Abstract
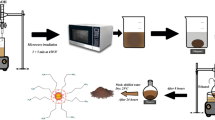
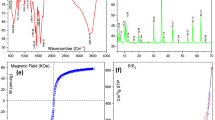
In this study, CoFe2O4@methycellulose (MC) was prepared as a novel magnetic nanocomposite by a facile, fast, and new microwave-assisted method using iron and cobalt salts in the presence of MC as a green biopolymer in alkaline medium and was then structurally evaluated by FESEM, EDS, Mapping, BET, VSM, XRD, TGA, and FTIR. Effective parameters on tetracycline (TC) removal such as pH, initial TC concentration, adsorbent dosage, and contact time were examined. The central composite design (CCD)–based response surface methodology (RSM) was employed to design the experiments and find optimal conditions. CoFe2O4@MC was synthesized with the particle size of about 50 nm, magnetic properties, and high specific surface area. The maximum TC adsorption efficiencies using CoFe2O4@MC from synthetic and real wastewater samples under optimal conditions were 79.45% and 74.85%, respectively. The data of TC adsorption on CoFe2O4@MC were fitted well with pseudo–second order kinetic and Langmuir isotherm models. The results of thermodynamic data indicated the exothermic and spontaneous nature of TC adsorption process using CoFe2O4@MC. CoFe2O4@MC showed high efficiency and chemical stability after 5 runs. Therefore, CoFe2O4@MC nanocomposite can be applied as a good and practical adsorbent for removing TC from synthetic and real wastewater.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ll Yu, Cao W, Wu SC, Yang C, Cheng Jh (2018) Removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution by MOF/graphite oxide pellets: Preparation, characteristic, adsorption performance and mechanism. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.110
Zhang Z, Ding C, Li Y, Ke H, Cheng G (2020) Efficient removal of tetracycline hydrochloride from aqueous solution by mesoporous cage MOF-818. SN Applied Sciences 2(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2514-9
Mahdizadeh H, Nasiri A, Gharaghani M, Yazdanpanah G (2020) Hybrid UV/COP advanced oxidation process using ZnO as a catalyst immobilized on a stone surface for degradation of acid red 18 dye. MethodsX 7:101118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2020.101118
Rajabizadeh K, Yazdanpanah G, Dowlatshahi S, Malakootian M (2020) Photooxidation Process Efficiency (UV/O3) for P-nitroaniline Removal from Aqueous Solutions Ozone: Sci Eng 42(5):420–427, https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2019.1679614
Dehghani M, Nozari M, Fakhraei Fard A, Ansari Shiri M, Shamsedini N (2019) Direct red 81 adsorption on iron filings from aqueous solutions; kinetic and isotherm studies. Environ Technol 40(13):1705–1713. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1428228
Dehghani M, Ansari Shiri M, Shahsavani S, Shamsedini N, Nozari M (2017) Removal of Direct Red 81 dye from aqueous solution using neutral soil containing copper. Desalin Water Treat 86:213–220. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.21332
Dehghani M, Nozari M, Golkari I, Rostami N, Shiri MA (2018) Adsorption and kinetic studies of hexavalent chromium by dehydrated Scrophularia striata stems from aqueous solutions. Desalin Water Treat 125:81–92. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.22953
Dehghani M, Nozari M, Golkari I, Rostami N, Shiri MA Adsorption of mercury (II) from aqueous solutions using dried Scrophularia striata stems: adsorption and kinetic studies, Desalin Water Treat 203 (2020) 1–13. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.26232.
Sayğılı H, Güzel F (2016) Effective removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution using activated carbon prepared from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) industrial processing waste. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 131:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.05.001
Bangari RS, Sinha N (2019) Adsorption of tetracycline, ofloxacin and cephalexin antibiotics on boron nitride nanosheets from aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 293:111376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111376
Amirmahani N, Mahdizadeh H, Malakootian M, Pardakhty A, Mahmoodi N (2020) Evaluating Nanoparticles Decorated on Fe3O4@SiO2-Schiff Base (Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS-HBA) in Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin from Aqueous Environments. J Inorg Organometallic Polym Mater 30(9):3540–3551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01499-5
Wang P, Wang X, Yu S, Zou Y, Wang J, Chen Z, Alharbi NS, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Chen Y (2016) Silica coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanospheres for high removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. Chem Eng J 306:280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.068
Dedi, Idayanti N, Kristiantoro T, Alam GFN, Sudrajat N, Magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite synthesized by mechanical alloying, AIP Conference Proceedings, AIP Publishing LLC, 2018, 020003. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5038285.
