Abstract
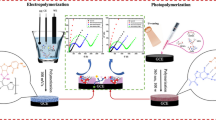
Hemoglobin (Hb) imprinted poly (ionic liquid)s (HIPILs) were fabricated on the surface of Pt wire modified with nano-gold (nAu) via simplified electrochemically mediated atom transfer radical polymerization (seATRP) in only 5 μL volumes. The micro upgrade seATRP was mainly carried out by two platinum wires electrode. The one platinum wire was bare and applied as the counter electrode, the other one was modified segmentally, which made it could be used both as a catalytic electrode of seATRP and the substrate of HIPILs. The HIPILs were prepared by using Hb as the template, 1-vinyl-3-propyl-imidazole sulfonate (VPIS) ionic liquids and N, N′-methylene bis-acrylamide (MBA) as the functional monomer and cross-linking agent of HIPILs, respectively. When a constant current was applied to the catalytic electrode, Fe (III) in Hb would be reduced to Fe (II), seATRP of VPIS would be triggered on the surface of Pt/nAu electrode. After Hb was removed, the HIPILs modified electrode (Pt/nAu/HIPILs) was obtained. The Pt/nAu/HIPILs electrode was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), cyclic voltammetry (CV), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Further experiments indicated that the Pt/nAu/HIPILs electrode could be utilized as electrochemical sensor to determine Hb by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). The linear response range was 1.0 × 10–12 ~ 1.0 × 10–1 mg/mL and the detection limit was 3.29 × 10–13 mg/mL (S/N = 3). Compared with other Hb sensors based on imprinting polymers, the broader linear range and lower detection limit suggested the promising prospect of the biosensor.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Che Lah NF, Ahmad AL, Mohd Amri MH, Chin JY (2022) Configuration of molecularly imprinted polymers for specific uptake of pharmaceutical in aqueous media through radical polymerization method. J Polym Res 29
Paruli E III, Soppera O, Haupt K, Gonzato C (2021) Photopolymerization and photostructuring of molecularly imprinted polymers. ACS Appl Polym Mater 3:4769–4790
Ozcelikay G, Kaya SI, Ozkan E, Cetinkaya A, Nemutlu E, Kır S, Ozkan SA (2022) Sensor-based MIP technologies for targeted metabolomics analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 146
Yang Z, Yang K, Cui Y, Shah T, Ahmad M, Zhang Q, Zhang B (2021) Synthesis of surface imprinted polymers based on wrinkled flower-like magnetic graphene microspheres with favorable recognition ability for BSA. J Mater Sci Technol 74:203–215
Ferreira JB, de Jesus MC, Dinali LAF, Filho JFA, Silva CF, Borges KB, Romao W (2021) Molecularly imprinted polymers as a selective sorbent for forensic applications in biological samples-a review. Anal Bioanal Chem 413:6013–6036
He S, Zhang L, Bai S, Yang H, Cui Z, Zhang X, Li Y (2021) Advances of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) and the application in drug delivery. Eur Polym J 143
Motia S, Bouchikhi B, El Bari N (2021) An electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer conjointly with a voltammetric electronic tongue for quantitative diphenyl phosphate detection in urine samples from cosmetic product users. Sens Actuators B Chem 332
Zaidi SA (2021) An overview of bio-inspired intelligent imprinted polymers for virus determination. Biosensors (Basel) 11
Ali GK, Omer KM (2022) Molecular imprinted polymer combined with aptamer (MIP-aptamer) as a hybrid dual recognition element for bio(chemical) sensing applications. Review Talanta 236:122878
Hu W, Xu L (2021) Investigation of eATRP for a carboxylic-acid-functionalized ionic liquid monomer. Macromol Chem Phys 222
