Abstract
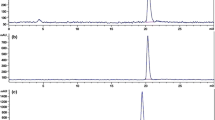
The aim of this study is to synthesize 125I-labeled 2-(4-iodophenethyl)-2-methylmalonic acid ([125I]IMA) for the development of new apoptosis imaging tracer. The optimized radiolabeling procedure provided [125I]IMA with high radiochemical yield (75.5 ± 5.2 %) and radiochemical purity (>99 %) within 100 min. Specific radioactivity of [125I]IMA was 31.0 MBq/μmol. Biodistribution study of [125I]IMA was carried out using ICR mouse and the result showed the uptake values in apoptotic cells of the testes of the male mice were 1.7–3.2 fold higher than those of leg muscle. Therefore, [125I]IMA will be a promising radiotracer for in vivo SPECT imaging of apoptotic cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson CB (1995) Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267(5203):1456–1462
Green DR, Kroemer G (2005) Pharmacological manipulation of cell death: clinical applications in sight? J Clin Invest 115(10):2610–2617
Reed JC (2006) Drug insight: cancer therapy strategies based on restoration of endogenous cell death mechanisms. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3(7):388–398
Belhocine T, Steinmetz N, Hustinx R, Bartsch P, Jerusalem G, Seidel L, Rigo P, Green A (2002) Increased uptake of the apoptosis-imaging agent 99mTc recombinant human Annexin V in human tumors after one course of chemotherapy as a predictor of tumor response and patient prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 8(9):2766–2774
Tait JF (2008) Imaging of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 49(10):1573–1576
Reshef A, Shirvan A, Akselrod-Ballin A, Wall A, Ziv I (2010) Small-molecule biomarkers for clinical PET imaging of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 51(6):837–840
Cohen A, Shirvan A, Levin G, Grimberg H, Reshef A, Ziv I (2009) From the Gla domain to a novel small-molecule detector of apoptosis. Cell Res 19(5):625–637
Höglund J, Shirvan A, Antoni G, Gustavsson SÅ, Långström B, Ringheim A, Sörensen J, Ben-Ami M, Ziv I (2011) 18F-ML-10, a PET tracer for apoptosis: first human study. J Nucl Med 52(5):720–725
Reshef A, Shirvan A, Waterhouse RN, Grimberg H, Levin G, Cohen A, Ulysse LG, Friedman G, Antoni G, Ziv I (2008) Molecular imaging of neurovascular cell death in experimental cerebral stroke by PET. J Nucl Med 49(9):1520–1528
Sobrio F, Médoc M, Martial L, Delamare J, Barré L (2013) Automated radiosynthesis of [18F]ML-10, a PET radiotracer dedicated to apoptosis imaging, on a TRACERLab FX-FN module. Mol Imag Biol 15(1):12–18
Oborski MJ, Laymon CM, Lieberman FS, Drappatz J, Hamilton RL, Mountz JM (2014) First use of 18F-labeled ML-10 PET to assess apoptosis change in a newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme patient before and early after therapy. Brain Behav 4(2):312–315
Kadirvel M, Fairclough M, Cawthorne C, Rowling EJ, Babur M, McMahon A, Birkket P, Smigova A, Freeman S, Williams KJ, Brown G (2014) Detection of apoptosis by PET/CT with the diethyl ester of [18F]ML-10 and fluorescence imaging with a dansyl analogue. Bioorg Med Chem 22(1):341–349
Bauwens M, De Saint-Hubert M, Cleynhens J, Brams L, Devos E, Mottaghy FM, Verbruggen A (2012) Radioiodinated phenylalkyl malonic acid derivatives as pH-sensitive SPECT tracers. PLoS ONE 7(6):e38428
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korea government (Grant no. 2012M2B2B1055245 and 2012M2A2A6011335) and Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, J., Shim, H.E., Mushtaq, S. et al. Radiosynthesis and in vivo evaluation of [125I]2-(4-iodophenethyl)-2-methylmalonic acid as a potential radiotracer for detection of apoptosis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 308, 23–29 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4346-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4346-4