Abstract
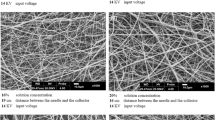
Coaxial electrospinning is an effective method to produce core-shell nanofibers, which is associated closely with the morphological stability of Taylor cone. However, the nozzle structure mainly influences the formation of Taylor cone during the coaxial electrospinning procedure. In the present work, since the numerical simulation is a novel and convenience method in the theoretical research of the coaxial electrospinning, the influence of different coaxial composite nozzle structures on Taylor cone shape was studied by ANSYS finite element simulation method. Different coaxial composite nozzle structures — concave type, flush type and convex type, were designed in this work. 2D electric field model of the nozzle structures was simulated by utilizing ANSYS finite element analysis software. The simulation results indicated that electric field intensity distribution of concave type nozzle structure was more uniform than those of the other two types. Therefore, a more stable coaxial Taylor cone was formed in the tip of concave type nozzle structure. To verify the accuracy of the simulation results, core-shell nanofibers were spun by using different coaxial composite nozzle structures. In each experiment, PAN and PVP were employed to be the shell and core solution respectively. Besides that high-speed camera was employed to monitor the coaxial electrospinning procedure. The cross-section morphology of electrospun nanofibers was characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The experimental results showed that when the concave type nozzle was used in the coaxial electrospinning process, Taylor Cone morphology was more stable than other type coaxial composite nozzle structures. The cross-section morphology of electrospun fibers observed by SEM revealed that the high stability in core-shell structure also occurred in coaxial electrospinning by using concave nozzle structure. Furthermore, the simulation and experimental results verified the concave type nozzle is the better nozzle structure for coaxial electrospinning to form stable coaxial Taylor cone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Xie, H. Mao, D.-G. Yu, G. R. Williams, and M. Jin, Fiber. Polym., 15, 78 (2014).
E. Zussman, A. L. Yarin, A. V. Bazilevsky, R. Avrahami, and M. Feldman, Adv. Mater., 18, 348 (2006).
S. N. Reznik, A. L. Yarin, E. Zussman, and L. Bercovici, Phys. Fluids, 18, 062101 (2006).
C. S. Kong, T. H. Lee, and H. S. King, J. Mater. Sci., 43, 8106 (2007).
F.-L. Zhou, R.-H. Gong, and I. Porat, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 115, 2591 (2010).
Y. Yang, Z. Jia, J. Liu, Q. Li, L. Hou, L. Wang, and Z. Guan, J. Appl. Phys., 103, 104307 (2008).
L. Xie, Y. Geng, and W. Qiu, “ANSYS Electromagnetic Field Analysis”, pp.111–112, PHEI, Beijing, 2012.
S. Xie and Y. Zeng, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 51, 5336 (2012).
X. Chen, Y. Zhai, J. Li, X. Fang, F. Fang, X. Chu, Z. Wei, and X. Wang, Appl. Surf. Sci., 319, 216 (2014).
J.-F. Zhang, D.-Z. Yang, and J. Nie, Polym. Int., 57, 1194 (2008).
Y. Hu and Z.-M. Huang, J. Appl. Phys., 101, 084307 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, Q., Huang, F. et al. The morphology of Taylor cone influenced by different coaxial composite nozzle structures. Fibers Polym 17, 624–629 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-5730-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-5730-6