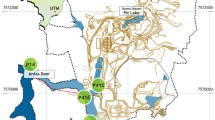
Abstract
Physico-chemical methods were used to assess the contamination status of water bodies near a uranium mine pit and tailings pond in northern Guangdong. The results of the evaluation showed that the content, Pi values and ecological risk index of U and Cd were high and exhibited serious hazard levels, while the remaining elements were weakly contaminated. On this basis, ecotoxicity evaluation was carried out using the ostracods Heterocypris sp. and Cypridopsis vidua. The results were consistent with the physico-chemical data, and both genera were sensitive indicators of the degree of water pollution, with the higher the degree of pollution, the greater the mortality of individuals and vice versa.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang B, Feng ZG, Ma Q, Chen R, Wang XL, Duan XZ, Han SL (2015) Pollution Characteristics and Environmental Availability of Uranium in Soil around a Uranium Waste Ro-ck Pile in Guangdong Province. Ecol and Environ 24:156–162. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.01.023
Chen YY, Zhang H, Hu N, Din DX, Dai ZR (2021) Research progress of in-situ leaching uranium groundwater remediation technology. Min Res and Dev 41:149–154. https://doi.org/10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2021.02.026
Shi CH (2017) Study on Combined Pollution Level and Remediation of Heavy Metals and Natural Radioactive Materials in a Waste Uranium Mine. Hunan University, China, Hunan province
Wang X, Yu HX, Xiong HL, Ma J (2017) Health Risk Assessment and Remediation Suggestions for a Typical Mining and Metallurgical Contaminated Site in South China. Chin J of Environ Eng 11:3823–3831. https://doi.org/10.12030/j.cjee.201603219
Liu YJ, Yang Y, Tan XL, Liu YY, Yang X, Li EG (2019) Evaluation and Source App-ortionment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in Typical Mining and Metallurgy Cities of Hubei Province. The Adm and Tech of Environ Monit 31:26–30. https://doi.org/10.19501/j.cnki.1006-2009.20190917.015
Zhang Y, Li YY (2020) Pollution Characteristics and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Water of Luling Coal Mine Section of Tuohe River. J of Chifeng Univ 36:9–14. https://doi.org/10.13398/j.cnki.issn1673-260x.2020.02.003
Tang ZP, Men Q, Chen L, Ma RL, Zhou XF (2019) Occurrence patterns of uranium and heavy metal elements in surface sediments of water body surrounding a uranium mine in northern Guangdong. Uranium Min And Metall 38:237–243. https://doi.org/10.13426/j.cnki.yky.2019.04.001
Chen M, Zheng XJ, Tao MX, Li FG, Hu LW, Shi YL, Liu YC (2020) Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in River Sediments of Taojiang River Basin. Environ Chem 39:2784–2791. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0044
Sun HY, Hu H, Gao P, Chen G, Jiao J, Yang ZC (2020) Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of Dagu River. Trans of Oceanol and Limnol 2020:95–104. https://doi.org/10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2020.05.013
Tang ZP, Jing ML, Ao HL, Liu S, Huang W, Han SL, Gao F, Chen L (2017) Study on Radioactivity and Heavy Metal Pollution of Surface Water Around a Uranium Mine in North Guangdong. Environ Eng 35:103–107. https://doi.org/10.13205/j.hjgc.201706022
Zhou J, Gao FJ, Zhang BJ, Ma B (2014) Potential Biotoxicity Risk Assessment of Toxic Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Sediments of Songhua River. Acta Sci Circumst 34:2701–2708. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0595
Zhang XL, Xu LC, Zhang H (2016) Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soil Around a Uranium Tailings Pond. Environ Monit in Chin 32:76–83. https://doi.org/10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2016.06.12
Zhang XL, Xu LC, Zhang H (2015) Pollution and Evaluation of Heavy Metals in Far-mland Soil Around a Uranium Tailings Pond. Environ Sci & Tech 38:221–226. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2015.06.037
National Environmental Protection Agency, National Bureau of Technical Supervision (1995) GB 15618 – 1995. Environ Qual Stand for Soils
