Abstract
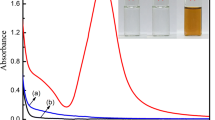
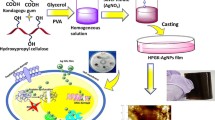
Biopolymers represent an excellent alternative to their synthetic analogues for use as natural stabilizers in the development of unique metal nanoparticles, owing to their attractive properties including low cost, environmentally friendly nature, renewability, biodegradability and biocompatibility. Herein, a new, straightforward chemical approach was investigated to synthesize Ag nanoparticle-decorated sulfonated carboxymethyl cellulose (AgNPs/S-CMC) nano-biocomposite materials with strong antimicrobial properties. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) was firstly chemically modified into sulfonated CMC (S-CMC), which was used as an environmentally friendly stabilizer and a nonhazardous reducing agent towards the fabrication of AgNPs in aqueous solution. Four types of AgNPs/S-CMC nano-biocomposites were fabricated to investigate the effect of the concentration of the S-CMC stabilizing/reducing agent on the fabrication of AgNPs, the physiochemical properties and the antimicrobial activity performance. The fabrication of AgNPs was investigated by UV-Vis spectra through characteristic surface plasmon resonance peak analysis, and the chemical structures were characterized by FTIR, FE-SEM, EDAX and XRD analyses. The synthesized AgNPs/S-CMC nano-biocomposites were tested as a potential antimicrobial agent, confirmed by the agar diffusion method, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) analysis against Gram-positive B. subtilis and Gram-negative E. coli bacterial strains. The obtained results confirm that the proposed nano-biocomposites exhibit excellent antimicrobial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koduru JR, Kailasa SK, Bhamore JR et al (2018) Phytochemical-assisted synthetic approaches for silver nanoparticles antimicrobial applications: A review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 256:326–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2018.03.001
Abdallah OM, EL-Baghdady KZ, Khalil MMH, et al (2020) Antibacterial, antibiofilm and cytotoxic activities of biogenic polyvinyl alcohol-silver and chitosan-silver nanocomposites. J Polym Res 27:74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02050-3
Mathew S, Mathew J, Radhakrishnan EK (2019) Polyvinyl alcohol/silver nanocomposite films fabricated under the influence of solar radiation as effective antimicrobial food packaging material. J Polym Res 26:223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1888-0
Meena Sharma A, Kumar R et al (2020) Chitosan embedded with Ag/Au nanoparticles: investigation of their structural, optical and sensing properties. J Polym Res 27:253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02233-y
Rigo C, Ferroni L, Tocco I et al (2013) Active Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci 14:4817–4840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14034817
Sabela MI, Makhanya T, Kanchi S et al (2018) One-pot biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Iboza Riparia and Ilex Mitis for cytotoxicity on human embryonic kidney cells. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 178:560–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.12.010
Sharma D, Kanchi S, Bisetty K (2019) Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles: A review. Arab J Chem 12:3576–3600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.11.002
Rai MK, Deshmukh SD, Ingle AP, Gade AK (2012) Silver nanoparticles: the powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 112:841–852. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05253.x
Mathew M, Sureshkumar S, Sandhyarani N (2012) Synthesis and characterization of gold–chitosan nanocomposite and application of resultant nanocomposite in sensors. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 93:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.12.028
Kanmani P, Rhim J-W (2014a) Properties and characterization of bionanocomposite films prepared with various biopolymers and ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 106:190–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.02.007
Bikiaris DN, Triantafyllidis KS (2013) HDPE/Cu-nanofiber nanocomposites with enhanced antibacterial and oxygen barrier properties appropriate for food packaging applications. Mater Lett 93:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.10.128
Rhim JW, Wang LF, Hong SI (2013) Preparation and characterization of agar/silver nanoparticles composite films with antimicrobial activity. Food Hydrocoll 33:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.04.002
Kanmani P, Rhim J-W (2014b) Physicochemical properties of gelatin/silver nanoparticle antimicrobial composite films. Food Chem 148:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.047
Li JH, Hong RY, Li MY et al (2009) Effects of ZnO nanoparticles on the mechanical and antibacterial properties of polyurethane coatings. Prog Org Coatings 64:504–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2008.08.013
Duncan TV (2011) Applications of nanotechnology in food packaging and food safety: Barrier materials, antimicrobials and sensors. J Colloid Interface Sci 363:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.07.017
Qayyum S, Oves M, Khan AU (2017) Obliteration of bacterial growth and biofilm through ROS generation by facilely synthesized green silver nanoparticles. PLoS One 12:e0181363. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181363
Xie Y, Chen L, Zhang X et al (2018) Integrating zwitterionic polymer and Ag nanoparticles on polymeric membrane surface to prepare antifouling and bactericidal surface via Schiff-based layer-by-layer assembly. J Colloid Interface Sci 510:308–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.09.071
