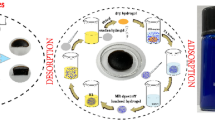
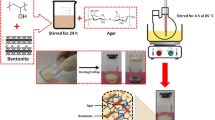
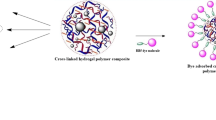
Abstract
In this work, two kinds of porous biochar composite hydrogel were prepared to effectively remove low-concentration dyes via simple one-pot aqueous polymerization. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), x-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM), and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to confirm the successful synthesis of the composite hydrogels and the mesoporous structure was further verified through BET method. The adsorption factors were also studied, and the two adsorbents presented high removal efficiency in low concentration methylene blue (MB) solution. The adsorption process fitted the Freundlich isotherm model well, and the adsorption kinetics followed the pseudo-second-order kinetics model. After eight cycle tests, the composite hydrogels still kept a high removal efficiency for MB. In conclusion, the prepared composite hydrogels can be used as an effective adsorbent for removing the dyes from wastewater.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
Artifon W, Cesca K, de Andrade CJ, de Souza AAU, de Oliveira (2021) Dyestuffs from textile industry wastewaters: trends and gaps in the use of bioflocculants. Process Biochem 111:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2021.10.030
Sharma K, Dalai AK, Vyas RK (2018) Removal of synthetic dyes from multicomponent industrial wastewaters. Rev Chem Eng 34(1):107–134. https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2016-0042
Dil EA, Ghaedi M, Asfaram A, Mehrabi F, Bazrafshan AA (2018) Optimization of process parameters for determination of trace Hazardous dyes from industrial wastewaters based on nanostructures materials under ultrasound energy. Ultrason Sonochem 40:238–248. https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2016-0042
Wang J, Zhang T, Mei Y, Pan B (2018) Treatment of reverse-osmosis concentrate of printing and dyeing wastewater by electro-oxidation process with controlled oxidation-reduction potential (ORP). Chemosphere 201:621–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.051
Gu S, Lian F, Yan K, Zhang W (2019) Application of polymeric ferric sulfate combined with cross-frequency magnetic field in the printing and dyeing wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol 80(8):1562–1570. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2019.401
Xu H, Yang B, Liu Y, Li F, Shen C, Ma C, Sand W (2018) Recent advances in anaerobic biological processes for textile printing and dyeing wastewater treatment: a mini-review. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34(11):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2548-y
Donkadokula NY, Kola AK, Naz I, Saroj D (2020) A review on advanced physico-chemical and biological textile dye wastewater treatment techniques. Rev Environ Sci Bio 19(3):543–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09543-z
Li D, Ning X, Yuan Y, Hong Y, Zhang J (2020) Ion-exchange polymers modified bacterial cellulose electrodes for the selective removal of nitrite ions from tail water of dyeing wastewater. J Environ Sci (China) 91:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.01.002
Shindhal T, Rakholiya P, Varjani S, Pandey A, Ngo HH, Guo W, Taherzadeh MJ (2021) A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered 12(1):70–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/216559.2020.1863034
Samsami S, Mohamadizaniani M, Sarrafzadeh MH, Rene ER, Firoozbahr M (2020) Recent advances in the treatment of dye-containing wastewater from textile industries: Overview and perspectives. Process Saf Environ Prot 143:138–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.05.034
Ayranci E, Duman O (2009) In-situ UV-visible spectroscopic study on the adsorption of some dyes onto activated carbon cloth. Sep Sci Technol 44(15):3735–3752. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390903182891
Duman O, Tunç S, Polat TG (2015) Determination of adsorptive properties of expanded vermiculite for the removal of CI Basic Red 9 from aqueous solution: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Appl Clay Sci 109:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.03.003
Duman O, Tunç S, Polat TG, Bozoğlan BK (2016) Synthesis of magnetic oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotube-κ-carrageenan-Fe3O4 nanocomposite adsorbent and its application in cationic Methylene Blue dye adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 147:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.03.099
Duman O, Polat TG, Diker CÖ, Tunç S (2020) Agar/κ-carrageenan composite hydrogel adsorbent for the removal of Methylene Blue from water. Int J Biol Macromol 160:823–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.191
Zainal SH, Mohd NH, Suhaili N, Anuar FH, Lazim AM, Othaman R (2021) Preparation of cellulose-based hydrogel: A review. J Mater Sci Technol 10:935–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.12.012
Qu B, Luo Y (2020) Chitosan-based hydrogel beads: Preparations, modifications and applications in food and agriculture sectors–A review. Int J Biol Macromol 152:437–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.240
