Abstract
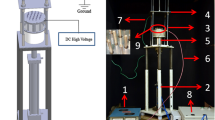
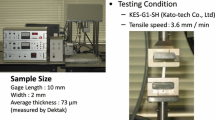
This study was carried out to evaluate the influence of high voltage polarity on a newly designed multi-pin upward electrospinning spinneret to produce poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. Two different high voltage polarity configurations were applied to the spinneret and collector, namely collector charging configuration (configuration-1) and spinneret charging configuration (configuration-2). The outcomes demonstrated that the collector charging configuration is better in case of upward multi-pin electrospinning setup, to their conservative framework in terms of stable Taylor cone formation, smaller fiber diameter and less bead formation. Electrical field profile in the electrospinning zone was investigated using finite element modelling for both the configurations. No difference in electric field intensity norm (|E|) was observed near the tip of the pins for both the polarities (configurations). Although having the same magnitude, the dominant electrical field component, Ez for configuration -1 is found to be of opposite sign to that of configuration -2. The electrostatic simulations also suggested that all the pins were not at the same potential and that there was a minor difference in pin potentials. Also, optimizations of pin length to reduce the potential differences between the pins were theoretically estimated through COMSOL3D simulation software.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seeram Ramakrishna ZM. et. al. (2005) An introduction to electrospinning and Nanofibers
Dias GC (2019) PVDF nanofibers obtained by solution blow spinning with use of a commercial airbrush. J Polym Res 26(87):1–12
Taylor G (1969) Electrically driven jets. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 313(1515):453–475. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1969.0205
Li D, Xia Y (2004) Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the wheel? Adv Mater 16:1151–1170. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200400719
Huang ZM, Zhang YZ, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2003) A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 63:2223–2253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00178-7
X. Fang DHR (1997) DNA fibers by electrospinning. J Macromol Sci Part B 36:169–173
Doshi J, Reneker DHJ (1995) Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J Electrost 35:151–160
Reneker DH (2000) Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solutions in electrospinning. J Appl Phys 87:4531
Kim FS, Guoqiang Ren SAJ (2011) One-dimensional nanostructures of π-conjugated molecular systems: assembly, properties, and applications from Photovoltaics, sensors, and Nanophotonics to Nanoelectronics. Chem Mater 23:682–732
Yarin AL, Koombhongse S, Reneker DH (2001) Bending instability in electrospinning of nanofibers. J Appl Phys 89:3018–3026
Yalcinkaya F (2017) Mechanically enhanced electrospun nanofibers for wastewater treatment. E3S web Conf 22:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20172200193
Parekh SA, David RN, Bannuru KKR et al (2018) Electrospun silver coated polyacrylonitrile membranes for water filtration applications. Membranes (Basel) 8:26–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030059
Naseeb N, Mohammed AA, Laoui T, Khan Z (2019) A novel PAN-GO-SiO2 hybrid membrane for separating oil and water from emulsified mixture. Materials (Basel) 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020212
P.S. Suja, C.R. Reshmi PS and AS (2017) Electrospun Nanofibrous membranes for water purification. J Polym Rev 57:467–504. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2017.1309664
Sundarrajan S, Tan KL, Soon Huat Lim SR (2014) Electrospun nanofibers for air filtration applications. MRS Singapore - ICMAT Symposia Proceedings ICMAT. Elsevier B.V, In, pp 159–163
Weng LXJ (2015) Smart electrospun nanofibers for controlled drug release: recent advances and new perspectives. Curr Pharm Des 21:1944–1959
Okuda T, Tominaga KKS (2010) Time-programmed dual release formulation by multilayered drug-loaded nanofiber meshes. J Control Release 143:258–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.12.029
Ball C, Woodrow K (2011) Electrospun fibers for drug delivery. Comprehensive Biomaterials. Elsevier Ltd., In, pp 445–462
Hu X, Shi Liu GZ (2014) Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J Control Release 185:12–21
Wen P, Zong M, Linhardt RJ et al (2017) Trends in food science & technology electrospinning : a novel nano-encapsulation approach for bioactive compounds. Trends Food Sci Technol 70:56–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.10.009
Prabu GTV, Chattopadhyay SK, Patil PG et al (2016) Moisture management finish on cotton fabric by electrospraying. Text Res J Vol 87:2154–2165. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517516665262
Niu H, Wang X, Li T (2012) Needleless electrospinning: developments and performances. Nanofibers - Production, Properties and Functional Applications, In, pp 17–35
Sapountzi E, Braiek M, Chateaux JF et al (2017) Recent advances in electrospun nanofiber interfaces for biosensing devices. Sensors (Switzerland) 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17081887