Isse AA, Lorandi F, Gennaro A (2019) Electrochemical approaches for better understanding of atom transfer radical polymerization. Curr Opin Electrochem 15:50–57
Yang W, Fang Q, Zhang L, Yin H, Wu C, Zhang W, Huang W, Ni X (2021) Synthesis and characterization of an innovative molecular imprinted polymers based on CdTe QDs fluorescence sensing for selective detection of sulfadimidine. J Polym Res 28
Hu Y, Liang B, Fang L, Ma G, Yang G, Zhu Q, Chen S, Ye X (2016) antifouling zwitterionic coating via electrochemically mediated atom transfer radical polymerization on enzyme-based glucose sensors for long-time stability in 37 degrees C serum. Langmuir 32:11763–11770
Bortolamei N, Isse AA, Magenau AJ, Gennaro A, Matyjaszewski K (2011) Controlled aqueous atom transfer radical polymerization with electrochemical generation of the active catalyst. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50:11391–11394
Michieletto A, Lorandi F, De Bon F, Isse AA, Gennaro A (2019) Biocompatible polymers via aqueous electrochemically mediated atom transfer radical polymerization. J Polym Sci 58:114–123
Fantin M, Lorandi F, Isse AA, Gennaro A (2016) Sustainable electrochemically-mediated atom transfer radical polymerization with inexpensive non-platinum electrodes. Macromol Rapid Commun 37:1318–1322
Sun Y, Lathwal S, Wang Y, Fu L, Olszewski M, Fantin M, Enciso AE, Szczepaniak G, Das S, Matyjaszewski K (2019) Preparation of well-defined polymers and DNA–polymer bioconjugates via small-volume eATRP in the presence of air. ACS Macro Lett 8:603–609
Sajid M, Plotka-Wasylka J (2022) Green analytical chemistry metrics: A review. Talanta 238:123046
Sripirom J, Sim WC, Khunkaewla P, Suginta W, Schulte A (2018) simple and economical analytical voltammetry in 15 mul volumes: Paracetamol voltammetry in blood serum as a working example. Anal Chem 90:10105–10110
Chmielarz P, Yan J, Krys P, Wang Y, Wang Z, Bockstaller MR, Matyjaszewski K (2017) Synthesis of nanoparticle copolymer brushes via surface-initiated seATRP. Macromolecules 50:4151–4159
Xu X, Xu X, Zeng Y, Zhang F (2021) Oxygen-tolerant photo-induced metal-free atom transfer radical polymerization. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 411
Llorente O, Agirre A, Calvo I, Olaso M, Tomovska R, Sardon H (2021) Exploring the advantages of oxygen-tolerant thiol-ene polymerization over conventional acrylate free radical photopolymerization processes for pressure-sensitive adhesives. Polym J 53:1195–1204
Poulose S, Jönkkäri I, Hedenqvist MS, Kuusipalo J (2021) Bioplastic films with unusually good oxygen barrier properties based on potato fruit-juice. RSC Adv 11:12543–12548
Enciso AE, Fu L, Russell AJ, Matyjaszewski K (2018) A breathing atom-transfer radical polymerization: fully oxygen-tolerant polymerization inspired by aerobic respiration of cells. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57:933–936
Liarou E, Whitfield R, Anastasaki A, Engelis NG, Jones GR, Velonia K, Haddleton DM (2018) Copper-mediated polymerization without external deoxygenation or oxygen scavengers. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57:8998–9002
Wang H, Li F, Dong Y, Li Z, Wang G-L (2019) Ferricyanide stimulated cathodic photoelectrochemistry of flower-like bismuth oxyiodide under ambient air: A general strategy for robust bioanalysis. Sens Actuators, B Chem 288:683–690
Kim SY, Park CS, Hosseini S, Lampert J, Kim YJ, Nazar LF (2021) Inhibiting oxygen release from Li-rich, Mn-rich layered oxides at the surface with a solution processable oxygen scavenger polymer. Adv Energy Mater 11
Ma P, Ma X, Chen F (2021) The construction of stimulus-responsive film electrode by the Cu-catalyzed radical polymerization and its application in multi-valued biologic systems. Electroanalysis 33:2437–2444