Jiang YZ (2010) New Progress in Biomarker Monitoring Environmental Pollution. Guangdong Chem Ind 37:150–152. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2010.04.070
Liao TC, Yi JQ, Li KZ, Tan YH (2019) Research Progress on Diversity and Ecology of Marine Planktonic Mesomorphs. Ecol Sci 38:190–198. https://doi.org/10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2019.06.028
Ruiz F, Abad M, Bodergat AM, Carbonel P, Rodríguez-Lázaro J, González-Regalado ML, Toscano A, García EX, Prenda J (2013) Freshwater ostracods as environmental tracers. Int J of Environ Sci and Tech 10:1115–1128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0249-5
Haruna W, Fumiyuki N, Ikuro K, Hiroaki F (2011) Toxicity Evaluation of Road Dust in the Runoff Process Using a Benthic Ostracod Heterocypris Incongruens. Sci of the Total Environ 409:2366–2372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.03.001
Rajendra K, Hioaki F, Fumiyuki N, Chihiro Y (2018) Carcinogenic Profile, Toxicity and Source Apportionment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Accumulated From Urban Road Dust in Tokyo, Japan. Ecotoxicol and Environ Saf 165:440–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.095
Wilailuk N, Fumiyuki N, Tomohiro T, Kazuo Y (2017) Development of a Chronic Sedim-ent Toxicity Test Using the Benthic Ostracod Heterocypris Incongruens and Their Application to Toxicity Assessments of Urban Road Dust. Ecotoxicol and Environ Saf 143:266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.05.011
Chen SM, Yu N, Zhou YY, Zhang Q (2010) Acute Toxicity Experiment of Cd2+, Zn2+ and Cu2+ in Physocypria Kraepelini(Ostracoda). Acta Micropaleontol Sin 27:118–124
Sanda I, Virtudes MH, Sonia H, Ruben RL, Irene B (2013) Response of Microcrustace-an Communities From the Surface-groundwater Interface to Water Contamination in Urban Riv-er System of the Jarama Basin (Central Spain). Environ Sci and Pollut Res 20:5813–5826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1529-9
Magda S, Magdalena W, Justyna R (2018) Assessment of Water Quality Contaminated with Arsenic Using Diatoms and Ostracodtoxkit F Test. E3S Web. of Conf 44:174–179. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20184400174
Kudłak B, Wolska L, Namieśnik J (2011) Determination of EC50 Toxicity Data of Selected Heavy Metals Toward Heterocypris Incongruens and Their Comparison to “Direct-contact” and Microbiotests. Environ Monit and Assess 174:509–516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1474-8
Khangarot BS, Das S (2009) Acute Toxicity of Metals and Reference Toxicants to a Freshwater Ostracod, Cypris Subglobosa Sowerby, 1840 and Correlation to EC50 Values of Other Test Models. J of Hazard Mater 172:641–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.038
BSI Standards Publication (2012) Water Quality-Determination of Freshwater Sediment Toxicity to Heterocypris Incongruens (Crustacea, Ostracoda): ISO 14321. The International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
Oleszczuk P (2008) Heterocypris Incongruens as a Tool to Estimate Sewage Sludge Toxicity. Environ Toxicol and Chem 27:864–872. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-234.1
Chen L, Liu J, Tang ZP, Liu S, Huang W, Han SL, Wang ZQ, Xie YS (2019) Distribution and Ecological Characteristics of Mesophytes in Dongting Lake. Acta Sedimentol Sin 37:143–154. https://doi.org/10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2018.126
Yao JG, Ma SX, Wei CQ, Li DP, Ma XM, Zhao QH, Ni B, Yu N (2016) New Records of the Present Ostracods in Yuandang Lake, East China. Acta Micropaleontol Sin 33:280–292. https://doi.org/10.16087/j.cnki.1000-0674.2016.03.006
Chen L, Liu J, Tang ZP, Huang W, Liu S, Han SL, Wang ZQ, Xie YS (2018) Ostracoda Species in DT01 Section of Dongting Lake. Acta Micropaleontol Sin 35:106–112. https://doi.org/10.16087/j.cnki.1000-0674.2018.01.009
