Abstract
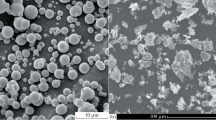
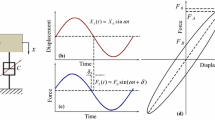
Novel smart thermoplastic magnetorheological elastomer composites containing micron-sized magnetic carbonyl iron (CI) particles were prepared with a poly(styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene) (SEBS) triblock copolymer utilized as the thermoplastic matrix rubber, and the structures and properties of the CI-SEBS composites were examined. The CI particles were uniformly dispersed in the composites prepared in the absence of the magnetic field at high temperatures T (>T\(_{\rm g}^{\rm S})\), and this isotropic composite exhibited a larger storage modulus G′ compared to the SEBS matrix at room temperature (< <T\(_{\rm g}^{\rm S})\) where the EB phase therein was rubbery while the PS phase was in the glassy state. In contrast, the SEBS composite prepared under the magnetic field (with the intensity ψ < 2.5 T) at high T (>T\(_{\rm g}^{\rm S})\) contained a chain structure of CI particles. This chain structure became longer and better aligned on an increase of ψ up to a saturation of the particle magnetization and on an increase of the time interval of applying the field (that allowed the particles to move and equilibrate their aligned structure). The modulus G′ of this “pre-structured” composite measured for both cases of ψ = 0 and ψ > 0 in the direction perpendicular to the chain structure at room temperature was enhanced compared to G′ of the isotropic composites. This difference of the filler effect (for ψ = 0) and the magnetorheological effect (for ψ > 0) between the pre-structured and isotropic composites was enhanced when the chain structure of the CI particles in the pre-structured composites became longer and better aligned. A mechanism(s) of this enhancement was discussed in relation to the morphologies (particle distribution) in the composites with the aid of a filler model and a molecular expression of the stress due to magnetically interacting particles.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batchelor G (1977) The effect of Brownian motion on the bulk stress in a suspension of spherical particles. J Fluid Mech 83(01):97–117
Boczkowska A, Awietjan SF, Wejrzanowski T, Kurzydlowski KJ (2009) Image analysis of the microstructure of magnetorheological elastomers. J Mater Sci 44(12):3135–3140 doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3417-8
Bose H, Roder R (2009) Magnetorheological elastomers with high variability of their mechanical properties. J Phys: Conference Series 149:012090. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/149/1/012090
Chen L, Gong XL, Jiang WQ, Yao JJ, Deng HX, Li WH (2007) Investigation on magnetorheological elastomers based on natural rubber. J Mater Sci 42(14):5483–5489
Csizmadia J, Mészáros I (2008) Magnetic saturation of poly (dimethyl-siloxane) matrix composites based magnetorheological elastomers. Mech Eng 52(1):3–8
Davis LC (1999) Model of magnetorheological elastomers. J Appl Phys 85:3348
Farshad M, Benine A (2004) Magnetoactive elastomer composites. Polym Test 23(3):347–353. doi:10.1016/s0142-9418(03)00103-x
Fetters L, Loshe DJ, Colby RH (2007) Chain dimension and entanglement spacings. In: Mark JE (ed) Physical properties of polymers handbook (2nd ed). Springer, New York, Chapter 25
Fuchs A, Zhang Q, Elkins J, Gordaninejad F, Evrensel C (2007) Development and characterization of magnetorheological elastomers. J Appl Polym Sci 105(5):2497–2508. doi:10.1002/app.24348
Guan XC, Dong XF, Ou JP (2008) Magnetostrictive effect of magnetorheological elastomer. J Magn Magn Mater 320 (3–4):158–163. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2007.05.043
Guth E (1945) Theory of filler reinforcement. J Appl Phys 16(1):20–25
Halpin J, Kardos J (1976) The Halpin-Tsai equations: a review. Polym Eng Sci 16(5):344–352
Holden G, Kricheldorf HR, Quirk RP (2004) Thermoplastic elastomers. Hanser Fachbuchverlag
Hu Y, Wang YL, Gong XL, Gong XQ, Zhang XZ, Jiang WQ, Zhang PQ, Chen ZY (2005) New magnetorheological elastomers based on polyurethane/Si-rubber hybrid. Polym Test 24(3):324–329. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2004.11.003
Jinkui W, Xinglong G, Lin C, Hesheng X, Zaiguo H (2009) Preparation and characterization of isotropic polyurethane magnetorheological elastomer through in situ polymerization. J Appl Polym Sci: 901–910. doi:10.1002/app.30563
Jongschaap R, Mellema J (1995) Stress tensor expressions for dispersions. J Rheol 39:953
