Abstract
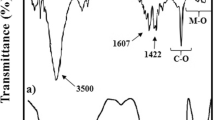
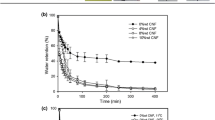
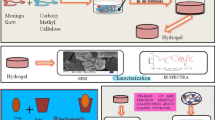
In this study synthesis of hydrogel and nanocomposite based on modified cellulose have been investigated. Hydrogels constitute a group of polymeric materials. The hydrophilic structure of which renders them capable of holding large amounts of water compared to their weight in their structure. As expected, natural hydrogels were gradually replaced by synthetic types due to their higher water absorption capacity, long service life, and wide varieties of raw chemical resources. Furthermore, the purpose of this work is to study the synthesis of a novel hydrogel based on carboxymethyl cellulose and acrylamide and itaconic acid. Synthesis carried out in aqueous medium, ammonium persulphate used as initiator and N, N-methylene bis acrylamide used as cross-linker. To study the morphological structure and characterize the synthesized hydrogel SEM, FTIR and TGA analysis carried out on the products. Results indicate that the water absorbency of the synthesize hydrogel is 67 g/g. The developed hydrogels have the potential to be used for biomedical use. To study the biomedical application drug release of hydrogel and nanocomposite have been studied and ofloxacin used as a drug model. Results showed a sustain control release of drug over 2.5 h from the synthesized hydrogel and 6 h from the CNT nanocomposite’s structure. The results of MTT assay performed on the synthesized hydrogel showed that the compound exhibits no toxicity at various concentrations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wichterle O, Lim D (1960) Hydrophilic gels for biological use. Nature 185:117–118
Kopeček J (2007) Hydrogel biomaterials: a smart future? Biomaterials 28:5185–5192
Lutolf MP (2009) Spotlight on hydrogels. Nat Mater 8:451–453
Sciences M, Popescu R, Ghica MV et al (2020) New opportunity to formulate intranasal vaccines and drug delivery systems based on Chitosan. Int J Mol Sci 21:1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145016
Xu J, Wang H, Jiang L et al (2021) Preparation of cellulose hydrogel dressing with evenly dispersed hydrophobic drugs by hydrogen bonding and encapsulation methods. Macromol Mater Eng n/a:2100286. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.202100286
Slaughter BV, Khurshid SS, Fisher OZ et al (2009) Hydrogels in regenerative medicine. Adv Mater 21:3307–3329
Hunt NC, Grover LM (2010) Cell encapsulation using biopolymer gels for regenerative medicine. Biotechnol Lett 32:733–742
Tang L, Wang L, Yang X et al (2021) Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based smart hydrogels: Design, properties and applications. Prog Mater Sci 115:100702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100702
Liu X, Liu J, Lin S, Zhao X (2020) Hydrogel machines. Mater Today 36:102–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2019.12.026
Banivaheb S, Dan S, Hashemipour H, Kalantari M (2021) Synthesis of modified chitosan TiO2 and SiO2 hydrogel nanocomposites for cadmium removal. J Saudi Chem Soc 25:101283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2021.101283
Ashrafizadeh M, Ahmadi Z, Mohamadi N et al (2020) Chitosan-based advanced materials for docetaxel and paclitaxel delivery: Recent advances and future directions in cancer theranostics. Int J Biol Macromol 145:282–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.145
Cascone S, Lamberti G (2020) Hydrogel-based commercial products for biomedical applications: A review. Int J Pharm 573:118803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118803
Richbourg NR, Peppas NA (2020) The swollen polymer network hypothesis: Quantitative models of hydrogel swelling, stiffness, and solute transport. Prog Polym Sci 105:101243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2020.101243
Turky G, Moussa MA, Hasanin M et al (2021) Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Hydrogel: Dielectric Study, Antimicrobial Activity and Biocompatibility. Arab J Sci Eng 46:17–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04655-8
Jafarigol E, Salehi MB, Mortaheb HR (2020) Preparation and assessment of electro-conductive poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) carboxymethyl cellulose/reduced graphene oxide hydrogel with high viscoelasticity. Chem Eng Res Des 162:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2020.07.020
Kumar B, Priyadarshi R, Sauraj et al (2020) Nanoporous sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly (sodium acrylate)/FeCl3 hydrogel beads: Synthesis and characterization. Gels 6
