of volatility and chemical persistence of lipid-soluble halogenated organic substances in marine organisms. Ambio 5:180–182
Newsome WH, Andrews P, Conacher BS, Rao RR, Chatt A (1993) Total organochlorine content of fish from the Great Lakes. J AOAC Int 76:703–706
Boyd RK (1993) Extractable organically bound chlorine (EOCl) in fish and sediments; the unidentified 85%. Technical Report No. 69, Institute of Marine Biosciences, National Research Council, Halifax, NS, Canada
Gether J, Lunde G, Steinnes E (1979) Determination of the total amount of organically bound chlorine, bromine, and iodine in environmental samples by neutron activation analysis. Anal Chim Acta 108:137–147
Norstrom RJ, Gilman AP, Hallet DJ (1981) Total organically-bound chlorine and bromine in Lake Ontario herring gull eggs, 1977, by instrumental neutron activation and chromatographic methods. Sci Total Environ 20:217–230
Baumann-Ofstad E, Martinsen K (1983) Persistent organochlorine compounds in seals from Norwegian coastal waters. Ambio 12:262–264
Watanabe I, Kashimoto T, Kawano M, Tatsukawa RA (1987) Study of organic bound halogens in human adipose, marine organisms and sediment by neutron activation and gas chromatographic analysis. Chemosphere 16:849–857
Kawano M, Falandysz J, Wakimoto T (2003) Instrumental neutron activation analysis of extractable organohalogens (EOX) in the Antarctic marine organisms. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 255:235–237
Kawano M, Falandysz J, Wakimoto T (2007) Instrumental neutron activation analysis of extractable organohalogens in the Antractic Weddel seal (Leptonychotes weddelli). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 272:501–504
Xu D, Chai Z, Zhang H, Mao X, Ouyang H, Sun H (2004) Study of organohalogens in foodstuffs and environmental samples by neutron activation analysis and related techniques. Nukleonika 49:101–106
Xu D, Dan M, Song Y, Chai Z, Zhuang G (2007) Instrumental neutron activation analysis of extractable organohalogens in PM2.5 and PM10 in Beijing. China J Radioanal Nucl Chem 271:115–118
Zhong W, Xu D, Chai Z, Mao X (2004) Neutron activation analysis of extractable organohalogens in milk from China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 259:485–488
Zhang H, Chai ZF, Sun HB, Zhang JL, Ouyang H, Xin L, Chuai YD (2007) Study of organohalogen contaminants in yogurt by NAA and GC-ECD. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 271:31–35
Xu D, Zhang Z, Jiang Q, Li Y, Chai Z (2008) Hybrid NAA method for assessment of the levels of organic halogen compounds in the atmosphere in China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:241–245
Zhang R, Zhang H, Chen Q, Luo J, Chai Z, Shen J (2017) Composition, distribution and risk of total fluorine, extractable organofluorine and perfluorinated compounds in Chinese teas. Food Chem 219:496–502
Zhang H, Chai Z, Sun H (2007) Human hair as a potential biomonitor for assessing persistent organic pollutants. Enviro Int 33:685–693
Mukai K, Fujimori T, Anh HQ, Fukutani S, Kunisue T, Nomiyama K, Takahashi S (2021) Extractable organochlorine (EOCl) and extractable organobromine (EOBr) in GPC-fractionated extracts from high-trophic-level mammals: species-specific profiles and contributions of legacy organohalogen contaminants. Sci Total Environ 756:143843
Sadiq Z, Tali SHS, Hajimiri H, Al-Kassawneh M, Jahanshahi-Anbuhi S (2022) Gold nanoparticles-based colorimetric assays for environmental monitoring and food safety evaluation. Crit Rev Anal Chem 26:1–36
Kiceniuk JW, Zwicker B, Chatt A (1998) Determination of extractable organic bromine and chlorine in biological compartments of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) by neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 235:291–294
Bottaro CS, Kiceniuk JW, Chatt A (1999) Spatial distribution of extractable organohalogens in northern pink shrimp in the north Atlantic. J Biol Trace Elem Res 71–72:149–166
Kiceniuk JW, Bottaro CS, Indrasena MW, Mass SJ, Ramaley L, Banoub J, Chatt A (2006) Characterization of extractable organochlorines from marine animals by neutron activation, mass spectrometry, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry. In: Proceedings of the international conference on application of radiotracers in chemical, environmental and biological sciences (ARCEBS 06), vol 1. Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics, University of Calcutta, Kolkata, India, pp 202–219
Chatt A (2013) Studies of total, bioaccessible, proteic, lipidic, and ionic species of iodine in nutritional materials by neutron activation analysis. In: Proceedings of the 11th biennial nuclear and radiochemistry symposium (NUCAR 2013) at R.D. University, Jabalpur, MP, India, Department of Atomic Energy, India, pp 91–96
Isaac-Olive K, Kyaw TT, Chatt A (2018) Estimation of anthropogenic organo-chlorine, bromine and iodine compounds in apolar lipid fractions of bovine milk by solid-phase extraction and neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 318:247–257