Luo F, Wu GR, Wang C, Zhang L (2016) Application of Nemerow Pollution Index Method and Single Factor Evaluation Method in Water Quality Assessment. Environ and Sustain Dev 41:87–89. https://doi.org/10.19758/j.cnki.issn1673-288x.2016.05.024
Dou L, Shen SZ, Du HY (2015) Distributional Characteristics and Sources of Elements in Soil From Typical Area of Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, Guangdong Province, China. Chin J of Geochem 34:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-015-0048-4
Beijing Research Institute of Chemical Engineering Metallurgy, Nuclear and Radiation Safety Center (2020) GB 23727 – 2020, Regulations for radiation protection and radiation environment protection in uranium mining and milling
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (2002) GB 3838 – 2002. Environmental quality standards for surface water
Shi MY, Wang ZW, Wang JB (2019) Application Progress of Hakanson Index Method in Evaluating Ecological Risk of Soil Heavy Metals. Chin J of Soil Sci 50:1002–1008. https://doi.org/10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2019.04.33
Rajendra K, Hiroaki F, Fumiyuki N (2014) Toxicity Assessment of Size-fractionated Urban Road Dust Using Ostracod Heterocypris Incongruens Direct Contact Test. J of Hazard Mater 264:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.10.058
Sevilla JB, Nakajima F, Kasuga I (2014) Comparison of Aquatic and Dietary Exposure of Heavy Metals Cd, Cu, and Zn to Benthic Ostracod Heterocypris Incongruens. Environ Toxicol and Chem 33:1624–1630. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2596
Wang F, Leung AOW, Wu SC, Yang MS, Wong MH (2009) Chemical and Ecotoxicolo-gical Analyses of Sediments and Elutriates of Contaminated Rivers Due to E-waste Recycling Acti-vities Using a Diverse Battery of Bioassays. Environ Pollut 157:2082–2090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.02.015
Shankar P, Dashner-Titus EJ, Truong L, Hayward K, Hudson LG, Tanguay RL (2021) Developmental Toxicity in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Exposed to Uranium: A Comparison with Lead, Cadmium, and Iron. Environ Pollut 269:116097. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2020.116097
Chen L, Xia LS, Liu J, Liu S, Huang W, Wang ZQ, Xie YS, Tang ZP (2020) Eval-uation of Radioactive Environment of Surface Water in a Uranium Mine in Hunan Province Based on Ostracod Ecological Characteristics. At Energy Sci and Tech 54:1355–1360. http://doi.org/10.7538 /yzk.2019.youxian.0679
Guo JB, Guo YM, Yu L, Zhong Z, Yang F (2016) Acute toxicity of Cr6+, Ni2+ and As3+ on Juvenile Pseudosciaena Crocea. J of Zhejiang Ocean Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 35:390–394. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-830X.2016.05.006
Traudt EM, Ranville JF, Smith SA, Meyer JS (2016) A Test of the Additivity of Acute Toxicity of Binary-metal Mixtures of Ni with Cd, Cu, and Zn to Daphnia Magna, Using the Inflection Point of the Concentration-response Curves. Environ Toxicol & Chem 35:1843–1851. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3342
Ding CJ (2013) Toxic Effects of Copper, Lead and Zinc on Daphnia Magna. Shandong Normal University, China, Shandong Province.
Zhao Y, Kong Q, Fu RS (2009) Single and Combined Toxic Effects of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Cr6+ on Passerine Fish. Water Technol 3:10–12.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41402002); Natural Science Founding of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2020JJ5481) and completed at the Hunan Key Laboratory of Rare Metal Minerals Exploitation and Geological Disposal of Wastes and Key Laboratory of National Defense of Uranium Mining and Metallurgy Biotechnology, University of South China. Thanks to the three anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Huo, Z., Zhou, X. et al. Evaluation of ecotoxicity of uranium smelting area receiving effluent using ostracods. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 331, 3427–3437 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08404-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08404-z