Abstract
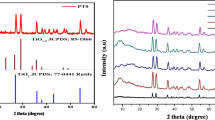
Fe and FeCo metal powders were produced using the pulsed wire evaporation process. The surfaces of Fe and FeCo metal powders were stabilized at room temperature by a thin oxide layer formed through passivation. Fe@GO and FeCo@GO, which are graphene oxide (GO) coated Fe and FeCo metal powders, were synthesized using a self-adhesion behavior. TEM analysis showed that the GO layer was around 6–8 nm thick and the passivation layer was thicker for Fe compared to FeCo. At 50 MHz, Fe@GO had µ′ = 6.84, µ″ = 0.17, and tangent loss of 0.025; FeCo@GO had µ′ = 9.64, µ″ = 0.14, and tangent loss of 0.014.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee MY, Choi YJ, Lee SH, Ahn JH, Lee BW (2022) Controlling properties of metal-polymer soft magnetic composites through microstructural deformation for power inductor applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33:15763–15772
Kim HK, An SY (2015) Nano-scale inter-lamellar structure of metal powder composites for high performance power inductor and motor applications. J Magn 20:138–147
Choi YJ, Ahn JH, Kim DH, Kim YR, Lee BW (2022) Core-loss reduction of Fe–Si–Cr crystalline alloy according to particle size in the high frequency band. Curr Appl Phys 39:324–330
Yeo JG, Kim DH, Choi YJ, Lee BW (2019) Improving power-inductor performance by mixing sub-micro Fe powder with amorphous soft magnetic composites. J Electron Mater 48:6018–6023
Baguley CA, Carsten B, Madawala UK (2008) The effect of DC bias conditions on ferrite core losses. IEEE Trans Magn 44:246–252
Zhou T, Liu Y, Cao P, Du J, Lin Z, Wang R, Jin L, Lian L, Harris V (2020) Cold Sintered metal–ceramic nanocomposites for high-frequency inductors. Adv Electron Mater 6:2000868–2000876
Xie Y, Yan P, Yan B (2018) Enhanced soft magnetic properties of iron-based powder cores with co-existence of Fe3O4–MnZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Metals 8:702–713
Snoek JL (1948) Dispersion and absorption in magnetic ferrites at frequencies above one Mc/s. Physica 14:207–217
Matsumoto M, Miyata Y (1997) Thin electromagnetic wave absorber for quasi-microwave band containing aligned thin magnetic metal particles. IEEE trans Magn 33:4459–4464
Cheng J, Zhang H, Ning M, Raza H, Zhang D, Zheng G, Zheng Q, Che R (2022) Emerging materials and designs for low- and multi-band electromagnetic wave absorbers: the search for dielectric and magnetic synergy? Adv Funct Mater 32:2200123–2200135
Baker C, Hasanain SK, Shah SI (2004) The magnetic behavior of iron oxide passivated iron nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 96:6657–6662
Baker C, Shah SI, Hasanain SK (2004) Magnetic behavior of iron and iron-oxide nanoparticles/polymer composites. J Magn Magn Mater 280:412–418
Peng Y, Nie J, Zhang W, Ma J, Bao C, Cao Y (2016) Effect of the addition of Al2O3 nanoparticles on the magnetic properties of Fe soft magnetic composites. J Magn Magn Mater 399:88–93
Xu L, Yan B (2017) Fe-6.5% Si/SiO2 powder cores prepared by spark plasma sintering: magnetic properties and sintering mechanism. Inter J Modern Phys B 31:1744011–17440017
Yang J, Guan G, Yan L, Xu J, Xiang J, Zhang K (2021) FeCo/Zno composite nanofibers for broadband and high efficiency microwave absorption. Adv Mater Inter 8:2101047–2101052
Wang Y, Zhang W, Luo C, Wu X, Yan G (2016) Superparamagnetic FeCo@SnO2 nanoparticles on graphene-polyaniline: synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Ceram Int 42:12496–12502
