Abstract
The attached and unattached radon and thoron progeny concentrations were measured in indoor environment using LR-115 detector-based Direct Progeny Sensors in a test village at Tehri Garhwal, India. The goal of this study is to determine radiological dosage attributed to inhalation of attached and unattached radon/thoron progeny. Human Respiratory Tract Model (HRTM) was used to estimate Inhalation Dose owing to nasal and mouth breathing. The average value of the annual effective dosage due to exposure of radon and thoron progeny was estimated to be 1.4 ± 0.4 mSv/y and 0.6 ± 0.2 mSv/y, respectively. The experimental techniques and results obtained are discussed in detail.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelikhah M, Shahrokhi A, Imani M, Chalupnik S, Kovács T (2021) Radiological assessment of indoor radon and thoron concentrations and indoor radon map of dwellings in mashhad, iran. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(1):1–15
Bourai AA, Aswal S, Dangwal A, Rawat M, Prasad M, Naithani NP, Joshi V, Ramola RC (2013) Measurements of radon flux and soil-gas radon concentration along the main Central Thrust, Garhwal Himalaya, using SRM and RAD7 detectors. Acta Geophys 61(4):950–957
Mishra R, Sapra BK, Mayya YS (2014) Multi-parametric approach towards the assessment of radon and thoron progeny exposures. Rev. Sci. Instrum 85(2):022105
Mú́llerová M, Kozak K, Kovács T, Csordás A, Grzadziel D, Holý K, Mazur J, Moravcsík A, Neznal M, Smetanová I 2014 Preliminary results of indoor radon survey in countries. Radiat Prot Dosim 160:210–213
Prasad M, Bossew P, Anil Kumar G, Mishra R, Ramola RC (2018) Dose assessment from the exposure to attached and unattached progeny of radon and thoron in indoor environment. Acta Geophys 66:1187–1194
Singh P, Saini K, Mishra R, Sahoo BK, Bajwa BS (2016) Attached, unattached fraction of progeny concentrations and equilibrium factor for dose assessments from 222Rn and 220Rn. Radiat Environ Biophys 55:401–410
Ramola RC, Prasad M, Kandari T, Pant P, Bossew P, Mishra R, Tokonami S (2016) Dose estimation derived from the exposure to radon, thoron and their progeny in the indoor environment. Sci Rep 6:31061
Saini K, Singh P, Singh P, Bajwa BS, Sahoo BK (2017) Seasonal variability of equilibrium factor and unattached fractions of radon and thoron in different regions of Punjab. India J Environ Radioact 167:110–116
Stajic JM, Nikezic D (2015) Measurement of radon exhalation rates from some building materials used in Serbian construction. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303:1943–1947
UNSCEAR (United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation) (2008) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly, Scientific Annexes A and B. United Nations, New York
UNSCEAR (United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation) (2000) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly, Scientific Annex B. United Nations, New York
Ramola RC, Gusain GS, Rautela BS, Sagar DV, Prasad G, Shahoo SK, Ishikawa T, Omori Y, Janik M, Sorimachi A, Tokonami S (2012) Levels of thoron and progeny in high background radiation area of southeastern coast of Odisha, India. Rad Prot Dosim 152(1–3):62–65
Mishra R, Prajith R, Sapra BK, Mayya YS (2010) Response of direct thoron progeny sensors (DTPS) to various aerosol concentrations and ventilation rates. Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 268(6):671–675
Mayya YS, Mishra R, Prajith R, Sapra BK, Kushwaha HS (2010) Wire-mesh capped deposition sensors: Novel passive tool for coarse fraction flux estimation of radon thoron progeny in indoor environments. Sci Total Environ 409(2):378–383
Hopke PK (1989) The initial behavior of 218Po in indoor air. Environ Int 15(1–6):299–308
Reineking A, Becker KH, Porstendörfer J (1985) Measurements of the unattached fractions of radon daughters in houses. Sci Total Enviro 45:261–270
Porstendörfer J (2002) Influence of physical parameters on doses from radon exposures. Int Congr Ser 1225(3):149–160
