Abstract
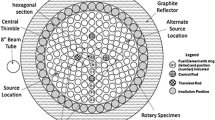
Stainless steel flux wires were used to determine the neutron energy spectra and total flux during the Reactor Accelerator Coupling Experiments (RACE) at The University of Texas at Austin. A LINAC electron accelerator produced 20 MeV electrons at a power of 1.6 kW, which struck a tungsten-copper target to produce bremsstrahlung radiation and photoneutrons. The neutrons produced in the target were multiplied by the subcritical core of a Triga reactor. The purpose of the RACE experiments is to develop a sub-critical accelerator driven system that would be capable of transmuting actinides from spent fuel. Flux measurements were made with 1.58 mm diameter stainless steel wires placed throughout the core between the fuel rods and cadmium covered and uncovered gold and indium foils above the target. The MAXED and GRAVEL computer codes were used to perform the spectrum unfolding. The composition of the stainless steel wires was determined using neutron activation analysis with comparators prior to the flux measurement. The reactions measured in the stainless steel to determine the flux were 50Cr(n,γ)51Cr, 58Ni(n,p)58Co, 54Fe(n,p)54Mn, and 58Fe(n,γ)59Fe. Flux measurements agreed well with an MCNP simulation of the experiment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. A. Abderrahim et al., Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 116 (2005) 433.
A. C. Mueller, Nucl. Phys., 751 (2005) 453c.
M. Plaschy et al., Annals Nucl. Energy, 32 (2005) 843.
T. Sasa, Progr. Nucl. Energy, 47 (2005) 314.
A. Brolly, P. Vertes, Acta Phys. Hung. New Series — Heavy Ion Physics, 19 (2004) 263.
A. Brolly, P. Vertes, Annals Nucl. Energy, 31 (2004) 585.
J. Wallenius, M. Eriksson, Nucl. Technol., 152 (2005) 367.
M. Reginatto, P. Goldhagen, Health Phys, 77 (1999) 579.
K. Kudo et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res., 476 (2002) 213.
D. D. Soete, Neutron Activation Analysis, Wiley-Interscience, London, 1972.
D. K. Mohapatra, P. Mohanakrishnan, Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 57 (2002) 25.
M. Tombakoglu, Y. Cecen, Burnup dependent core neutronic calculation for research and training reactors via SCALE4.4, in: Intern. Conf. Nuclear Energy in Central Europe, Portoroz, Slovenia, 2001.
A. Corana et al., ACM Trans. Mathemat. Software, 13 (1987) 262.
S. R. Malkawi, N. Ahmad, Annals Nucl. Energy, 27 (2000) 311.
A. Seghour, F. Z. Seghour, Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res., 555 (2005) 347.
R. Soule et al., Nucl. Sci. Eng., 148 (2004) 124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Green, T., Biegalski, S., O’Kelly, S. et al. Neutron energy spectrum determination and flux measurement using MAXED, GRAVEL, and MCNP for RACE experiments. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 276, 279–284 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-007-0446-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-007-0446-0