Medříková Z, Jakubec P, Ranc V et al (2019) Carboxymethylcellulose-based magnetic Au or Ag nanosystems: Eminent candidates in catalysis, sensing applications based on SERS, and electrochemistry. Appl Mater Today 14:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2018.12.001
Ghosh S, Maji S, Mondal A (2018) Study of selective sensing of Hg2+ ions by green synthesized silver nanoparticles suppressing the effect of Fe3+ ions. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 555:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.07.012
Jo H, Sim M, Kim S et al (2016) Electrically conductive graphene/polyacrylamide hydrogels produced by mild chemical reduction for enhanced myoblast growth and differentiation. Acta Biomater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.035
Gurusamy V, Krishnamoorthy R, Gopal B et al (2017) Systematic investigation on hydrazine hydrate assisted reduction of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial properties. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem 47:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2015.1137074
Jayaprakash N, Judith Vijaya J, John Kennedy L et al (2015) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized from serine. Mater Sci Eng C 49:316–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.012
Ge L, Xu Y, Li X et al (2018) Fabrication of Antibacterial Collagen-Based Composite Wound Dressing. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:9153–9166. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b01482
Emam HE, Zahran MK (2015) Ag0 nanoparticles containing cotton fabric: Synthesis, characterization, color data and antibacterial action. Int J Biol Macromol 75:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.12.050
Elsupikhe RF, Shameli K, Ahmad MB et al (2015) Green sonochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles at varying concentrations of κ-carrageenan. Nanoscale Res Lett 10:302. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-0916-1
Elsupikhe RF, Shameli K, Ahmad MB (2015) Sonochemical method for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles in κ-carrageenan from silver salt at different concentrations. Res Chem Intermed 41:8515–8525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-014-1907-z
Goel A, Meher MK, Gupta P et al (2019) Microwave assisted κ-carrageenan capped silver nanocomposites for eradication of bacterial biofilms. Carbohydr Polym 206:854–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.11.033
Tomšič B, Simončič B, Orel B et al (2007) Biodegradability of cellulose fabric modified by imidazolidinone. Carbohydr Polym 69:478–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.01.003
Srivastava A, Mandal P, Kumar R (2016) Solid state thermal degradation behaviour of graft copolymers of carboxymethyl cellulose with vinyl monomers. Int J Biol Macromol 87:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.004
Guru GS, Prasad P, Shivakumar HR, Rai SK (2008) Studies on the Compatibility of Pullulan-Carboxymethyl Cellulose Blend Using Simple Techniques. Malaysian Polym J 3:13–23
Sannino A, Demitri C, Madaghiele M (2009) Biodegradable Cellulose-based Hydrogels: Design and Applications. Materials (Basel) 2:353–373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020353
Biswal DR, Singh RP (2004) Characterisation of carboxymethyl cellulose and polyacrylamide graft copolymer. Carbohydr Polym 57:379–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.04.020
Bajpai SK, Mohan YM, Bajpai M et al (2007) Synthesis of Polymer Stabilized Silver and Gold Nanostructures. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:2994–3010. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2007.911
Esumi K, Suzuki A, Yamahira A, Torigoe K (2000) Role of Poly(amidoamine) Dendrimers for Preparing Nanoparticles of Gold, Platinum, and Silver. Langmuir 16:2604–2608. https://doi.org/10.1021/la991291w
Vimala K, Samba Sivudu K, Murali Mohan Y et al (2009) Controlled silver nanoparticles synthesis in semi-hydrogel networks of poly(acrylamide) and carbohydrates: A rational methodology for antibacterial application. Carbohydr Polym 75:463–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.08.009
Huang H, Yang X (2004) Synthesis of polysaccharide-stabilized gold and silver nanoparticles: a green method. Carbohydr Res 339:2627–2631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2004.08.005
Chen J, Wang J, Zhang X, Jin Y (2008) Microwave-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by carboxymethyl cellulose sodium and silver nitrate. Mater Chem Phys 108:421–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.10.019
Mukherjee P, Ahmad A, Mandal D et al (2001) Fungus-Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Immobilization in the Mycelial Matrix: A Novel Biological Approach to Nanoparticle Synthesis. Nano Lett 1:515–519. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0155274
Mukherjee P, Ahmad A, Mandal D et al (2001) Bioreduction of AuCl4− Ions by the Fungus, Verticillium sp. and Surface Trapping of the Gold Nanoparticles Formed D.M. and S.S. thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India, for financial assistance. Angew Chemie Int Ed 40:3585. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3773(20011001)40:193585::AID-ANIE35853.0.CO;2-K
Xiao Y, Pavlov V, Levine S et al (2004) Catalytic Growth of Au Nanoparticles by NAD(P)H Cofactors: Optical Sensors for NAD(P)+-Dependent Biocatalyzed Transformations. Angew Chemie 116:4619–4622. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.200460608