Guo Y, Bae J, Fang Z, Li P, Zhao F, Yu G (2020) Hydrogels and hydrogel-derived materials for energy and water sustainability. Chem Rev 120(15):7642–7707. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00345
Jabir L, El-Hammi H, Mohammed N, Jilal I, El Idrissi A, Amhamdi H, Laatikainen K (2022) Cellulose based pH-sensitive hydrogel for highly efficient dye removal in water treatment: kinetic, thermodynamic, theoretical and computational studies. Cellulose 29(8):4539–4564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04564-z
Meng Y, Li C, Liu X, Lu J, Cheng Y, Xiao LP, Wang H (2019) Preparation of magnetic hydrogel microspheres of lignin derivate for application in water. Sci Total Environ 685:847–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.278
Lee YC (2018) Vinh Van Tran, Duckshin Park. Environ Sci 25:24569–24599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2605-y
Liang Y, Wang X, An W, Li Y, Hu J, Cui W (2019) A g-C3N4@ ppy-rGO 3D structure hydrogel for efficient photocatalysis. Appl Surf Sci 466:666–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.059
He J, Cui A, Ni F, Deng S, Shen F, Yang G (2018) A novel 3D yttrium based-graphene oxide-sodium alginate hydrogel for remarkable adsorption of fluoride from water. J Colloid Interf Sci 531:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.07.017
Wang Y, Zhang W, Liu M, Geng Z, Li Y, Feng L, Zhu Y (2020) Enhanced removal of pollutant in a BiPO4–SiO2 hybrid hydrogel via an adsorption–enrichment and in situ photocatalysis synergy. J Mater Sci 55(17):7441–7452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04529-2
Akl ZF, Zaki EG, ElSaeed SM (2021) Green Hydrogel-Biochar Composite for Enhanced Adsorption of Uranium. ACS Omega 6(50):34193–34205. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c01559
Zhang W, Song J, He Q, Wang H, Lyu W, Feng H, Chen L (2020) Novel pectin based composite hydrogel derived from grapefruit peel for enhanced Cu (II) removal. J Hazard Mater 384:121445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121445
Sharma G, Thakur B, Kumar A, Sharma S, Naushad M, Stadler FJ (2020) Gum acacia-cl-poly (acrylamide)@ carbon nitride nanocomposite hydrogel for adsorption of ciprofloxacin and its sustained release in artificial ocular solution. Macromol Mater Eng 305(9):2000274. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.202000274
Zheng Y, Wang X, Zhang C, Zong L (2022) Synthesis, characterization, and swelling behaviors of chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) superabsorbent using tetraallylammonium bromine as crosslinker. Polym Bull 2022:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04289-w
Czarnecka E, Nowaczyk J (2021) Synthesis and characterization superabsorbent polymers made of starch, acrylic acid, acrylamide, poly (Vinyl alcohol), 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid. Int J Mol Sci 22(9):4325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094325
Yang Y, Ma S, Zhao Y, Jing M, Xu Y, Chen J (2015) A field experiment on enhancement of crop yield by rice straw and corn stalk-derived biochar in Northern China. Nat Sustain 7(10):13713–13725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094325
Wu Z, Chen X, Yuan B, Fu ML (2020) A facile foaming-polymerization strategy to prepare 3D MnO2 modified biochar-based porous hydrogels for efficient removal of Cd (II) and Pb (II). Chemosphere. 239:124745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124745
Zhuang M, Zhao J, Li S, Liu D, Wang K, Xiao P, Chu Z (2017) Functionalized biochar derived from heavy metal rich feedstock: phosphate recovery and reusing the exhausted biochar as an enriched soil amendment. Chemosphere 198:351–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.113
El-saied HA, Shahr El-Din AM, Masry BA, Ibrahim AM (2020) A promising superabsorbent nanocomposite based on grafting biopolymer/nanomagnetite for capture of 134Cs, 85Sr and 60Co radionuclides. J Polym Environ 28(6):1749–1765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01720-z
Mittal H, Parashar V, Mishra SB, Mishra AK (2014) Fe3O4 MNPs and gum xanthan based hydrogels nanocomposites for the efficient capture of malachite green from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 255:471–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01720-z
Tien HN, Hien NTM, Oh ES, Chung J, Kim EJ, Choi WM, Hur SH (2013) Synthesis of a highly conductive and large surface area graphene oxide hydrogel and its use in a supercapacitor. J Mater Chem A 1(2):208–211. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2TA00444E
Kumar N, Mittal H, Parashar V, Ray SS, Ngila JC (2016) Efficient removal of rhodamine 6G dye from aqueous solution using nickel sulphide incorporated polyacrylamide grafted gum karaya bionanocomposite hydrogel. RSC Adv 6(26):21929–21939. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA24299A
Dhiman J, Prasher SO, ElSayed E, Patel RM, Nzediegwu C, Mawof A (2021) Effect of hydrogel based soil amendments on heavy metal uptake by spinach grown with wastewater irrigation. J Clean Prod. 311:127644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127644
