Abstract
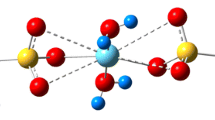
Two shot solution polymerised NR/PEO block copolymer (BC) was used as an absorbent in this study. This polymer has got polyethylene oxide (PEO) immobilised on hydrophobic natural rubber and it was used for complexation studies with the selected 3d transition metal ions. The prepared complexes were subjected to various analytical techniques such as energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy(FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies, extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis and X-ray absorption near edge spectroscopy (XANES). EDX analysis confirms presence of the respective metal ion in each complex. FTIR spectroscopy reveals the 72 helical conformation of polyethylene oxide segments in BC which is retained with some deformation upon complexation. The BC-metal ion interaction is confirmed by broadening of the C-O-C triplet peak. XRD analysis revealed that PEO lattice undergoes expansion during complexation inorder to accommodate the respective metal ion. From the EXAFS results it was observed that each metal ion shows only one peak that corresponds to the oxygen shell indicating the presence of only one type of metal ion bonding. The EXAFS gives hexa coordinated pattern for Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes while a tetra coordination for the Cu(II) complex. Metal-oxygen distance in a given complex is constant and unique which varies with the metal ion. XANES shows a distorted octahedral symmetry (Oh) with sp3d2 hybridisation for the hexa coordinated complexes and a square planar symmetry with dsp2 hybridisation for the tetra coordinated complex. Feasibility of 1 s → 3d transition confirms +2 oxidation state of the metal ions. The combined result of EXAFS and FTIR shows the best fit structure of the complexes in which metal ions are encapsulated within the PEO helical tunnel.










Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Wilkinson SM, Sheedy TM, New EJ (2016) Synthesis and characterization of metal complexes with schiff base ligands. J Chem Educ 93:5–8
Luo S, Zhang S, Wang Y et al (2010) Complexes of ionic liquids with poly(ethylene glycol)s. J Organomet Chem 75:1888–1891
Reddy MJ, Kumar JS, Subba Rao UV, Chu PP (2006) Structural and ionic conductivity of PEO blend PEG solid polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 177:253–256
Syrlybaeva R, Movsum-zade N, Safiullina I et al (2015) Polymer-metal complexes of polyacrylonitrile and its copolymers : synthesis and theoretical study. J Polym Res 22:100 (1-8)
Chatani Y, Okamura S (1987) Crystal structure of poly(ethylene oxide)-sodium iodide complex. Polymer 28:1815–1820
Brandell D, Liivat A, Aabloo A, Thomas JO (2005) Molecular dynamics simulation of the crystalline short-chain polymer system LiPF6·PEO6(Mw~ 1000). J Mater Chem 15:4338–4345
Okada T (1993) Complexation of poly(oxyethy1ene) in analytical chemistry. Analyst 118:959–971
Young W, Epps TH (2009) Salt doping in PEO-containing block copolymers: counterion and concentration effects. Macromolecules 68:2672–2678
Buwalda SJ, Dijkstra PJ, Feijen J (2012) Poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(L-lactide) star block copolymer hydrogels crosslinked by metal-ligand coordination. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 50:1783–1791
Yanagida S, Takahashi K, Okahara M (1977) Metal-ion complexation of noncyclic poly(ethylene) derivatives. I. Solvent extraction of alkali and alkaline earth metal thiocyanates and iodides. Bull Chem Soc Japan 50:1386–1390
Awano H, Ono K, Murakami K (1982) The interaction of a neutral polymer with small ions in solution. II. The binding of alkali metal ions to poly(oxyethylene) in several organic solvents. Bull Chem Soc Japan 55:2530–2536
Miyazaki T, Yanagida S, Itoh A, Okahara M (1982) Synthesis and alkali-cation complexing properties of 12-crown-4 derivatives. Bull Chem Soc Japan 55:2005–2009
Awano H, Ono K, Murakami K (1982) The interaction of a neutral polymer with small ions in solution. I. A method for the analysis of ion binding to a neutral polymer. Bull Chem Soc Japan 55:2525–2529