Kchit N, Bossis G (2008) Piezoresistivity of magnetorheological elastomers. J Phys: Condens Matter 20:204136. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/20/20/204136
Kchit N, Bossis G (2009) Electrical resistivity mechanism in magnetorheological elastomer. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:105505. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/42/10/105505
Kchit N, Lancon P, Bossis G (2009) Thermo-resistance and giant magnetoresistance of magnetorheological elastomers. J Phys Appl Phys 42:105506. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/42/10/105506
Kim I, Bae S, Kim J (2008) Composition effect on high frequency properties of carbonyl-iron composites. Mater Lett 62(17–18):3043–3046. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2008.01.134
Lokander M, Reitberger T, Stenberg B (2004) Oxidation of natural rubber-based magnetorheological elastomers. Polymer Degrad Stab 86(3):467–471. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2004.05.019
Piotr Z, et al. (2010) Isotropic magnetorheological elastomers with thermoplastic matrices: structure, damping properties and testing. Smart Mater Struc 19(4):045014
Song HJ, Wereley NM, Bell RC, Planinsek JL, Filer JA II (2009) Field dependent response of magnetorheological elastomers utilizing spherical Fe particles versus Fe nanowires. In: Institute of Physics Publishing, p 012097
Stepanov GV, Abramchuk SS, Grishin DA, Nikitin LV, Kramarenko EY, Khokhlov AR (2007) Effect of a homogeneous magnetic field on the viscoelastic behavior of magnetic elastomers. Polymer 48(2):488–495
Sun T, Gong X, Jiang W, Li J, Xu Z, Li W (2008) Study on the damping properties of magnetorheological elastomers based on cis-polybutadiene rubber. Polym Test 27(4):520–526
von Lockette PR, Kadlowec J, Koo JH (2006) Particle mixtures in magnetorheological elastomers (MREs) - art. no. 61700T. Smart Structures and Materials 2006: Active Materials: Behavior and Mechanics 6170:T1700–T1700. doi:10.1117/12.658750
von Lockette PR, Lofland SE, Koo JH, Kadlowec J, Dermond M (2008) Dynamic characterization of bimodal particle mixtures in silicone rubber magnetorheological materials. Polym Test 27(8):931–935. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2008.08.007
Wang Y, Hu Y, Deng H, Gong X, Zhang P, Jiang W, Chen Z (2006) Magnetorheological elastomers based on isobutylene–isoprene rubber. Polym Eng Sci 46(3):264–268
Woods BKS, Wereley N, Hoffmaster R, Nersessian N (2007) Manufacture of bulk magnetorheological elastomers using vacuum assisted resin transfer molding. Int J Mod Phys B 21(28–29):5010–5017
Wu JK, Gong XG, Chen L, Xia HS, Hu ZG (2009) Preparation and characterization of isotropic polyurethane magnetorheological elastomer through in situ polymerization. J Appl Polym Sci 114(2):901–910. doi:10.1002/app.30563
Yang TI, Brown RNC, Kempel LC, Kofinas P (2008) Magneto-dielectric properties of polymer-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. J Magn Magn Mater 320(21): 2714–2720
Yin HM, Sun LZ, Chen JS (2002) Micromechanics-based hyperelastic constitutive modeling of magnetostrictive particle-filled elastomers. Mech Mater 34(8):505–516
Zhang XZ, Gong XL, Zhang PQ, Li WH (2007) Existence of bound-rubber in magnetorheological elastomers and its influence on material properties. Chin J Chem Phys 20(2):173–179. doi:10.1360/cjcp2007.20(2).173.7
Zhou GY, Wang Q (2005) Design of a smart piezoelectric actuator based on a magnetorheological elastomer. Smart Mater Struc 14(4):504–510. doi:10.1088/0964-1726/14/4/007
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Science and Technology Research and Development Program from the Ministry of Railways of China (grant No. J2011J002), Minhang District-Shangai Jiao Tong University Science and Technology Cooperation Special Fund, National Undergraduate Innovative Test Program (grant No. 091024822), and partly by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Area “Soft Matter Physics” from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan (grant No. 18068009). The authors also thank Instrumental Analysis Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University for the assistance for the MR measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Qiao, X., Watanabe, H. et al. Mechanical and structural investigation of isotropic and anisotropic thermoplastic magnetorheological elastomer composites based on poly(styrene-b-ethylene-co-butylene-b-styrene) (SEBS). Rheol Acta 51, 37–50 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-011-0582-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-011-0582-x