Abstract
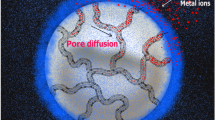
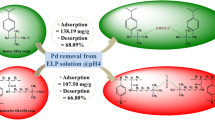
The effect of a surface modification process known as "mussel-inspired modification" on the adsorption dynamics of hydrophobic adsorbent, namely XAD1180, was studied based on equilibrium adsorption data. In the study, three anionic colorants (i.e., Sunset yellow, SY; Allura red, AR; and Tartrazine, TZ) were used as the model compounds. The role of some experimental parameters, such as pH (4–7), ionic strength (0.01–0.50 mM) and colorant concentration (25–125 mg/L), were investigated to determine optimal conditions leading to the highest adsorption. Equilibrium adsorption data were obtained under optimal conditions by stepwise frontal analysis method (SFA) and modeled on the basis of some common adsorption isotherm models (i.e., Langmuir and Freundlich). The adsorption dynamics of the XAD1180 resin have been found to vary significantly after PD coating. After the PD coating process, it was found that the highly hydrophobic background material, XAD1180, gained a pH-sensitive character, thereby replacing a sharp decrease in the adsorption capacity at pH = 5.0–7.0 with an increase in pH = 4.0. Another dramatic effect of the PD coating was observed with Langmuir monolayer adsorption capacities, so that the PD layer was found to increase the monolayer saturation capacity of the XAD1180 (from 8.0 to 17 µmol/g for SY, from 7.7 to 9.9 µmol/g for AR, and from 5.3 to 9.1 µmol/g for TZ). It was also deduced from the Freundlich isotherm parameter, KF, that there was, in general, a clear increment in the overall effect of adsorption capacity and the average affinity after mussel-inspired surface modification process.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All the data are already given in the manuscript.
References
Wang Z, Yang HC, He F et al (2019) Mussel-inspired surface engineering for water-remediation materials. Matter 1:115–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2019.05.002
Lee H, Dellatore SM, Miller WM, Messersmith PB (2007) Mussel-Inspired Surface Chemistry for Multifunctional Coatings. Sci 80(318):426–430. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1147241
Wang H, Wang Z, Yue R et al (2020) Rapid preparation of adsorbent based on mussel inspired chemistry and simultaneous removal of heavy metal ions in water. Chem Eng J 383:123107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123107
Lee H, Rho J, Messersmith PB (2009) Facile conjugation of biomolecu les onto surfaces via mussel adhesive protein inspired coatings. Adv Mater 21:431–434. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200801222
Yang X, Yan L, Wu Y et al (2019) Biomimetic hydrophilization engineering on membrane surface for highly-efficient water purification. J Memb Sci 589:117223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117223
Zhang Y, Cheng X, Jiang X et al (2020) Robust natural nanocomposites realizing unprecedented ultrafast precise molecular separations. Mater Today 36:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2020.02.002
Kang SM, You I, Cho WK et al (2010) One-step modification of superhydrophobic surfaces by a mussel-inspired polymer coating. Angew Chemie Int Ed 49:9401–9404. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201004693
Guo H, Deng Y, Tao Z et al (2016) Does hydrophilic polydopamine coating enhance membrane rejection of hydrophobic endocrine-disrupting compounds? Environ Sci Technol Lett 3:332–338. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.6b00263
Wardani AK, Ariono D, Subagjo WIG (2019) Hydrophilic modification of polypropylene ultrafiltration membrane by air-assisted polydopamine coating. Polym Adv Technol 30:1148–1155. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.4549
Ahmad A, Siddique JA, Laskar MA et al (2015) New generation Amberlite XAD resin for the removal of metal ions: A review. J Environ Sci 31:104–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.12.008
Wawrzkiewicz M (2013) Removal of C.I. Basic Blue 3 dye by sorption onto cation exchange resin, functionalized and non-functionalized polymeric sorbents from aqueous solutions and wastewaters. Chem Eng J 217:414–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.119
Bişgin AT, Uçan M, Narin İ, Soylak M (2015) A comparative study for separation, preconcentration and determination of Tartrazine (E 102) in soft drink samples by two kinds of Amberlite resins. Food Anal Methods 8:2141–2149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0099-5