Wang J, Tian M, Li S, Wang R, Du F, Xue Z (2018) Ligand-free iron-based electrochemically mediated atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate. Polym Chem 9:4386–4394
Park S, Chmielarz P, Gennaro A, Matyjaszewski K (2015) Simplified electrochemically mediated atom transfer radical polymerization using a sacrificial anode. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54:2388–2392
Zaborniak I, Chmielarz P (2020) Miniemulsion switchable electrolysis under constant current conditions. Polym Adv Technol 31:2806–2815
Chmielarz P, Sobkowiak A (2017) Ultralow ppm seATRP synthesis of PEO-b-PBA copolymers. J Polym Res 24
Zaborniak I, Chmielarz P, Martinez MR, Wolski K, Wang Z, Matyjaszewski K (2020) Synthesis of high molecular weight poly(n-butyl acrylate) macromolecules via seATRP: From polymer stars to molecular bottlebrushes. Eur Polym J 126
Chmielarz P, Park S, Sobkowiak A, Matyjaszewski K (2016) Synthesis of β-cyclodextrin-based star polymers via a simplified electrochemically mediated ATRP. Polymer 88:36–42
Szczepaniak G, Fu L, Jafari H, Kapil K, Matyjaszewski K (2021) Making ATRP more practical: oxygen tolerance. Acc Chem Res 54:1779–1790
Liu H, Yu H (2019) Ionic liquids for electrochemical energy storage devices applications. J Mater Sci Technol 35:674–686
Shahriman MS, Mohamad S, Mohamad Zain NN, Alias Y, Chandrasekaram K, Raoov M (2021) Paper-based polymeric ionic liquid for thin film micro extraction of sulfonamides in environmental water samples prior to HPLC-DAD analysis. Microchem J 171
Xie W, Zhang J, Zeng Y, Wang H, Yang Y, Zhai Y, Miao D, Li L (2020) Highly sensitive and selective detection of 4-nitroaniline in water by a novel fluorescent sensor based on molecularly imprinted poly(ionic liquid). Anal Bioanal Chem 412:5653–5661
Lu Y, Hu J, Zeng Y, Zhu Y, Wang H, Lei X, Huang S, Guo L, Li L (2020) Electrochemical determination of rutin based on molecularly imprinted poly (ionic liquid) with ionic liquid-graphene as a sensitive element. Sens Actuators B Chem 311
Wu Y, Wang Y, Wang X, Wang C, Li C, Wang Z (2019) Electrochemical sensing of α-fetoprotein based on molecularly imprinted polymerized ionic liquid film on a gold nanoparticle modified electrode surface. Sensors (Basel) 19
Sun Y, Zhang J, Li J, Zhao M, Liu Y (2017) Preparation of protein imprinted polymers via protein-catalyzed eATRP on 3D gold nanodendrites and their application in biosensors. RSC Adv 7:28461–28468
Sun Y, Du H, Deng Y, Lan Y, Feng C (2015) Preparation of polyacrylamide via surface-initiated electrochemical-mediated atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-eATRP) for Pb2+ sensing. J Solid State Electrochem 20:105–113
Sun Y, Feng X, Hu J, Bo S, Zhang J, Wang W, Li S, Yang Y (2020) Preparation of hemoglobin (Hb)-imprinted poly(ionic liquid)s via Hb-catalyzed eATRP on gold nanodendrites. Anal Bioanal Chem 412:983–991
Jijana AN, Mphuthi N, Shumbula P, Vilakazi S, Sikhwivhilu L (2021) The ultra-sensitive electrochemical detection of As(III) in ground water using disposable L-cysteine/Lipoic Acid functionalised gold nanoparticle modified screen-printed electrodes. Electrocatalysis 12:310–325
Paixão TRLC (2020) Measuring electrochemical surface area of nanomaterials versus the Randles−Ševčík equation. ChemElectroChem 7:3414–3415
Yang Y, Sun Y, Jin M, Bai R, Liu Y, Wu Y, Wang W, Feng X, Li S (2020) Fabrication of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) imprinted poly(ionic liquid)s via eATRP and its application in electrochemical sensor. Electroanalysis 32:1772–1779
Yan CN, Liu Q, Xu L, Bai LP, Wang LP, Li G (2019) Photoinduced metal-free surface initiated ATRP from hollow spheres surface. Polymers (Basel) 11