Amutha Chinnappan, Chinnappan Baskar, Shikha Baskar GR and SR (2017) An overview of electrospun nanofibers and their application in energy storage, sensors and wearable/flexible electronics. J Mater Chem C https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TC03058D
Kumar J, Lee S-H, Senecal KJ et al (2002) Electrospun nanofibrous membranes for highly sensitive optical sensors. Nano Lett 2:1273–1275. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl020216u
Jirsak O, Petrik S (2012) Recent advances in nanofibre technology: needleless electrospinning. Int J Nanotechnol 9:836. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijnt.2012.046756
Wu D, Huang X, Lin L et al (2010) High throughput tip-less electrospinning via a circular cylindrical electrode. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10:4221–4226. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2010.2194
Niu H, Lin T, Wang X (2009) Needleless electrospinning. I A comparison of cylinder and disk nozzles. J Appl Polym Sci 114:3524–3530
Paper O (2017) Blow-assisted multi-jet electrospinning of poly-L-lactic acid nanofibers. J Polym Res 24:24–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1233-4
Haitao Niu Tong Lin Xungai Wang (2009) Needleless electrospinning I. A comparison of cylinder and disk nozzles. J Appl Polym Sci 114:. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.30891
Niu H, Lin T (2012) Fiber generators in needleless electrospinning. J Nanomater 2012:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/725950
Ali U, Wang X, Lin T (2012) Effect of nozzle polarity and connection on electrospinning of polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. J Text Inst 103:1160–1168. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2012.664869
Abdel-Hady F, Alzahrany A, Hamed M (2011) Experimental validation of upward electrospinning process. ISRN Nanotechnol 2011:1–14. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/851317
Niu H, Wang X, Lin T (2012) Upward needleless electrospinning of nanofibers. J Eng Fiber Fabr 7:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/155892501200702s03
Wu C-M, Chiou H-G, Siang-Ling Lin J-ML (2012) Effects of electrostatic polarity and the types of electrical charging on electrospinning behavior. J Appl Polym Sci 126:E89–E97
chidchanok mit-uppatham et. al (2004) Effects of solution concentration, emitting electrode polarity, solvent type, and salt addition on electrospun polyamide-6 fibres: a preliminary report. Macromol Symp 293–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.200451227
Sutasinpromprae J, Jitjaicham S, Nithitanakul M, et al (2006) Preparation and characterization of ultrafine electrospun polyacrylonitrile fibers and their subsequent pyrolysis to carbon fibers. Polym Int 833:825–833. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.2040
Kilic A, Oruc F, Demir A (2008) Effects of polarity on electrospinning process. Text Res J 78:532–539. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517507081296
Lukas D, Sarkar A, Pokorny P (2008) Self-organization of jets in electrospinning from free liquid surface: a generalized approach. J Appl Phys 103:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2907967
Ng J, Supaphol P (2018) Rotating-disk electrospinning : needleless electrospinning of poly ( caprolactone ), poly ( lactic acid ) and poly ( vinyl alcohol ) nanofiber mats with controlled morphology. J Polym Res 25(155):1–9
Angammana CJ, Jayaram SH (2011) Effects of electric field on the multi-jet electrospinning process and Fiber morphology. IEEE Trans Ind Appl:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2010.2103392
Ahad N, Saion E, Gharibshahi E (2012) Structural , thermal , and electrical properties of PVA-sodium salicylate solid composite polymer electrolyte. J Nanomater 2012:. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/857569
Lee H, Yamaguchi K, Nagaishi T, Murai M (2017) RSC advances enhancement of mechanical properties of polymeric nano fi bers by controlling crystallization behavior using a simple freezing / thawing process †. RCS Adv 7:43994–44000. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra06545k
Billmeyer FW (1984) Textbook of polymer science, third edit. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Singapore
Hou X, Yang X, Zhang L et al (2010) Stretching-induced crystallinity and orientation to improve the mechanical properties of electrospun PAN nanocomposites. Mater Des 31:1726–1730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.01.051
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Re-KCT student Project support centre for nanofiber analysis and other characterizations. The first author acknowledges the support from ICAR-Central Institute for Research on Cotton Technology, Mumbai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabu, G.T.V., Dhurai, B. & Saxena, A. Influence of high voltage polarity in multi-pin upward electrospinning system on the Fiber morphology of poly (vinyl alcohol). J Polym Res 27, 47 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-2005-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-2005-0