Summary
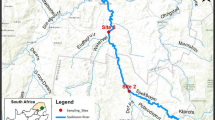
The Lerma is one of the most important rivers of Mexico, where it drains highly populated and industrialized regions. The concentration of six major and trace elements: titanium, manganese, iron, zinc, copper and lead in the surface sediments of the upper course of Lerma river was investigated, in order to identify its distribution along the river and to recognize the principal sites of pollution. The surface sediment samples were collected at 8 sites distributed following the stream flow direction of the river. Major and trace elements concentrations were determined by energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry. The results show that the metal concentrations in the sediments decrease in the sequence: Fe > Ti > Mn > Zn > Cu > Pb. Concentration of Fe, Mn and Ti were significantly higher than the other metals in site 8,200 meters downstream the Alzate Dam. The high concentrations and spatial variations of Zn, Cu and Pb in the middle sites of the upper course of the Lerma River indicate that the river pollution is probably associated with urban and industrial discharges.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tejeda, S., Zarazúa-Ortega, G., Avila-Pérez, P. et al. Major and trace elements in sediments of the upper course of Lerma river. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 270, 9–14 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-006-0342-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-006-0342-z