Salama A (2018) Preparation of CMC-gP (SPMA) super adsorbent hydrogels: Exploring their capacity for MB removal from waste water. Int J Biol Macromol 106:940–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.097
Unugul T, Nigiz FU (2020) Preparation and characterization an active carbon adsorbent from waste mandarin peel and determination of adsorption behavior on removal of synthetic dye solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 231(11):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04903-5
Moharrami P, Motamedi E (2020) Application of cellulose nanocrystals prepared from agricultural wastes for synthesis of starch-based hydrogel nanocomposites: Efficient and selective nanoadsorbent for removal of cationic dyes from water. Bioresour Technol 313:123661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123661
Sharma S, Sharma G, Kumar A, AlGarni TS, Naushad M, ALOthman ZA, Stadler FJ (2022) Adsorption of cationic dyes onto carrageenan and itaconic acid-based superabsorbent hydrogel: Synthesis, characterization and isotherm analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 421:126729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126729
Duman O, Ayranci E (2005) Structural and ionization effects on the adsorption behaviors of some anilinic compounds from aqueous solution onto high-area carbon-cloth. J Hazard Mater 120:173–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.12.030
Duman O, Ayranci E (2006) Adsorption characteristics of benzaldehyde, sulphanilic acid, and p-phenolsulfonate from water, acid, or base solutions onto activated carbon cloth. Sep Sci Technol 41:3673–3692. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390600915072
Ayranci E, Duman O (2007) Removal of anionic surfactants from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto high area activated carbon cloth studied by in situ UV spectroscopy. J Hazard Mater 148:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.02.006
Abou Taleb MF, Abou El Fadl FI, Albalwi H (2021) Adsorption of toxic dye in wastewater onto magnetic NVP/CS nanocomposite hydrogels synthesized using gamma radiation. Sep Purif Technol 266:118551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118551
Makhado E, Hato MJ (2021) Preparation and characterization of sodium alginate-based oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes hydrogel nanocomposite and its adsorption behaviour for methylene blue dye. Front Chem 9:576913. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.576913
Aljeboree AM, Radia ND, Jasim LS, Alwarthan AA, Khadhim MM, Salman AW, Alkaim AF (2022) Synthesis of a new nanocomposite with the core TiO2/hydrogel: Brilliant green dye adsorption, isotherms, kinetics, and DFT studies. J Ind Eng Chem 109:475–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2022.02.031
Jamali M, Akbari A (2021) Facile fabrication of magnetic chitosan hydrogel beads and modified by interfacial polymerization method and study of adsorption of cationic/anionic dyes from aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105175
Jain P, Sahoo K, Mahiya L, Ojha H, Trivedi H, Parmar AS, Kumar M (2021) Color removal from model dye effluent using PVA-GA hydrogel beads. J Environ Manage 281:111797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111797
Jasim LS, Aljeboree AM (2021) Hydrogels in the removal of industrial pollution: Adsorption characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye from aqueous solutions. J Environ Sci 19:789–799. https://doi.org/10.22124/CJES.2021.5209
Franciski MA, Peres EC, Godinho M, Perondi D, Foletto EL, Collazzo GC, Dotto GL (2018) Development of CO2 activated biochar from solid wastes of a beer industry and its application for methylene blue adsorptionn. Waste Manage 78:630–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.06.040
Ahmed MJ, Okoye PU, Hummadi EH, Hameed BH (2019) High-performance porous biochar from the pyrolysis of natural and renewable seaweed (Gelidiella acerosa) and its application for the adsorption of methylene blue. Bioresour Technol 278:159–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.054
Kong SH, Lam SS, Yek PNY, Liew RK, Ma NL, Osman MS, Wong CC (2019) Self-purging microwave pyrolysis: an innovative approach to convert oil palm shell into carbon-rich biochar for methylene blue adsorption. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94:1397–1405. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5884
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Dongying scientific development fund (DJ2020026) (DJ2021021) (DJ2021018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiangpeng Wang: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing—original draft, Writing—review &editing. Yunxiang Zheng: Investigation. Lina Zong: Data curation. Chunxiao Zhang:Conceptualization. Xiaoting Ren: Investigation. Yu Ding: Supervision. Chengquan Zhang: Project administration. Yue Zhou: Resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Zheng, Y., Zong, L. et al. Porous biochar composite hydrogel for effective removal of low-concentration methylene blue from wastewater. J Polym Res 29, 467 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03295-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03295-w