Cui E, Pan F, Xiang Z, Liu Z, Yu L, Xiong J, Li X, Lu W (2021) Engineering dielectric loss of FeCo/polyvinylpyrrolidone core-shell nanochains@graphene oxide composites with excellent microwave absorbing properties. Adv Eng Mater 23:2000827–2200835
Tan Q, Tao L, Rehman JU, Zhong M, Wang L, Chen C, Xiong H, Xie W, Zhong Z (2019) Improved microwave absorbing properties of core-shell FeCo@C nanoparticles. Mater Res Experss 6:075034–075044
Long H, Wu X, Lu Y, Zhang H, Hao J (2022) Effect of polyimide-phosphating double coating and annealing on the magnetic properties of Fe–Si–Cr SMCs. Materials 15:3350–3364
Yang B, Li X, Yang X, Yu R (2017) Chemical synthesis of Fe/Fe3O4 core-shell composites with enhanced soft magnetic performances. J Magn Magn Mater 428:6–11
Lee HM, Uhm YR, Rhee CK (2008) Phase control and characterization of Fe and Fe-oxide nanocrystals synthesized by pulsed wire evaporation method. J Alloys comp 461:604–607
Kim DH, Lee BW (2017) Microstructural and magnetic characterization of Fe nanosized powder synthesized by pulsed wire evaporation. J Magn 22:100–103
Uhm YR, Kim WW, Kim SJ, Kim CS, Rhee CK (2003) Magnetic nanoparticles of Fe2O3 synthesized by the pulsed wire evaporation method. J Appl Phys 93:7196–7198
Lee PC, Kim SY, Ko YK, Ha JU, Jeoung SK, Shin D, Kim JH, Kim MG (2022) Tribological properties of polyamide 46/graphene nanocomposites. Polymers 14:1139–1149
Gupta RK, Alahmed ZA, Yakuphanoglu F (2013) Graphene oxide based low cost battery. Mater Lett 112:75–77
Siburian R, Sihotang H, Raja SL, Supeno M, Simanjuntak C (2018) New route to synthesize of graphene nano sheets. Orient J Chjem 34:182–187
Baldokhin YV, Kolotyrkin PY, Petrov YI, Shafranovsky EA (1994) Some specific features of fine Fe and Fe-Ni particles. J Appl Phys 76:6496–6498
Panda RN, Gajbhiye NS, Balaji G (2001) Magnetic properties of interacting single domain Fe3O4 particles. J Alloy Comp 326:50–53
Srikanth H, Hajndl R, Chirinos C, Sanders J, Sampath A, Sudarshan TS (2001) Magnetic studies of polymer-coated Fe nanoparticles synthesized by microwave plasma polymerization. Appl Phys Lett 79:3503–3505
Hu P, Chang T, Chen WJ, Deng J, Li SL, Zuo YG, Kang L, Yang F, Hostetter M, Volinsky AA (2019) Temperature effects on magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by the sol-gel explosion-assisted method. J Alloy Comp 773:605–611
Kodama D, Shindoda K, Sato K, Sato Y, Jeyadevan B, Tohji K (2006) Synthesis of Fe-Co Alloy particles by modified polyol process. IEEE Trans Mag 42:2796–2798
Gupta V, Patra MK, Shukla A, Saini L, Songara S, Jani R, Vadera SR, Kumar N (2014) Synthesis and investigations on microwave absorption properties of core–shell FeCo(C) alloy nanoparticles. Sci Adv Mater 6:1196–1202
Acknowledgements
It was presented at the International Conference on Nuclear Analytical Techniques in 2022 (NAT2022). The author is grateful to Professor Chul Sung Kim at the Department of Physics, Kookmin University, South Korea for providing Mössbauer spectroscopy. This paper is written with support for research funding from aSSIST University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has no possible conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
An, S.Y. Mössbauer and magnetic properties of graphene oxides coatings on Fe and FeCo powders for high frequency applications. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 332, 5105–5112 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-08984-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-08984-4