Abstract
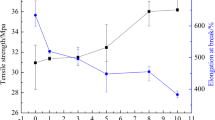
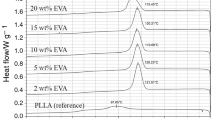
Methyl methacrylate (MMA), butyl acrylate (BA) and 1-butyl-3-vinylimdazolium tetrafluoroborate ([BVIM][BF4]) copolymer (MMA-BA-IL) was prepared and used to enhance the electroactive phase content, toughness and dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) tests indicated that crystal transformation of PVDF from α-phase to β/γ-phase occurred due to ion-dipole interaction between PVDF and [BVIM][BF4]. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) results showed MMA-BA-IL copolymer dispersed in the PVDF uniformly and the partial replacement of MMA components by [BVIM][BF4] decreased the miscibility between PVDF and MMA-BA copolymer. MMA-BA-IL copolymer improved the tensile ductility and impact toughness of PVDF. When the content of MMA-BA-IL was beyond 10 wt%, the elongation at break was higher than 400% and the impact strength was higher than 600 J/m. Deformation mechanism researches proved that shear yielding of the PVDF matrix and debonding/cavitation of the MMA-BA-IL copolymer particles were the major toughening mechanisms. The addition of MMA-BA-IL copolymer enhanced the dielectric properties of PVDF significantly. When the MMA-BA-IL content was 15 wt%, the dielectric constant of the PVDF/MMA-BA-IL blend increased to 54.3 at the 100 Hz frequency, which improved by 246% relative to that of the pure PVDF.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang X, Shen Y, Xu B, Zhang Q, Gu L, Jiang J, Ma J, Lin Y, Nan CW (2016) Giant energy density and improved discharge efficiency of solution-processed polymer nanocomposites for dielectric energy storage. Adv Mater 28:2055–2061
Huang XY, Jiang PK (2015) Core-Shell structured high-k polymer nanocomposites for energy storage and dielectric applications. Adv Mater 27:546–554
Lin HJ, Li L, Ren J, Cai ZB, Qiu L, Yang Z, Peng HS (2013) Conducting polymer composite film incorporated with aligned carbon nanotubes for transparent, flexible and efficient supercapacitor. Sci Rep 3:1353
Roy S, Thakur P, Hoque NA, Bagchi B, Sepay N, Khatun F, Kool A, Das S (2017) Electroactive and high dielectric folic acid/PVDF composite film rooted simplistic organic photovoltaic self-charging energy storage cell with superior energy density and storage capability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 19:24198–24209
Xia XD, Wang Y, Zhong Z, Weng GJ (2017) A frequency-dependent theory of electrical conductivity and dielectric permittivity for graphene-polymer nanocomposites. Carbon 111:221–230
Yang MH, Zhao H, He DL, Hu CH, Chen HW, Bai JB (2017) Carbon coated boron nitride Nanosheets for polymer nanocomposites with enhanced dielectric performance. Materials 10:741
Li R, Zhou J, Liu HJ, Pei JZ (2017) Effect of polymer matrix on the structure and electric properties of piezoelectric lead Zirconatetitanate/polymer composites. Materials 10:945
Su R, Lu ZD, Zhang DW, Liu Y, Wang ZP, Li JN, Bian JH, Li YX, Hu XH, Gao JH, Yang YD (2016) High energy density performance of polymer nanocomposites induced by designed formation of BaTiO3@sheet-likeTiO2 hybrid Nanofillers. J Phys Chem C 120:11769
Karan SK, Das AK, Bera R, Paria SA, Maitra N, Shrivastava K, Khatua BB (2016) Effect of γ-PVDF on enhanced thermal conductivity and dielectric property of Fe-rGO incorporated PVDF based flexible nanocomposite film for efficient thermal management and energy storage applications. RSC Adv 6:37773–37783
Thaku VK, Tan EJ, Lin MF, Lee PS (2011) Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-graft-poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate): a novel material for high energy density capacitors. J Mater Chem 21:3751–3759
Xie LY, Huang X, Yang K, Li ST, Jiang PK (2014) "grafting to" route to PVDF-HFP-GMA/BaTiO3 nanocomposites with high dielectric constant and high thermal conductivity for energy storage and thermal management applications. J Mater Chem A 2:5244–5251
Kim P, Jones SC, Hotchkiss PJ, Haddock JN, Kippelen B, Marder S, Perry JW (2007) Phosphonic acid-modified barium Titanate polymer nanocomposites with high permittivity and dielectric strength. Adv Mater 19:1001–1005
Kim P, Doss NM, Tillotson JP, Hotchkiss PJ, Pan MJ, Marder SR, Li JY, Calame JP, Perry JW (2009) High energy density nanocomposites based on surface-modified BaTiO3 and a ferroelectric polymer. ACS Nano 3:2581–2592
Wang GS, Wu YY, Zhang XJ, Li Y, Guo L, Cao MS (2014) Controllable synthesis of uniform ZnO nanorods and their enhanced dielectric and absorption properties. J Mater Chem A 2:8644–8651
Li ZT, Zhang X, Li GH (2014) In situ ZnO nanowire growth to promote the PVDF piezo phase and the ZnO-PVDF hybrid self-rectified nanogenerator as a touch sensor. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:5475–5479
Mohamadi S, Sharifi-Sanjani N, Foyouhi A (2013) Evaluation of graphene nanosheets influence on the physical properties of PVDF/PMMA blend. J Polym Res 20:1
Wang L, Dang ZM (2005) Arbon nanotube composites with high dielectric constant at low percolation threshold. Appl Phys Lett 87:284–291