Nasatto PL, Pignon F, Silveira JL, Duarte MER, Noseda MD, Rinaudo M (2015) Methylcellulose, a cellulose derivative with original physical properties and extended applications. Polymers 7(5):777–803. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7050777
Malakootian M, Nasiri A, Asadipour A, Faraji M, Kargar E (2019) A facile and green method for synthesis of ZnFe2O4@CMC as a new magnetic nanophotocatalyst for ciprofloxacin removal from aqueous media. MethodsX 6:1575–1580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.06.018
Tamaddon F, Mosslemin MH, Asadipour A, Gharaghani MA, Nasiri A (2020) Microwave-assisted preparation of ZnFe2O4@methyl cellulose as a new nano-biomagnetic photocatalyst for photodegradation of metronidazole. Int J Biol Macromol 154:1036–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.069
Nasiri A, Malakootian M, Heidari MR, Asadzadeh SN (2021) CoFe2O4@Methylcelloluse as a New Magnetic Nano Biocomposite for Sonocatalytic Degradation of Reactive Blue 19. J Polym Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02074-w
Nasiri A, Tamaddon F, Mosslemin MH, Faraji M (2019) A microwave assisted method to synthesize nanoCoFe2O4@methyl cellulose as a novel metal-organic framework for antibiotic degradation. MethodsX 6:1557–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.06.017
Nasiri A, Tamaddon F, Mosslemin MH, Amiri Gharaghani M, Asadipour A (2019) Magnetic nano-biocomposite CuFe2O4@methylcellulose (MC) prepared as a new nano-photocatalyst for degradation of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution, Environ Health Eng. Manag J 6(1): 41–51. https://doi.org/10.15171/ehem.2019.05.
Tamaddon F, Nasiri A, Yazdanpanah G (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin using CuFe2O4@methyl cellulose based magnetic nanobiocomposite. MethodsX 7:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.12.005
Chen Y, Xu R, Li Y, Liu Y, Wu Y, Chen Y, Zhang J, Chen S, Yin H, Zeng Z, Wang S (2020) La(OH)3-modified magnetic CoFe2O4 nanocomposites: A novel adsorbent with highly efficient activity and reusability for phosphate removal. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 599:124870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124870
Malakootian M, Nasiri A, Mahdizadeh H (2018) Preparation of CoFe2O4/activated carbon@chitosan as a new magnetic nanobiocomposite for adsorption of ciprofloxacin in aqueous solutions. Water Sci Technol 78(10):2158–2170. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.494
Malakootian M, Nasiri A, Mahdizadeh H (2019) Metronidazole adsorption on CoFe2O4 /activated carbon@chitosan as a new magnetic biocomposite: Modelling, analysis, and optimization by response surface methodology. Desalin Water Treat 164:215–227. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24433
Chang S, Zhang Q, Lu Y, Wu S, Wang W (2020) High-efficiency and selective adsorption of organic pollutants by magnetic CoFe2O4/graphene oxide adsorbents: Experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. Sep Purif Technol 2020:238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116400
Yekta S, Sadeghi M, Mirzaei D, Zabardasti A, Farhadi S (2019) Removal of nerve agent sarin simulant from aqueous solution using the ZSM-5/CoFe2O4 NPs adsorbent. J Iran Chem Soc 16(2):269–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-018-1504-y
Thuong NT, Thu NTN, Giang BL, Trinh ND, Quynh BTP (2019) Adsorptive removal of Pb (Ii) using exfoliated graphite adsorbent: Influence of experimental conditions and magnetic CoFe2O4 decoration. IIUM Eng J 20(1): 202–215. https://doi.org/10.31436/iiumej.v20i1.965.
Palza H, Delgado K, Govan J (2019) Novel magnetic CoFe2O4/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites for recoverable anionic adsorbents for water treatment. Appl Clay Sci 2019:183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105350
Cai K, Shen W, Ren B, He J, Wu S, Wang W (2017) A phytic acid modified CoFe2O4 magnetic adsorbent with controllable morphology, excellent selective adsorption for dyes and ultra-strong adsorption ability for metal ions. Chem Eng J 330:936–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.009
Zhang M, Mao Y, Wang W, Yang S, Song Z, Zhao X (2016) Coal fly ash/CoFe2O4 composites: A magnetic adsorbent for the removal of malachite green from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 6(96):93564–93574. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra08939a
Tran TV, Nguyen DTC, Le HT, Bach LG, Vo DVN, Lim KT, Nong LX, Nguyen TD (2019) Combined Minimum-Run Resolution IV and Central Composite Design for Optimized Removal of the Tetracycline Drug Over Metal-Organic Framework-Templated Porous Carbon. Molecules 24(10):1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101887
Foroughi M, Rahmani AR, Asgari G, Nematollahi D, Yetilmezsoy K, Samarghandi MR (2019) Optimization and Modeling of Tetracycline Removal from Wastewater by Three-Dimensional Electrochemical System: Application of Response Surface Methodology and Least Squares Support Vector Machine. Environ Model Assess 25:327–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-019-09675-9
Wu J, Zhang H, Oturan N, Wang Y, Chen L, Oturan MA (2012) Application of response surface methodology to the removal of the antibiotic tetracycline by electrochemical process using carbon-felt cathode and DSA (Ti/RuO2–IrO2) anode. Chemosphere 87(6):614–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.036
Topal M, Topal EIA (2020) Optimization of tetracycline removal with chitosan obtained from mussel shells using RSM. J Ind Eng Chem 84:315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.01.013
Foroughi M, Azqhandi MHA, Kakhki S (2020) Bio-inspired, high, and fast adsorption of tetracycline from aqueous media using Fe3O4-g-CN@PEI-β-CD nanocomposite: Modeling by response surface methodology (RSM), boosted regression tree (BRT), and general regression neural network (GRNN). J Hazard Mater 388:121769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121769
Samadi MT, Zolghadrnasab H, Godini K, Poormohammadi A, Ahmadian M, Shanesaz S (2015) Kinetic and adsorption studies of reactive black 5 removal using multi-walled carbon nanotubes from aqueous solution, Der Pharma Chemica 7(5): 267–274. http://eprints.umsha.ac.ir/id/eprint/1854.
