Abstract
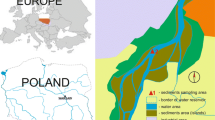
The Funil Reservoir (Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil) is an environment degraded by constant discharge of nutrients and pollution coming from the most industrialized region of the country. As a consequence of eutrophication, there are continuous cyanobacteria blooms, which cause acute and chronic toxicity to zooplankton. In this context, Phase I of Toxicity Identification Evaluation (TIE) was performed on Daphnia similis using water and interstitial water from the reservoir, with the aim of identifying classes of compounds responsible for toxicity. The results indicated that water toxicity was due to cyanobacteria resulting from blooms in the reservoir and surfactants. Metals, especially copper, contributed to sediment toxicity. This research is the first attempt to describe the nature of toxicity in this reservoir using this method.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA/AWWA/WPCF (1992). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 18th ed. New York. 1268 p.
ABNT - Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (2009). NBR 12713 Ecotoxicologia aquática - Toxicidade aguda - Método de ensaio com Daphnia spp (Cladocera, Crustacea). Rio de Janeiro, RJ. 23p.
Alerj - Assembléia Legislativa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (2006). Relatório técnico. Rio Paraíba do Sul – Reservatório do Funil: poluição e degradação ambiental. Comissão Permanente de Defesa do Meio Ambiente. Rio de Janeiro, RJ.
Ankley, G. T., Katko, A., & Arthur, J. W. (1990a). Identification of ammonia as an important sediment-associated toxicant in the lower Fox River and Green Bay, Wisconsin. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 9, 313–322.
Ankley, G. T., Peterson, G. S., Lukasewycz, M. T., & Jensen, D. A. (1990b). Characteristics of surfactants in toxicity identification evaluations. Chemosphere, 21(l-2), 3–12.
Ankley, G. T., Phipps, G. L., Leonard, E. N., Benoit, D. A., Mattson, V. R., Kosian, P. A., Cotter, A. M., Dierkes, J. R., Hansen, D. J., & Mahony, J. D. (1991). Acid volatile sulfide as a factor mediating cadmium and nickel bioavailability in contamined sediments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 10, 1299–1307.
Ankley, G. T., & Schubauer-Berigan, M. K. (1995). Background and overview of current sediment toxicity identification procedures. Journal of Aquatic Ecosystem Health, 4, 133–419.
Ankley, G. T., & Mount, D. R. (1996). Retrospective analysis of the ecological risk of contaminant mixtures in aquatic sediments. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 2(3), 434–440.
Araújo, R. P. A., Botta-Paschoal, C. M. R., Silvério, P. F., Almeida, F. V., Rodrigues, P. F., Umbuzeiro, G. A., Jardim, W. F., & Mozeto, A. A. (2006). Application of toxicity identification evaluation to sediment in a highly contaminated water reservoir in southeastern Brazil. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25(2), 581–588.
Azcue, J. M., Pfeiffer, W. C., Fiszman, M., & Malm, O. (1987). Heavy metals in drinking waters from the Paraiba do Sul-Guandu River System, Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. Water Science Technology, 19, 1181–1183.
Badaró-Pedroso, C., Santos, M. C. F., Carr, R. S. (1998). Utilization of a marine TIE study to characterize toxicants in produced water samples. In: 5 Encontro Brasileiro de Ecotoxicologia-ECOTOX, Itajaí, Brazil
Borglin, S., Wilke, A., Jepsem, R., & Lick, W. (1996). Parameters affecting the desorption of hydrophobic organic chemicals from suspended sediments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 15(10), 2254–2262.
Branco, C. W. C., Rocha, M. I. A., Pinto, G. F. S., Gômara, G. A., & De Filippo, R. (2002). Limnological features of Funil reservoir (RJ, Brazil) and indicator properties of rotifers and cladocerans of the zooplankton community. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research and Management, 7, 87–92.
BRASIL (2012). Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. Estabelece as diretrizes gerais e os procedimentos referenciais para o gerenciamento do material a ser dragado em águas sob jurisdição nacional. Resolução n° 454, 01 de novembro de 2012. Diário Oficial da União, Brasília, DF
Buratini, S. V., Aragão, M. A., Araújo, R. P. A., Prósperi, V. A., & Werner, L. I. (2007). Avaliação e Identificação da Toxicidade no Rio Baquirivu-Guaçu (Alto Tietê). Journal of the Brazilian Society of Ecotoxicology, 2(3), 257–262.
Burgess, R. M., Ho, K. T., Tagliabue, M. D., Kuhn, A., Comeleo, R., Comeleo, P., Modica, G., & Morrison, G. E. (1995). Toxicity characterization of an industrial and a municipal effluent discharging to the marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 30(8), 524–535.
EMBRAPA - Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária (1997). Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos. Manual de métodos de análise de solo. 2. ed., 212 p. Rio de Janeiro, RJ.
Espindola, E. L. G., Paschoal, C. M. R., Tonissi, F. B., Magalhães, R. (1998). Avaliação ecotoxicológica de sedimento como instrumento de controle de qualidade da água do reservatório de Salto Grande, Americana - SP. In: IV Simpósio de Ecossistemas Brasileiros. Águas de Lindóia, SP. Anais. 4, 99–111.
Faria, L. C., & Pasquini, C. (1991). Flow-injection determination of inorganic forms of nitrogen by gas-diffusion and conductimetry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 245, 183–190.
Ferrão-Filho, A. S., Azevedo, S. M. F. O., & De Mott, W. (2000). Effects of toxic and non-toxic cyanobacteria on the life history of tropical and temperate cladocerans. Freshwater Biology, 45, 1–19.
