Abstract
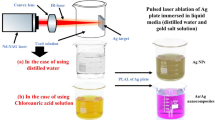
For some pressurized water reactors, 110mAg colloids deposite on the piping surface and auxiliary systems of the primary loop during the oxidation operation process, becoming one of the most important radionuclides. The decreasing concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) during the oxidation operation process may be the cause of the deposition of 110mAg colloids. In this work, Ag colloids with particle size of 20–60 nm were first synthesized. Then the effects of reaction temperature, concentration of H2O2 and reaction time on the oxidation and removal of Ag colloids were studied. The results showed that at least 5 ppm H2O2 was needed to achieve significant oxidation and removal of Ag colloids at 80 °C. The results of this work were then applied during the shutdown of a PWR. The oxidation operation process was improved to maintain the concentration of H2O2 at 4–8 ppm during the whole process. The deposition of 110mAg colloids was then effectively mitigated, and the RCV radiation index was reduced by 28.2%. This work demonstrates the importance of H2O2 in reducing the deposition of Ag colloids during the oxidation operation process, providing a new idea and methodology to reduce shutdown dose rate of PWRs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khurram M, Yahya AA-Z, Mohammad SA, Abdulsalam A (2021) Primary coolant activity of 54Mn, 59Fe, 58Co, 60Co, and 51Cr in system integrated small and modular reactor. Annal Nucl Energy 160:108356
EPRI (2009) Plant specific recommendations for PWR radiation source term reduction. EPRI, Palo Alto, CA
Fu P (2009) Study on categories and control technologies of radiation source terms in DAYA BAY and LING AO PWRS primary system master, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai
Dairiki J (1982) Radioactive decay data tables: a handbook of decay data for application to radiation dosimetry and radiological assessments. Nucl Sci Eng J Am Nucl Soc 82(4):477–478. https://www.researchgate.net/journal/Nuclear-science-and-engineering-the-journal-of-the-American-Nuclear-Society-0029-5639
Carola A (2014) Impacts of silver and Ag-110m on radiation field generation: review of operating experiences. EPRI, Palo Alto
Darroudi M, Ahmad MB, Hakimi M, Zamiri R, Zak AK, Hosseini HA, Zargar M (2013) Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of γ-irradiated silver nanoparticles in aqueous gelatin. Int J Miner Metall Mater 20(04):403–409
Park JS, Kuang J, Lim Y-M, Gwon H-J, Nho Y-C (2012) Characterization of silver nanoparticle in the carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel prepared by a Gamma Ray Irradiation. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12(1):743–747
Tang XD, Wei JC, Gao YM, Chen R (2019) Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticle. J Yunnan Norm Uni (Nat Sci Ed)39(4):55–58
Bhui DK, Bar H, Sarkar P, Sahoo GP, Misra A (2009) Synthesis and UV–vis spectroscopic study of silver nanoparticles in aqueous SDS solution. J Mol Liq 145(1):33–37
Wang Y, Xiong N, Zhou J (2014) Fluorescence enhancement effect of silver nanoparticles with different surface modifiers and sizes. Spectrasc Spectr Anal 34(12):3292–3296
Acknowledgements
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, G., Li, F., Fang, J. et al. Reduced deposition of 110mAg colloids by improved oxidation operation process during shutdown of a PWR. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 331, 111–118 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08109-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08109-9