Hines CC, Bauer CB, Rogers RD (2007) Lanthanide polyether complexation chemistry: the interaction of hydrated lanthanide(III) nitrate salts with an acyclic 18-crown-6 analog, pentaethylene glycol. New J Chem 31:762–769
Barthélemy PP, Desreux JF, Massaux J (1986) Complexation of lanthanides by linear polyethers in propylene carbonate: a “crown-like” behaviour. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans:2497–2499
Glasse MD, Idris R, Latham RJ et al (2002) Polymer electrolytes based on modified natural rubber. Solid State Ionics 147:289–294
Yoshizawa M, Marwanta E, Ohno H (2000) Preparation and characteristics of natural rubber/poly(ethylene oxide) salt hybrid mixtures as novel polymer electrolytes. Polymer 41:9049–9053
Samani MR, Borghei SM, Olad A, Chaichi MJ (2010) Removal of chromium from aqueous solution using polyaniline - poly ethylene glycol composite. J Hazard Mater 184:248–254
Staunton E, Christie AM, Martin-Litas I et al (2004) Structure of the poly(ethylene oxide)-zinc chloride complex. Angew Chem Int Ed 116:2155–2157
Tummler B, Maass G, Vogtle F et al (1979) Open-chain polyethers. Inflence of aromatic donor end groups on thermodynamics and kinetics of alkali metal ion complex formation. J Am Chem Soc 101:2588–2598
Bessbousse H, Rhlalou T, Verchere J-F, Lebrun L (2009) Novel metal-complexing membrane containing poly(4-vinylpyridine ) for removal of Hg(II) from aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B 113:8588–8598
Niitani T, Shimada M, Kawamura K, Kanamura K (2005) Characteristics of new-type solid polymer electrolyte controlling nano-structure. J Power Sources 146:386–390
Sadoway DR (2004) Block and graft copolymer electrolytes for high-performance, solid-state, lithium batteries. J Power Sources 129:1–3
Ramesh S, Yuen TF, Shen CJ (2008) Conductivity and FTIR studies on PEO-LiX [X: CF3SO3-, SO42-] polymer electrolytes. Spectrochim Acta Part A 69:670–675
Armand M (1994) The history of polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 69:309–319
Baril D, Michot C, Armand M (1997) Electrochemistry of liquids vs. solids: polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 94:35–47
Latham RJ, Linford RG, Schlindwein WS (1989) Cation-oxygen geometry in polymer electrolytes: interpretation of EXAFS results. Faraday Discuss Chem Soc 88:103–111
Cai H, Hu R, Egami T et al (1992) Local structure studies of PEO-based NiBr2 electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 37:1663–1665
Bandara HMN, Linford RG, Latham RJ, Schlindwein WS (1995) XAFS studies of polymer electrolytes. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 369:547–557
Latham RJ, Linford RG, Pynenburg RAJ, Schlindwein WS (1993) Factors affecting X-ray absorption fine structure of zinc in oxygen-plus-halide environments within polymer electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 140:1056–1060
Latham RJ, Linford RG, Pynenburg RAJ et al (1993) Plasticiser-induced local structure in polymer electrolytes. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 89:349–354
Latham RJ, Linford RG (1996) Polymer electrolytes — low molecular weight analogues as mimics of high concentration crystalline phase materials. Solid State Ionics 85:193–196
Cole M, Latham RJ, Linford RG et al (1989) EXAFS of polymer electrolytes. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 135:383–388
Andrews KC, Cole M, Latham RJ et al (1988) EXAFS studies of divalent polymeric electrolytes: an investigation of PEO4:CaI2 at room temperature. Solid State Ionics 28–30:929–935
Cole M, Sheldon MH, Glasse MD et al (1989) EXAFS and thermal studies on zinc polymeric electrolytes. Appl Phys A Solids Surfaces 49:249–257
Einset AG, Schlindwein WS, Latham RJ, Linford RG, Pynenburg R (1991) Investigation of ZnBr2:PEO polymer electrolyte characteristics. J Electrochem Soc 138:1569–1574
Latham RJ, Linford RG, Pynenburg R, Schlindwein WS (1992) EXAFS and related studies of mixed polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 37:1529–1531
Chintapalli S, Frech R (1995) Ionic association and conductivity in poly(ethylene oxide) and poly (propylene oxide) metal salt systems. Electrochim Acta 40:2093–2099
Berthier C, Gorecki W, Minier M et al (1983) Microscopic investigation of ionic conductivity in alkali metal salts-poly(ethylene oxide) adducts. Solid State Ionics 11:91–95