Sharma S, Kumar A, Mehra R, Kaur M, Mishra R (2018) Assessment of progeny concentrations of 222Rn/220Rn and their related doses using deposition-based direct progeny sensors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(12):11440–11453
UNSCEAR (United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation) (1993) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes United Nations, New York
Bangotra P, Mehra R, Kaur K, Kanse S, Mishra R, Sahoo BK (2015) Estimation of EEC, unattached fraction and equilibrium factor for the assessment of radiological dose using pin-hole cup dosimeters and deposition based progeny sensors. J Environ Radioact 148:67–73
Butterweck G, Schuler C, Vezzù G, Müller R, Marsh JW, Thrift S, Birchall A (2002) Experimental determination of the absorption rate of unattached radon progeny from respiratory tract to blood. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 102(4):343–348
Kaur M, Kumar A, Mehra R, Mishra R (2017) Assessment of attached and unattached progeny concentrations of 222Rn/220Rn and their contribution to dose using deposition-based progeny sensors. Environ Earth Sci 76:557
Kendall GM, Smith TJ (2002) Doses to organs and tissues from radon and its decay products. J Radiol Prot 22(4):389–406
Edling C, Wingren G, International OA-E (1986) U (1986) Quantification of the lung cancer risk from radon daughter exposure in dwellings—an epidemiological approach. Environ Int 12(1–4):55–60
Sevc J, Kunz E, Physics VP-H (1976) U (1976) Lung cancer in uranium miners and long-term exposure to radon daughter products. Health Phys 30(6):433–437
Tokonami S, Matsuzawa T, Ishikawa T, Iimoto T, Yonehara H, Yanada Y, (2003) Changes of indoor aerosol characteristics and their associated variation on the dose conversion factor due to radon progeny inhalation. Radioisotopes 52(6):285–292
Ashok GV, Nagaiah N, Shiva Prasad NG (2012) Indoor radon concentration and its possible dependence on ventilation rate and flooring type. Radiat Prot Dosim 148(1):92–100
Chamberlain AC, Dyson ED (1956) The dose to the trachea and bronchi from the decay products of radon and thoron. Br J Radiol 29(342):317–325
UNSCEAR (United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation)(2019) Sources, effects and risk of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly Scientific Annexes A and B. United Nation, New York
Porstendörfer J (2001) Physical parameters and dose factors of the radon and thoron decay products. Radiat Prot Dosim 94(4):365–373
Singla AK, Kansal S, Rani S, Mehra R (2021) Radiological risk assessment due to attached unattached fractions of radon and thoron progeny in Hanumangarh district Rajasthan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 330:1473–1483
Singla AK, Kansal S, Mehra R (2021) Dose distribution to individual tissues and organs due to exposure of alpha energies from radon and thoron to local population of Hanumangarh, Rajasthan, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 327:1073–1085
Singh B, Kant K, Garg M, Singh A, Sahoo BK (2019) A study of seasonal variations of radon, thoron and their progeny levels in different types of dwellings in Faridabad district, Southern Haryana, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 320:841–857
Huet C, Tymen G, Boulaud D (2001) Size distribution, equilibrium ratio and unattached fraction of radon decay products under typical indoor domestic conditions. Sci Total Environ 272(1–3):97–103
Hopke PK, Jensen B, Li CS, Montassier N, Wasiolek P, Cavallo AJ, Gatsby K, Socolow RH, James AC (1995) Assessment of the exposure to and dose from radon decay products in normally occupied homes. Environ Sci Technol 29(5):1359–1364
Kojima H, Abe S (1988) Measurements of the total and unattached radon daughters in a house. Radiat Prot Dosim 24(1–4):241–244
Reineking A, Porstendorfer J (1990) Unattached fraction of short-lived rn decay products in indoor and outdoor environments: An improved single-screen method and results. Health Phys 58(6):715–727
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) (2010) Lung cancer risk from radon and progeny and statement on radon, ICRP Publication 115
