Abstract
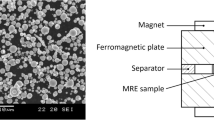
This work studies the influence of synthesis variables on the lineal viscoelastic properties of elastomers filled with soft magnetic particles. Three matrices [natural rubber (NR), high-temperature vulcanising silicone rubber (HTV-SR), and room-temperature vulcanising (RTV-SR)] and three volumetric particle contents (0%, 15%, and 30%) were studied. Anisotropic samples were synthesised with a softer matrix to obtain a larger magnetorheological (MR) effect, and the variation of their properties under an external magnetic field was examined. All samples were characterised within the lineal viscoelastic (LVE) region using a rheometer, because the MR effect is larger within this region. The influence of the matrix, particle content, and pre-structure on the viscoelastic properties of the synthesised samples was studied. The storage and loss modulus increased with the frequency owing to the viscoelastic behaviour of an elastomer in the rubbery phase. Both moduli also increased with the filler content. The influence of the filler is dependent on the matrix, and the maximum variation was seen in the NR-based samples. However, the maximum MR effect was seen in the samples with a softer matrix, and the effect was enhanced in the anisotropic samples. In this work, the MR effect on the loss modulus was studied, and the tendencies were found to be similar to those of the storage modulus. The main contribution of this work is that all dynamic behaviour results were comparable because all synthesis variables and characterisation conditions were identical. Therefore, how the particle content, frequency, and magnetic field affects each matrix can be studied.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen L, Gong XL, Li WH (2008) Effect of carbon black on the mechanical performances of magnetorheological elastomers. Polym Test 27:340–345. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2007.12.003
Chen L, Gong X, Jiang W, Yao J, Deng H, Li W (2007) Investigation on magnetorheological elastomers based on natural rubber. J Mater Sci 42:5483–5489. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-0975-x
Chen L, Gong X, Li W (2008) Damping of Magnetorheological Elastomers. Chinese J Chem Phys 21:581–585. doi:10.1088/1674-0068/21/06/581-585
Lokander M, Stenberg B (2003) Improving the magnetorheological effect in isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials. Polym Test 22:677–680. doi:10.1016/S0142-9418(02)00175-7
Stepanov GV, Chertovich AV, Kramarenko EY (2012) Magnetorheological and deformation properties of magnetically controlled elastomers with hard magnetic filler. J Magn Magn Mater 324:3448–3451. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.02.062
Yu M, Qi S, Fu J, Zhu M (2015) A high-damping magnetorheological elastomer with bi-directional magnetic-control modulus for potential application in seismology. Appl Phys Lett 107:111901. doi:10.1063/1.4931127
Ivaneyko D, Toshchevikov VP, Saphiannikova M, Heinrich G (2011) Magneto-sensitive elastomers in a homogeneous magnetic field: A regular rectangular lattice model. Macromol Theory Simul 20:411–424. doi:10.1002/mats.201100018
Melenev P, Raikher Y, Stepanov G, Rusakov V, Polygalova L (2011) Modeling of the Field-Induced Plasticity of Soft Magnetic Elastomers. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 22:531–538. doi:10.1177/1045389X11403819
Gong X, Fan Y, Xuan S, Xu Y, Peng C (2012) Control of the damping properties of magnetorheological elastomers by using polycaprolactone as a temperature-controlling component. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:6395–6403. doi:10.1021/ie300317b
Hu Y, Wang YL, Gong XL, Gong XQ, Zhang XZ, Jiang WQ, Zhang PQ, Chen ZY (2005) New magnetorheological elastomers based on polyurethane/Si-rubber hybrid. Polym Test 24:324–329. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2004.11.003
Fan Y, Gong X, Xuan S, Zhang W, Zheng J, Jiang W (2011) Interfacial friction damping properties in magnetorheological elastomers. Smart Mater Struct 20:35007. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/20/3/035007
Ju BX, Yu M, Fu J, Yang Q, Liu XQ, Zheng X (2012) A novel porous magnetorheological elastomer: preparation and evaluation. Smart Mater Struct 21:35001. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/21/3/035001
Zhu J-T, Xu Z-D, Guo Y-Q (2012) Magnetoviscoelasticity parametric model of an MR elastomer vibration mitigation device. Smart Mater Struct 21:75034. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/21/7/075034
Lokander M, Stenberg B (2003) Performance of isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials. Polym Test 22:245–251. doi:10.1016/S0142-9418(02)00043-0
Gordaninejad F, Wang X, Mysore P (2012) Behavior of thick magnetorheological elastomers. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 23:1033–1039. doi:10.1177/1045389X12448286
Ge L, Gong X, Fan Y, Xuan S (2013) Preparation and mechanical properties of the magnetorheological elastomer based on natural rubber/rosin glycerin hybrid matrix. Smart Mater Struct 22:115029. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/22/11/115029