Dang ZM, Wang L, Yin Y, Zhang Q, Lei QQ (2007) Giant dielectric Permittivities in functionalized carbon-nanotube/electroactive-polymer nanocomposites. Adv Mater 19:852–857
He F, Lau S, Chan HL, Fan JT (2010) High dielectric permittivity and low percolation threshold in nanocomposites based on poly(vinylidene fluoride) and exfoliated graphite Nanoplates. Adv Mater 21:710–715
Dang ZM, Lin YH, Nan CW (2003) Novel ferroelectric polymer composites with high dielectric constants. Adv Mater 15:1625–1629
Dias JC, Lopes AC, Magalhaes B, Botelho G, Silva MM, Esperanca JMSS, Lanceros-Mendez S (2015) High performance electromechanical actuators based on ionic liquid/poly(vinylidene fluoride). Polym Test 48:199–205
Mejri R, Dias JC, Lopes AC, Hentat SB, Silva MM, Botelho G, Ferro M, Esperanca JMSS, Maceiras A, Laza JM, Vilas JL, Leon LM, Lanceros-Mendez S (2015) Effect of ionic liquid anion and cation on the physico-chemical properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/ionic liquid blends. Eur Polym J 71:304–313
Mejri R, Dias JC, Lopes AC, Hentati SB, Marins MS, Costa CM, Lanceros-Mendez S (2016) Effect of anion type in the performance of ionic liquid/poly(vinylidene fluoride) electromechanical actuators. J Non-Cryst Solids 453:8–15
Xing CY, Zhao MM, Zhao LP, You JC, Cao XJ, Li YJ (2013) Ionic liquid modified poly(vinylidene fluoride): crystalline structures, miscibility, and physical properties. Polym Chem 24:5726–5734
Xing CY, Wang YY, Zhang C, Li LF, Li YJ, Li JY (2015) Immobilization of ionic liquids onto the poly(vinylidene fluoride) by Electron beam irradiation. Ind Eng Chem Res 38:9351–9359
Xing CY, You JC, Li YJ, Li JY (2015) Nanostructured poly(vinylidene fluoride)/ionic liquid composites: formation of organic conductive Nanodomains in polymer matrix. J Phys Chem C 36:21155–21164
Xing CY, Wang YY, Huang XY, Li YJ, Li JY (2016) Poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites with simultaneous organic Nanodomains and inorganic nanoparticles. Macromolecules 3:1026–1035
Xing CY, Zhao LP, You JC, Dong WY, Cao XJ, Li JY (2012) Impact of ionic liquid-modified multiwalled carbon nanotubes on the crystallization behavior of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J Phys Chem B 116:8312–8320
Bi XJ, Song SX, Sun SL (2017) Performance improvement of poly(vinylidene fluoride) by in situ copolymerization of methyl methacrylate and ionic liquid. Macromol Res 12:1–9
Martins P, Lopes AC, Lanceros-Mendez S (2014) Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): determination, processing and applications. Prog Polym Sci 4:683–706
Bahader A, Gui HG, Fang HG, Wang P, Wu SJ, Ding YS (2016) Preparation and characterization of poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites containing amphiphilic ionic liquid modified multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Polym Res 6:184
Martins P, Costa CM, Lanceros-Mendez S (2011) Nucleation of electroactive β-phase poly(vinilidene fluoride) with CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4 nanofillers: a new method for the preparation of multiferroic nanocomposites. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 1:233–237
Martin P, Costa CM, Benelmekki M, Botello G, Lanceros-Mendes S (2012) On the origin of the electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride) β-phase nucleation by ferrite nanoparticles via surface electrostatic interactions. CrystEngComm 14: 2807–2811
Martins P, Caparros C, Gonçalves R, Martins PM, Benelmekki M, Botelho G, Lanceros-Mendes S (2012) Role of nanoparticle surface charge on the nucleation of the electroactive β-poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites for sensor and actuator applications. J Phys Chem C 116:15790–15794
Andrew JS, Clarke DR (2008) Enhanced ferroelectric phase content of polyvinylidene difluoride fibers with the addition of magnetic nanoparticles. Langmuir 16:8435–8438
Song HH, Yang SJ, Sun SL, Zhang HX (2013) Effect of miscibility and crystallization on the mechanical properties and transparency of PVDF/PMMA blends. Polym -Plast Technol Eng 52:221–227
Sencadas V, Lanceros-méndez S, Sabater iSR, Andrio BA, Gómez RJL (2012) Relaxation dynamics of poly(vinylidene fluoride) studied by dynamical mechanical measurements and dielectric spectroscopy. Eur Phys J E 35:41–52
Leones R, Costa CM, Machado AV, Esperança JMSS, Silva MM, Lanceros-Méndez S (2013) Development of solid polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) and the [N 1 1 1 2(OH) ][NTf2 ] ionic liquid for energy storage applications. Solid State Ionics 253:143–150
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51273025), Jilin Provincial Science & Technology Department (20170203010GX) and The Education Department of Jilin Province (JJKH20170551KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, S., Bi, X., Jiang, S. et al. Enhanced electroactive phase, toughness and dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) with addition of MMA-BA-IL copolymer. J Polym Res 25, 157 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1561-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1561-z