Baron R, Zayats M, Willner I (2005) Dopamine-, <scp>l</scp> -DOPA-, Adrenaline-, and Noradrenaline-Induced Growth of Au Nanoparticles: Assays for the Detection of Neurotransmitters and of Tyrosinase Activity. Anal Chem 77:1566–1571. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac048691v
Pelissari FM, Yamashita F, Garcia MA et al (2012) Constrained mixture design applied to the development of cassava starch–chitosan blown films. J Food Eng 108:262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.09.004
Vijayalakshmi K, Gomathi T, Latha S et al (2016) Removal of copper(II) from aqueous solution using nanochitosan/sodium alginate/microcrystalline cellulose beads. Int J Biol Macromol 82:440–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.09.070
Nasrollahzadeh M, Mohammad Sajadi S, Babaei F, Maham M (2015) Euphorbia helioscopia Linn as a green source for synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their optical and catalytic properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 450:374–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.03.033
Pal A, Esumi K, Pal T (2005) Preparation of nanosized gold particles in a biopolymer using UV photoactivation. J Colloid Interface Sci 288:396–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.03.048
He F, Zhao D, Liu J, Roberts CB (2007) Stabilization of Fe−Pd Nanoparticles with Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose for Enhanced Transport and Dechlorination of Trichloroethylene in Soil and Groundwater. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0610896
Ajitha B, Ashok Kumar Reddy Y, Reddy PS (2014) Biogenic nano-scale silver particles by Tephrosia purpurea leaf extract and their inborn antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 121:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.10.077
Su J-F, Huang Z, Yuan X-Y et al (2010) Structure and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose/soy protein isolate blend edible films crosslinked by Maillard reactions. Carbohydr Polym 79:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.07.035
Olad A, Zebhi H, Salari D et al (2018) Synthesis, characterization, and swelling kinetic study of porous superabsorbent hydrogel nanocomposite based on sulfonated carboxymethylcellulose and silica nanoparticles. J Porous Mater 25:1325–1335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-017-0543-6
Tarun K, Gobi N (2012) Calcium alginate/PVA blended nano fibre matrix for wound dressing. Indian J Fibre Text Res 37:127–132
Yang J, Pan J (2012) Hydrothermal synthesis of silver nanoparticles by sodium alginate and their applications in surface-enhanced Raman scattering and catalysis. Acta Mater 60:4753–4758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.05.037
Sajjadi M, Nasrollahzadeh M, Mohammad Sajadi S (2017) Green synthesis of Ag/Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposite using Euphorbia peplus Linn leaf extract and evaluation of its catalytic activity. J Colloid Interface Sci 497:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.02.037
Suárez-Cerda J, Alonso-Nuñez G, Espinoza-Gómez H, Flores-López LZ (2015) Synthesis, kinetics and photocatalytic study of “ultra-small” Ag-NPs obtained by a green chemistry method using an extract of Rosa “Andeli” double delight petals. J Colloid Interface Sci 458:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.07.049
Shankar SS, Rai A, Ahmad A, Sastry M (2004) Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core–Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.03.003
Bukzem AL, Signini R, dos Santos DM et al (2016) Optimization of carboxymethyl chitosan synthesis using response surface methodology and desirability function. Int J Biol Macromol 85:615–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.01.017
Upadhyaya L, Singh J, Agarwal V et al (2014) In situ grafted nanostructured ZnO/carboxymethyl cellulose nanocomposites for efficient delivery of curcumin to cancer. J Polym Res 21:550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0550-0
Nasrollahzadeh M, Atarod M, Sajadi SM (2016) Green synthesis of the Cu/Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Morinda morindoides leaf aqueous extract: A highly efficient magnetically separable catalyst for the reduction of organic dyes in aqueous medium at room temperature. Appl Surf Sci 364:636–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.209
Khodadadi B, Bordbar M, Nasrollahzadeh M (2017) Achillea millefolium L. extract mediated green synthesis of waste peach kernel shell supported silver nanoparticles: Application of the nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of a variety of dyes in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 493:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.012
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Department of Chemistry, King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia, for providing research facilities and granting the permission to publish this work. This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, King Abdulaziz University Administration of Support for Research and Development Initiatives, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, under the research scheme Post-Doctoral Researcher awarded to Dr Ajahar Khan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Alamry, K.A., Oves, M. et al. A facile and green approach for the fabrication of nano-biocomposites by reducing silver salt solution into silver nanoparticles using modified carboxymethyl cellulose for antimicrobial potential. J Polym Res 28, 95 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02437-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02437-w