Kim Y, Jeong D, Shinde VV et al (2020) Azobenzene-grafted carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels with photo-switchable, reduction-responsive and self-healing properties for a controlled drug release system. Int J Biol Macromol 163:824–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.071
Liu Y, Zhu Y, Mu B et al (2021) Synthesis, characterization, and swelling behaviors of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(acrylic acid)/semi-coke superabsorbent. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03545-9
Rajput RL, Narkhede JS, Mujumdar A, Naik JB (2020) Synthesis and evaluation of luliconazole loaded biodegradable nanogels prepared by pH-responsive Poly (acrylic acid) grafted Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose using amine based cross linker for topical targeting: In vitro and Ex vivo assessment. Polym Technol Mater 59:1654–1666. https://doi.org/10.1080/25740881.2020.1759633
Masry BA, Shahr El-Din AM, Al-Aidy HA (2021) Ceric-ions redox initiating technique for Zirconium and Niobium separation through graft copolymerization of natural polysaccharides. Sep Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2021.1919708
Dan S, Kalantari M, Kamyabi A, Soltani M (2021) Synthesis of chitosan-g-itaconic acid hydrogel as an antibacterial drug carrier: optimization through RSM-CCD. Polym Bull 1–24
Shamloo A, Aghababaie Z, Afjoul H et al (2021) Fabrication and evaluation of chitosan/gelatin/PVA hydrogel incorporating honey for wound healing applications: An in vitro, in vivo study. Int J Pharm 592:120068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.120068
Bagher Z, Ehterami A, Safdel MH et al (2020) Wound healing with alginate/chitosan hydrogel containing hesperidin in rat model. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 55:101379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101379
Rahnama H, Nouri Khorasani S, Aminoroaya A et al (2021) Facile preparation of chitosan-dopamine-inulin aldehyde hydrogel for drug delivery application. Int J Biol Macromol 185:716–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.199
Dan S, Banivaheb S, Hashemipour H, kalantari M, (2020) Synthesis, characterization and absorption study of chitosan-g-poly(acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) hydrogel. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03190-8
Dan S, Banivaheb S, Hashemipour H (2021) Synthesis, characterization and absorption study of chitosan-g-poly (acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) hydrogel. Polym Bull 78:1887–1907
Fathiraja P, Gopalrajan S, Karunanithi M et al (2021) Response surface methodology model to optimize concentration of agar, alginate and carrageenan for the improved properties of biopolymer film. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03797-5
Pourjavadi A, Barzegar S, Zeidabadi F (2007) Synthesis and properties of biodegradable hydrogels of κ-carrageenan grafted acrylic acid-co-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid as candidates for drug delivery systems. React Funct Polym 67:644–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2007.04.007
Lanthong P, Nuisin R, Kiatkamjornwong S (2006) Graft copolymerization, characterization, and degradation of cassava starch-g-acrylamide/itaconic acid superabsorbents. Carbohydr Polym 66:229–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.03.006
Pourjavadi A, Mahdavinia GR (2006) Superabsorbency, pH-sensitivity and swelling kinetics of partially hydrolyzed chitosan-g-poly(acrylamide) hydrogels. Turkish J Chem 30:595–608
Sood S, Gupta VK, Agarwal S et al (2017) Controlled release of antibiotic amoxicillin drug using carboxymethyl cellulose-cl-poly (lactic acid-co-itaconic acid) hydrogel. Int J Biol Macromol 101:612–620
Pourjavadi A, Mahdavinia GR (2006) Superabsorbency, pH-sensitivity and swelling kinetics of partially hydrolyzed chitosan-g-poly (acrylamide) hydrogels. Turkish J Chem 30:595–608
Yang F, Li G, He YG et al (2009) Synthesis, characterization, and applied properties of carboxymethyl cellulose and polyacrylamide graft copolymer. Carbohydr Polym 78:95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.04.004
Huang Y, Lu J, Xiao C (2007) Thermal and mechanical properties of cationic guar gum/poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel membranes. Polym Degrad Stab 92:1072–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.02.011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that, they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shekari, G., Kalantari, M. & Hashemipour, H. Synthesis, optimization, characterization, and potential drug release application of nanocomposite hydrogel based on carboxymethyl cellulose-g-itaconic acid/acrylamide. J Polym Res 29, 292 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03127-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03127-x