Bagus PS, Nelin CJ, Brundle CR, Crist BV, Lahiri N, Rosso KM (2021) Combined multiplet theory and experiment for the Fe 2p and 3p XPS of FeO and Fe2O3. J Chem Phys 154:094709
Wei Y, Zeng Q, Huang J, Guo X, Wang L, Wang L (2020) Preparation of gas-responsive imprinting hydrogel and their gas-driven switchable affinity for target protein recognition. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:24363–24369
Bai R, Sun Y, Zhao M, Han Z, Zhang J, Sun Y, Dong W, Li S (2021) Preparation of IgG imprinted polymers by metal-free visible-light-induced ATRP and its application in biosensor. Talanta 226:122160
Sun Y, Du H, Lan Y, Wang W, Liang Y, Feng C, Yang M (2016) Preparation of hemoglobin (Hb) imprinted polymer by Hb catalyzed eATRP and its application in biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 77:894–900
Bo S, Sun Y, Li S, Zhou Y, Feng X, Li C (2021) Preparation of hemoglobin (Hb) imprinted polymers with CO2 response and its biosensing application. J Solid State Electrochem 25:1645–1655
Motia S, Bouchikhi B, El Bari N (2021) An electrochemical molecularly imprinted sensor based on chitosan capped with gold nanoparticles and its application for highly sensitive butylated hydroxyanisole analysis in foodstuff products. Talanta 223:121689
Kalaiyarasan G, Joseph J (2019) Cholesterol derived carbon quantum dots as fluorescence probe for the specific detection of hemoglobin in diluted human blood samples. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 94:580–586
Liu Y, Wang Y, Jiang K, Sun S, Qian S, Wu Q, Lin H (2020) A persistent luminescence-based label-free probe for the ultrasensitive detection of hemoglobin in human serum. Talanta 206:120206
Duan H, Wang X, Wang Y, Li J, Luo C (2015) Bioreceptor multi-walled carbon nanotubes@Fe3O4@SiO2–surface molecular imprinted polymer in an ultrasensitive chemiluminescent biosensor for bovine hemoglobin. RSC Adv 5:88492–88499
Li N, Liu X, Zhu J, Zhou B, Jing J, Wang A, Xu R, Wen Z, Shi X, Guo S (2020) Simple and sensitive detection of acrylamide based on hemoglobin immobilization in carbon ionic liquid paste electrode. Food Control 109
Wang Z, Li F, Xia J, Xia L, Zhang F, Bi S, Shi G, Xia Y, Liu J, Li Y, Xia L (2014) An ionic liquid-modified graphene based molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of bovine hemoglobin. Biosens Bioelectron 61:391–396
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Nature Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 2021-MS-273), Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program (No. 2020921109), High-end Research Incubation Scheme of Liaoning Normal University (No. GD20L001), and Undergraduate Research Training Project of Liaoning Normal University (No. CX202102008, 202110165098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ailu Cui: Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation, Zuan Yang: Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation, Xuewei Feng: Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation, Huanying Zhao: Formal analysis, Writing- Reviewing and Editing, Peiran Meng: Formal analysis, Writing- Reviewing and Editing, Yanxuan Xie: Formal analysis, Writing- Reviewing and Editing, Linan Miao: Formal analysis, Writing- Reviewing and Editing, Yue Sun: Conceptualization, Methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, A., Yang, Z., Feng, X. et al. Preparation and properties of hemoglobin (Hb)-imprinted poly (ionic liquid)s via seATRP in only 5 μL Volumes. J Polym Res 29, 384 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03237-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03237-6