Ferrão-Filho, A. S., Costa, S. M., Ribeiro, M. G. L., & Azevedo, S. M. F. O. (2008). Effects of a saxitoxin-producer strain of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) on the swimming movements of cladocerans. Environmental Toxicology, 23, 161–168.
Ferrão-Filho, A. S., Soares, M. C. S., Magalhães, V. F., & Azevedo, S. M. F. O. (2009a). Biomonitoring of cyanotoxins in two tropical reservoirs by cladoceran toxicity bioassays. Ecotoxicology and Envionmental Safety, 72, 479–489.
Ferrão-Filho, A. S., Soares, M. C., Rocha, M. I. A., Magalhães, V. F., & Azevedo, S. M. F. O. (2009b). Florações de cianobactérias tóxicas no reservatório do Funil: dinâmica sazonal e consequências para o zooplâncton. Oecologia Brasiliensis, 13(2), 346–365.
Ferraz, M. A., Choueri, R. B., Aline Vecchio Alves, A. V., Puscedu, F. H., Cortez, F. S., Santos, A. R., Pereira, C. D. S., & Cesar, A. (2012). Toxicity identification and evaluation of interstitial water sample of submarine sewage outfall of Santos (SP), Brazil. Unisanta BioScience, 1(1), 16–21.
Giesy, J. P., Graney, R. L., Newsted, J. L., Rosiu, C. J., Benda, A., Kreis, R. G., Jr., & Horvath, F. J. (1988). A comparison of three sediment bioassay methods using Detroit river sediments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 7, 483–498.
Ho, K. T., Burges, R. M., Pelletier, M. C., Serbst, J. R., Ryba, S. A., Cantwell, M. G., Kuhn, A., & Raczelowski, P. (2002). An overview of toxicant identification in sediments and dredged materials. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44, 286–293.
INEA - Instituto Estadual do Ambiente (2014). www.inea.rj.gov.br. Accessed 19 Jul 2014.
Koroleff, F. (1976). Determination of nutrients, In: Grasshoff, K. (ed.) Methods of seawater analysis. Verlag Chemie Weinhein.
Kuehl, D. W., Ankley, G. T., Burkhard, L. P., & Jensen, D. (1990). Bioassay directed characterization of the acute toxicity of a creosote leachate. Hazardous Waste Hazardous Mater, 7, 283–291.
Nilin, J., Castro, C. B., Pimentel, M. F., Franklin Júnior, W., Matos, R. F. G., Lotufo, T. M. C., & Costa-Lotufo, L. V. (2007). Water toxicity assessment of the Ceará River Estuary (Brazil). Journal of the Brazilian Society of Ecotoxicology, 2, 1–7.
Norberg-King, T. J., Ankley, G. T., & Robert, E. (1991). Application of toxicity identification evaluation procedures to the ambient waters of the Colusa basin drain. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 10, 891–901.
Novo, E. M. L. M., Stech, J. L.; Londe, L. R., Assireu, A., Barbosa, C. C., Alcântara, E. H., Souza, A. F. (2009). Integração de dados do sistema automático de monitoramento de variáveis ambientais (SIMA) e de imagens orbitais na avaliação do estado trófico do Reservatório da UHE Funil. Anais XIV Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto. Natal, Brasil. INPE. p. 4797 – 4804. 25–30.
Picone, M., Bergamin, M., Volpato, E., Delaney, E., Turetta, C., Ranaldo, M., Capodaglio, G., & Nasci, C. (2009). Sequential toxicity identification evaluation (TIE) for characterizing toxicity of Venice Lagoon sediments: comparison of two different approaches. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 538–545.
Pires, L. E. B., Bohrer-Morel, M. B. (2003). Avaliação e identificação da toxicidade (AIT) do efluente de um Pólo Industrial. In: VI Congreso SETAC LA, Buenos Aires. Libro de Resúmenes
Rocha, M. I. A., Branco, C. W. C., Sampaio, G. F., Gômara, G. A., & De Filippo, R. (2002). Spatial and temporal variation of limnological features, Microcystis aeruginosa and zooplankton in an eutrophic reservoir (Funil Reservoir, Rio de Janeiro). Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia, 14(3), 73–86.
Schubauer-Berigan, M. K., Dierkes, J. R., Ankley, G. T. (1990). Toxicity identification evaluation of contaminated sediments in Buffalo River, NY and Saginaw River, MI. Duluth: National Effluent Toxicity Assessment Center. 107p. (Technical Report 20–90).
Ungemach, H. (1960). Sedimentchemismus und seine Beziehung zum Stoffhaushalt in 40 europaischen Seen. Germany: Universität Kiel. 420p.
USEPA - United States Environmental Protection Agency (1991). Methods for aquatic toxicity identification evaluations: phase I. Toxicity characterization procedures. Second edition. Final Report. Duluth, MN: Environmental Research Laboratory. EPA/600/6-91/003.
USEPA - United States Environmental Protection Agency. (1996). Method 3050 B: acid digestion of sediments, sludges, and soils. Washington: EUA.
USEPA - United States Environmental Protection Agency (2007). Sediment toxicity identification evaluation: phases I, II and III Guidance Document. Washington D. C., EPA/600/R-07/080.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Furnas for supporting the field work, Dr. Arnola Rietzler for the material used in this study, Dr. Antonio Mozeto for laboratory assistance, and CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior) for the award of a scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matos, M.F., Botta, C.M.R. & Fonseca, A.L. Toxicity Identification Evaluation (Phase I) of water and sediment samples from a tropical reservoir contaminated with industrial and domestic effluents. Environ Monit Assess 186, 7999–8006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3982-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3982-4