Mohan VM, Raja V, Bhargav PB et al (2007) Structural, electrical and optical properties of pure and NaLaF4 doped PEO polymer electrolyte films. J Polym Res 14:283–290
Shriver DF, Papke BL, Patner MA, Dupon R, Wong T, Brodwin M (1981) Structure and ion transport in polymer-salt complexes. Solid State Ionics 5:83–88
Jayathilaka PARD, Dissanayake MAKL, Albinsson I, Mellander BE (2002) Effect of nano - porous Al2O3 on thermal, dielectric and transport properties of the (PEO)9LiTFSI polymer electrolyte systems. Electrochim Acta 47:3257–3268
Passerini S, Cndni R, Scrosati B (1989) Characterization of poly(ethylene oxide) copper salt polymer electrolytes. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 49:425–429
Lundrerg RD, Bailey FE, Callard RW (1966) Interactions of inorganic salts with poly(ethylene oxide). J Polym Sci Part A-1(4):1563–1577
Choudhary S, Sengwa RJ (2017) Morphological, structural, dielectric and electrical properties of PEO–ZnO nanodielectric films. J Polym Res 24:54 (1-12)
Liao CS, Ye WB (2003) Enhanced ionic conductivity in poly(ethylene oxide)/layered double hydroxide nanocomposite electrolytes. J Polym Res 10:241–246
Dhatarwal P, Sengwa RJ (2017) Dielectric and electrical characterization of (PEO–PMMA)–LiBF4–EC plasticized solid polymer electrolyte films. J Polym Res 24:135 (1-10)
Siva Kumar J, Vijaya Kumar K, Subrahmanyam AR, Jaipal Reddy M (2007) Conductivity study of polyethylene oxide (PEO) complexed with sodium bicarbonate. J Mater Sci 42:5752–5755
Jannasch P (2002) Ionic conductivity in physical networks of polyethylene-polyether-polyethylene triblock copolymers. Chem Mater 14:2718–2724
Alloin F, Sanchez JY, Armand MB (1992) Conductivity measurements of LiTFSI triblock copolymers with a central POE sequence. Electrochim Acta 37:1729–1731
Lobitz P, Fiillbier H, Reiche A, Illner JC (1992) Ionic conductivjty in poly(ethylene oxide)-copolymer mixtures with LiI. Solid State Ionics 58:41–48
Yuan R, Teran AA, Gurevitch I et al (2013) Ionic conductivity of low molecular weight block copolymer electrolytes. Macromolecules 46:914–921
Devaux D, Gle D, Phan TNT et al (2015) Biexcitonic bound and continuum states of homogeneously and inhomogeneously broadened exciton resonances. Chem Mater 27:4682–4692
Chandrasekharan Nair R, Gopakumar S, Gopinathan Nair MR (2007) Synthesis and characterization of block copolymers based on natural rubber and polypropylene oxide. J Appl Polym Sci 103:955–962
McMaster WH, Del Grande NK, Mallett JH, Hubbell JH (1970) Compilation of X-ray cross sectionS. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables A8:448–444
Bandyopadhyay P, Segre CU Periodic Table. http://www.csrri.iit.edu/mucal.html
Kushwaha S, Sreedhar B, Padmaja P (2012) XPS, EXAFS, and FTIR as tools to probe the unexpected adsorption-coupled reduction of U(VI) to U(V) and U(IV) on borassus flabellifer -based adsorbents. Langmuir 28:16038–16048
Tiwari N, Kumar S, Ghosh AK et al (2017) Structural investigations of (Mn, Dy) co-doped ZnO nanocrystals using X-ray absorption studies. RSC Adv 7:56662–56675
Newville M, Ravel B, Haskel D et al (1995) Analysis of multiple-scattering XAFS data using theoretical standards. Phys B Phys Condens Matter 208–209:154–156
Papke BL, Ratner MA, Shriver DF (1981) Vibrational spectroscopy and structure of polymer electrolytes, poly(ethylene oxide) complexes of alkali metal salts. J Phys Chem Solids 42:493–500
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank RRCAT, Indore, India for the arrangement of EXAFS analysis, Anu A S, Analytical Engineer, IIUCNN, Mahatma Gandhi University, Kottayam for EDX analysis, Dr. Shibin N B, IUIC, Mahatma Gandhi University, Kottayam for FTIR analysis, Dr. Simon, St. Thomas College, Pala for XRD analysis and Dr. Jiji Abraham, Vimala College, Trissur for motivation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mrudula, M.S., Tiwari, N., Jha, S.N. et al. Structural studies on transition metal ion complexes of polyethylene oxide-natural rubber block copolymers. J Polym Res 26, 191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1837-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1837-y