Varga Z, Filipcsei G, Zrínyi M (2006) Magnetic field sensitive functional elastomers with tuneable elastic modulus. Polymer (Guildf) 47:227–233. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2005.10.139
Li J, Gong X, Xu Z, Jiang W (2008) The effect of pre-structure process on magnetorheological elastomer performance. Int J Mater Res 99:1358–1364. doi:10.3139/146.101775
Sun TL, Gong XL, Jiang WQ, Li JF, Xu ZB, Li WH (2008) Study on the damping properties of magnetorheological elastomers based on cis-polybutadiene rubber. Polym Test 27:520–526. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2008.02.008
Payne AR (1962) The dynamic properties of carbon black-loaded natural rubber vulcanizates. Part I J Appl Polym Sci 6:57–63. doi:10.1002/app.1962.070061906
Ferry JD (1980) Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York,
Qiao X, Lu X, Li W, Chen J, Gong X, Yang T, Li W, Sun K, Chen X (2012) Microstructure and magnetorheological properties of the thermoplastic magnetorheological elastomer composites containing modified carbonyl iron particles and poly(styrene- b -ethylene-ethylenepropylene- b -styrene) matrix. Smart Mater Struct 21:115028. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/21/11/115028
Agirre-Olabide I, Berasategui J, Elejabarrieta MJ, Bou-Ali MM (2014) Characterization of the linear viscoelastic region of magnetorheological elastomers. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 25:2074–2081. doi:10.1177/1045389X13517310
Agirre-Olabide I, Elejabarrieta MJ, Bou-Ali MM (2015) Matrix dependence of the linear viscoelastic region in magnetorheological elastomers. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 26:1880–1886. doi:10.1177/1045389X15580658
Dong X, Ma N, Qi M, Li J, Chen R, Ou J (2012) The pressure-dependent MR effect of magnetorheological elastomers. Smart Mater Struct 21:75014. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/21/7/075014
Jones DIG (2001) Handbook of viscoelastic vibration damping. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester,
Schubert G, Harrison P (2015) Large-strain behaviour of Magneto-Rheological Elastomers tested under uniaxial compression and tension, and pure shear deformations. Polym Test 42:122–134. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2015.01.008
Nashif AD, Jones DIG, Henderson JP (1985) Vibration damping. John Wiley & Sons, New York,
Phewthongin N, Saeoui P, Sirisinha C (2006) Rheological behavior of CPE/NR blends filled with precipitated silica. J Appl Polym Sci 100:2565–2571. doi:10.1002/app.22550
Aloui S, Klüppel M (2015) Magneto-rheological response of elastomer composites with hybrid-magnetic fillers. Smart Mater Struct 24:25016. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/24/2/025016
Raa Khimi S, Pickering KL, Mace BR (2015) Dynamic properties of magnetorheological elastomers based on iron sand and natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 132:41506. doi:10.1002/app.41506
Ju B, Tang R, Zhang D, Yang B, Yu M, Liao C (2015) Temperature-dependent dynamic mechanical properties of magnetorheological elastomers under magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater 374:283–288. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.08.012
Han Y, Zhang Z, Faidley LE, Hong W (2012) Microstructure-based modeling of magneto-rheological elastomers. Proc. SPIE, Behavior and Mechanics of Multifunctional Materials and Composites, 8342:83421B. doi:10.1117/12.925492
Jung HS, Kwon SH, Choi HJ, Jung JH, Kim YG (2016) Magnetic carbonyl iron/natural rubber composite elastomer and its magnetorheology. Compos Struct 136:106–112. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.10.008
Yang C, Fu J, Yu M, Zheng X, Ju B (2015) A new magnetorheological elastomer isolator in shear-compression mixed mode. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 26:1290–1300. doi:10.1177/1045389X14541492
Lu X, Qiao X, Watanabe H, Gong X, Yang T, Li W, Sun K, Li M, Yang K, Xie H, Yin Q, Wang D, Chen X (2012) Mechanical and structural investigation of isotropic and anisotropic thermoplastic magnetorheological elastomer composites based on poly(styrene-b-ethylene-co-butylene-b-styrene) (SEBS). Rheol Acta 51:37–50. doi:10.1007/s00397-011-0582-x
Boczkowska A, Awietjan SF, Wroblewski R (2007) Microstructure–property relationships of urethane magnetorheological elastomers. Smart Mater Struct 16:1924–1930. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/16/5/049
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Department of Education of the Basque Government for the Research Predoc Grant PRE_2014_1_284, AVISANI (PI-2016-1-0026), ACTIMAT, IT009-16 and the AVISANI (DPI2015-71198-R) research project from the Spanish government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agirre-Olabide, I., Elejabarrieta, M.J. Effect of synthesis variables on viscoelastic properties of elastomers filled with carbonyl iron powder. J Polym Res 24, 139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1299-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1299-z