Oliveira RL, Vieira JG, Barud HS, Assunção R, Filho R, G, Ribeiro SJ, Messadeqq Y, (2015) Synthesis and Characterization of Methylcellulose Produced from Bacterial Cellulose under Heterogeneous Condition. J Braz Chem Soc 26(9):1861–1870. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20150163
Wiercigroch E, Szafraniec E, Czamara K, Pacia MZ, Majzner K, Kochan K, Kaczor A, Baranska M, Malek K (2017) Raman and infrared spectroscopy of carbohydrates: A review. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 185:317–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.05.045
Sekiguchi Y, Sawatari C, Kondo T (2003) A gelation mechanism depending on hydrogen bond formation in regioselectively substituted O-methylcelluloses. Carbohydr Polym 53(2):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0144-8617(03)00050-x
Rodrigues Filho G, De Assunção RM, Vieira JG, Meireles CDS, Cerqueira DA, Da Silva BH, Ribeiro SJ, Messaddeq Y (2007) Characterization of methylcellulose produced from sugar cane bagasse cellulose: Crystallinity and thermal properties. Polym Degrad Stab 92(2):205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2006.11.008
De Carvalho OG, Filho GR, Vieira JG, De Assunção RM, da Silva MC, Cerqueira DA, de Oliveira RJ, Silva WG, De Castro Motta LA (2010) Synthesis and application of methylcellulose extracted from waste newspaper in CPV-ARI Portland cement mortars. J Appl Polym Sci 118(3):1380–1385. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.32477
Waldron RD (1955) Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys Rev 99(6):1727. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.99.1727
El-Sayed AM (2002) Influence of zinc content on some properties of Ni–Zn ferrites. Ceram Int 28(4):363–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-8842(01)00103-1
Mallapur MM, Shaikh PA, Kambale RC, Jamadar HV, Mahamuni PU, Chougule BK (2009) Structural and electrical properties of nanocrystalline cobalt substituted nickel zinc ferrite. J Alloys Compd 479(1–2):797–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.01.142
Habibi MH, Parhizkar J (2015) Cobalt ferrite nano-composite coated on glass by Doctor Blade method for photo-catalytic degradation of an azo textile dye Reactive Red 4: XRD. FESEM and DRS investigations, Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 150:879–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.06.040
Farhadi S, Siadatnasab F (2016) Synthesis and structural characterization of magnetic cadmium sulfide–cobalt ferrite nanocomposite, and study of its activity for dyes degradation under ultrasound. J Mol Struct 1123:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.06.032
Mehran E, Shayesteh SF, Sheykhan M (2016) Structural and magnetic properties of turmeric functionalized CoFe2O4 nanocomposite powder. Chin Phys B 25(10):107504. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/25/10/107504
Samaila Bawa W, Mansor H, Wan Daud Wan Y, Zulkifly A (2010) X-ray diffraction studies on crystallite size evolution of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared using mechanical alloying and sintering. Appl Surf Sci 256(10):3122–3127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.11.084
Kalam A, Al-Sehemi AG, Assiri M, Du G, Ahmad T, Ahmad I, Pannipara M (2018) Modified solvothermal synthesis of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) magnetic nanoparticles photocatalysts for degradation of methylene blue with H2O2/visible light. Results Phys 8:1046–1053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.01.045
Nguyen VT, Nguyen TB, Chen CW, Hung CM, Chang JH, Dong CD (2019) Influence of pyrolysis temperature on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons production and tetracycline adsorption behavior of biochar derived from spent coffee ground. Bioresour Technol 284:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.096
He J, Ni F, Cui A, Chen X, Deng S, Shen F, Huang C, Yang G, Song C, Zhang J (2020) New insight into adsorption and co-adsorption of arsenic and tetracycline using a Y-immobilized graphene oxide-alginate hydrogel: Adsorption behaviours and mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 701:134363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134363
Malakootian M, Bahraini S, Zarrabi M, Malakootian M (2016) Removal of Tetracycline antibiotic from aqueous solutions using natural and modified pumice with magnesium chloride, Adv Environ Biol 10: 46–56. https://doi.org/10.17795/jjhr-37583.