WHO (World Health Organization) (2009) Handbook on indoor radon. A public health perspective
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) (1993) Protection against radon-222 at home and at work. ICRP Publication 65
Prasad M, Rawat M, Dangwal A, Yadav M, Gusain GS, Mishra R, Ramola RC (2015) Measurements of radon and thoron progeny concentrations in dwellings of Tehri Garhwal, India, using LR-115 deposition-based DTPS/DRPS technique. Radiat Prot Dosim 167(1–3):102–106
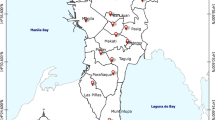
Panwar P, Prasad M, Ramola RC (2021) Study of soil-gas and indoor radon concentration in a test village at Tehri Garhwal, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 330:1383–1391
Mishra R, Sapra BK, Mayya YS (2009) Development of an integrated sampler based on direct 222Rn 220Rn progeny sensors in flow-mode for estimating unattached attached progeny concentration. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 267:3574–3579
Mishra R, Mayya YS (2008) Study of a deposition-based direct thoron progeny sensor (DTPS) technique for estimating equilibrium equivalent thoron concentration (EETC) in indoor environment. Radiat Meas 43(8):1408–1416
Mehta V, Singh SP, Chauhan RP, Mudahar GS (2015) Surface chemical etching behavior of lr-115 type ii solid state nuclear track detector. Rom Reports Phys 67(3):865–871
Ramola RC, Prasad M, Rawat M, Dangwal A, Gusain GS, Mishra R, Sahoo SK, Tokonami S (2015) Comparative study of various techniques for environmental radon, thoron and progeny measurements. Radiat Prot Dosim 167(1–3):22–28
Operation Manual: Spark Counter (MODEL PSI-sc 1) Polltech Instruments, www.polltechinstruments.com
Mehra R, Bangotra P, Kaur K, Kanse S, Mishra R (2015) Estimation of attached and unattached progeny of 222Rn and 220Rn concentration using deposition based progeny sensors. Radiat Prot Dosim 167(1–3):92–96
Mishra R, Prajith R, Sapra BK, Mayya YS (2010) An integrated approach for the assessment of the thoron progeny exposures using direct thoron progeny sensors. Radiat Prot Dosim 141(4):363–366
Knoll GF (2000) Radiation Detection and Measurement, 3rd edn. John Wiley
Knutson EO (1988) Modeling indoor concentrations of radon’s decay products. In: Nazaroff WW, Nero AV (eds) Radon and its decay products in indoor air. Wiley, New York, pp 161–199
Porstendörfer J (1997) Radon: Measurements related to dose. Environ Int 22:563–583
El-Hussein A (1996) Unattached fractions, attachment and deposition rates of radon progeny in indoor air. Appl Radiat Isot 47(5–6):515–523
Mohery M, El-Hussein A, Alddin SH, Howaity S et al (2012) Unattached fractions and aerosol attached of radon progeny in indoor air. Int J Phys Sci 7(29):5089–5096
Guo L, Zhang L, Guo Q (2016) Variation of the unattached fraction of radon progeny and its contribution to radon exposure. J Radiol Prot 36(2):N34–N41
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) (2018) Occupational Intakes of Radionuclides: ICRP Publication137(Part 3)
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) (2007) The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103
UNSCEAR (United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation) (2010) Summary of low-dose radiation effects on health.
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) (2010) Lung Cancer Risk from Radon and Progeny and statement on radon. ICRP Publication 115
Gusain GS, Prasad G, Prasad Y, Ramola RC (2009) Comparison of indoor radon level with radon exhalation rate from soil in Garhwal Himalaya. Radiat Meas 44(9–10):1032–1035
Ramola RC, Prasad G, Gusain GS (2011) Estimation of indoor radon concentration based on radon flux from soil and groundwater. Appl Radiat Isot 69(9):1318–1321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panwar, P., Joshi, A., Prasad, M. et al. Radiological dose estimation due to exposure to attached and unattached fractions of radon and thoron progeny concentrations. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 331, 1967–1974 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08103-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-08103-1