Lira MA, Navarro R, Saucedo I et al (2016) Influence of the textural characteristics of the support on Au(III) sorption from HCl solutions using Cyphos IL101-impregnated Amberlite resins. Chem Eng J 302:426–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.059
Wang CC, Gómez RA, Fernandez LP (2013) Determination of sildenafil by preconcentration on surfactant coated polymeric resin followed by spectrofluorimetry. J Pharm Anal 3:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2012.11.001
Belkhouche N-E, Didi MA (2010) Extraction of Bi(III) from nitrate medium by D2EHPA impregnated onto Amberlite XAD-1180. Hydrometallurgy 103:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2010.02.015
Narin I, Tuzen M, Soylak M (2004) Aluminium determination in environmental samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after solid phase extraction on Amberlite XAD-1180/pyrocatechol violet chelating resin. Talanta 63:411–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2003.11.005
An B, Fu Z, Xiong Z et al (2010) Synthesis and characterization of a new class of polymeric ligand exchangers for selective removal of arsenate from drinking water. React Funct Polym 70:497–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2010.01.006
Rajesh N, Manikandan S (2008) Spectrophotometric determination of lead after preconcentration of its diphenylthiocarbazone complex on an Amberlite XAD-1180 column. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 70:754–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2007.09.007
Dong Z, Wang D, Liu X et al (2014) Bio-inspired surface-functionalization of graphene oxide for the adsorption of organic dyes and heavy metal ions with a superhigh capacity. J Mater Chem A 2:5034–5040. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14751G
Gezici O, Ayar A (2009) Stepwise frontal analysis to derive equilibrium sorption data for copper and aniline on functionalized sporopollenin. Clean (Weinh) 37:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200900001
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02268a002
Freundlich HMF (1906) Über die adsorption in lösungen. Zeitschrift für Phys Chemie 57:385–470
Rossi M, Nardinocchi P, Wallmersperger T (2019) Swelling and shrinking in prestressed polymer gels: an incremental stress–diffusion analysis. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 475:20190174. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2019.0174
Alberti G, Narducci R (2009) Evolution of permanent deformations (or memory) in Nafion 117 membranes with changes in temperature, relative humidity and time, and its importance in the development of medium temperature PEMFCs. Fuel Cells 9:410–420. https://doi.org/10.1002/fuce.200800148
Wang S, Qiao N, Yu J et al (2016) Effect of ionic strength on the adsorption behavior of phenol over modified activated clay. Desalin Water Treat 57:4174–4182. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.989269
Gezici O, Kara H, Ersöz M, Abali Y (2005) The sorption behavior of a nickel-insolubilized humic acid system in a column arrangement. J Colloid Interface Sci 292:381–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.06.009
Ayar A, Gezici O, Küçükosmanoǧlu M (2007) Adsorptive removal of Methylene blue and Methyl orange from aqueous media by carboxylated diaminoethane sporopollenin: On the usability of an aminocarboxilic acid functionality-bearing solid-stationary phase in column techniques. J Hazard Mater 146:186–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.009
Ayar A, Gürsal S, Gürten AA, Gezici O (2008) On the removal of some phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions by using a sporopollenin-based ligand-exchange fixed bed - Isotherm analysis. Desalination 219:160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.05.012
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Nigde Ömer Halisdemir University for the facilities provided.
Funding
The study was performed by the facilities provided by Nigde Ömer Halisdemir University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No ethics approval is necessary for this work.
Consent for publication
Authors agree in submitting this work to Journal of Polymer Research.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gezici, O., Bişgin, A.T. Generation of a pH-blind/pH-sensitive alternating surface on a hydrophobic resin by mussel-inspired chemistry and investigating the effect of surface modification on the adsorption dynamics of some anionic colorants. J Polym Res 28, 58 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02428-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02428-x