LeFsay AM (2016) Development of liquid chromatographic and mass spectrometric methods for the identification of chlorinated triacylglycerols in natural oils. PhD Thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
Benville PEB, Tindle RC (1970) Dry ice homogenization procedure for fish samples in pesticide residue analysis. J Agric Food Chem 18:948–949
Martinsen K, Kringstand A, Calberg GE (1988) Methods for determination of sum parameters and characterization of organohalogen compounds in spent bleach liquors from pulp mills and water, sediment and biological samples from receiving waters. Water Sci Technol 20(2):13–24
Bottaro CS (1999) Studies of extractable organohalides in northern pink shrimp Pandalus Borealis. PhD thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
Bottaro CS, Kiceniuk JW, Chatt A (2005) Studies of extractable organohalogen species. Part I: optimization of extraction methods. In: Proceeings of the 2005 nuclear and radiochemistry symposium (NUCAR 2005), Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar, India, pp 52–59
Ryan DE, Stuart DC, Chattopadhyay A (1978) Rapid multielement neutron activation analysis using a SLOWPOKE reactor. Anal Chim Acta 100:87–93
Holzbecher J, Chatt A, Ryan DE (1985) SLOWPOKE epi-cadmium neutron flux in activation analysis of trace elements. Can J Spectros 30:67–72
Zhang W (1997) Studies on anticoincidence gamma-ray spectrometry in neutron activation analysis. PhD thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
Zhang W, Chatt A (2014) Anticoincidence counting further improves detection limits of short-lived products by pseudo-cyclic instrumental neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 302:1201–1211
Currie LA (1968) Limits for qualitative detection and quantitative determination application to radiochemistry. Anal Chem 40:586–593
Labrada EG (2003) Studies on organohalogens in cod brain tissues by neutron activation analysis. MSc thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
Isaac-Olive K (2005) Speciation of iodine in bovine milk by neutron activation analysis. PhD thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
Isaac-Olive K, Acharya R, Chatt A (2008) Fractionation analysis of iodine in bovine milk by preconcentration neutron activation analysis. Talanta 77:827–832
Isaac-Olive K, Chatt A (2012) Studies of total, organic and inorganic iodine in Canadian bovine milk samples with varying milk fat content using ion-exchange chromatography and neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 294:479–486
Isaac-Olive K, Chatt A (2014) Expanded uncertainties of preconcentration neutron activation measurements of extractable organo-chlorine, bromine and iodine compounds in bovine milk lipids. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 302:1213–1224
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Indrasena WM, Kiceniuk J, Chatt A. Personal communication
Anderson A (2000) Salmon color and the consumer. In: IIFET Proceeding, pp 1–3
Christie WW (2003) Lipid analysis (isolation, separation, identification and structural analysis of lipids), 3rd edn. The Oily Press, Bridgewater
Jayasinghe C, Gotoh N, Wada S (2003) Variation in lipid classes and fatty acids composition of salmon shark (Lamna ditropis) liver with season and gender. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 134:287–295
Mass SJ (2000) Mass spectrometric methods for detecting chlorinated compounds in lipid extracts from various marine animals. MSc thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada
LeFsay AM, Guy RD, Chatt A, White RL (2013) Synthesis and tandem mass spectrometry of chlorinated triacylglycerols. Chem Phys Lipids 174:55–63
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thankfully acknowledge the cooperation of the Dalhousie University SLOWPOKE-2 Reactor (DUSR) facility for irradiations, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada for Research Operating/Discovery, Strategic Research Operating and Equipment, Major Facilities Access, and Research Network grants to AC, and the Dalhousie University Faculty of Graduate Studies for a graduate stipend to NHOB. This paper was presented as a plenary Lecture at the International Conference on Nuclear Analytical Techniques 2022 (NAT2022) held in Daejeon, Korea during 2022 December 07-09.
Funding
No funding was received for the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. All authors contributed from the design of experiments through the interpretation of the data to the preparation of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bahroun, N.H.O., Kiceniuk, J.W. & Chatt, A. Studies of extractable organohalogens in farmed Atlantic salmon muscle and skin by neutron activation in conjunction with size exclusion and solid phase extraction chromatography. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 5155–5173 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09022-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09022-z