Hami HK, Abbas RF, Waheb AA, Abed MA, Maryoosh AA (2019) Isotherm and pH Effect Studies of Tetracycline Drug Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Cobalt Oxide Surface, Al-Nahrain J Sci 22(2): 12–18. https://doi.org/10.22401/anjs.22.2.02.
Mohammed AA, Kareem SL (2019) Adsorption of tetracycline fom wastewater by using Pistachio shell coated with ZnO nanoparticles: Equilibrium, kinetic and isotherm studies. Alex Eng J 58(3):917–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2019.08.006
Zhu H, Chen T, Liu J, Li D (2018) Adsorption of tetracycline antibiotics from an aqueous solution onto graphene oxide/calcium alginate composite fibers. RSC Adv 8(5):2616–2621. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra11964j
Xu D, Gao Y, Lin Z, Gao W, Zhang H, Karnowo K, Hu X, Sun H, Syed-Hassan SSA, Zhang S (2019) Application of biochar derived from pyrolysis of waste fiberboard on tetracycline adsorption in aqueous solution. Front Chem 7:943. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00943
Guler UA, Sarioglu M (2014) Removal of tetracycline from wastewater using pumice stone: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336x-12-79
Zhao C, Ma J, Li Z, Xia H, Liu H, Yang Y (2020) Highly enhanced adsorption performance of tetracycline antibiotics on KOH-activated biochar derived from reed plants. RSC Adv 10(9):5066–5076. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra09208k
Aslan S, Yalçin K, Hanay Ö, Yildiz B (2016) Removal of tetracyclines from aqueous solution by nanoscale Cu/Fe bimetallic particle. Desalin Water Treat 57(31):14762–14773. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1067870
Hao Y-M, Man C, Hu Z-B (2010) Effective removal of Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution by amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 184(1–3):392–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.048
Naiya TK, Bhattacharya AK, Das SK (2009) Adsorption of Cd (II) and Pb (II) from aqueous solutions on activated alumina. J Colloid Interface Sci 333(1):14–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.01.003
Hu J, Chen G, Lo IM (2005) Removal and recovery of Cr (VI) from wastewater by maghemite nanoparticles. Water Res 39(18):4528–4536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.05.051
Pils JR, Laird DA (2007) Sorption of tetracycline and chlortetracycline on K-and Ca-saturated soil clays, humic substances, and clay humic complexes. Environ Sci Technol 41(6):1928–1933. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062316y.s001
Li Z, Schulz L, Ackley C, Fenske N (2010) Adsorption of tetracycline on kaolinite with pH-dependent surface charges. J Colloid Interface Sci 351(1):254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.07.034
Rathod M, Haldar S, Basha S (2015) Nanocrystalline cellulose for removal of tetracycline hydrochloride from water via biosorption: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Ecol Eng 84:240–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.09.031
Erşan M (2016) Removal of tetracycline using new biocomposites from aqueous solutions. Desalin Water Treat 57(21):9982–9992. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1033765
Li K, Ji F, Liu Y, Tong Z, Zhan X, Hu Z (2013) Adsorption removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution by anaerobic granular sludge: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Water Sci Technol 67(7):1490–1496. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.016
Huízar-Félix AM, Aguilar-Flores C, Martínez-de-la Cruz A, Barandiarán JM, Sepúlveda-Guzmán S, Cruz-Silva R (2019) Removal of tetracycline pollutants by adsorption and magnetic separation using reduced graphene oxide decorated with α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 9(3):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030313
Acknowledgement
This paper was the result of a research project (ethics code number: IR.KMU.REC.1399.337 and project number: 98001200) approved by the Student Research Committee of Kerman University of Medical Sciences, which was carried out by the financial support of the Vice–Chancellor for Research and Technology of this university. We would like to thank the Student Research Committee and Environmental Health Engineering Research Center of Kerman University of Medical Sciences for their financial and scientific support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasiri, A., Malakootian, M., Shiri, M.A. et al. CoFe2O4@methylcellulose synthesized as a new magnetic nanocomposite to tetracycline adsorption: modeling, analysis, and optimization by response surface methodology. J Polym Res 28, 192 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02540-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02540-y