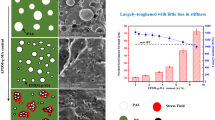
Abstract
Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) functionalized methyl methacrylate-butadiene-styrene core-shell particles (PB-g-MSG) were prepared to toughen poly (butylene terephthalate) (PBT) and polycarbonate (PC) blends. T-dodecyl mercaptan (TDDM) was used to modify the grafting character of the core-shell particles. The addition of TDDM decreased the grafting degree, particles size and crosslinking degree of PB-g-MSG particles. At the same time, the free methyl methacrylate-co-styrene-co-glyceryl methacrylate copolymer (f-MSG) increased. The f-MSG reacted with PBT and suppressed the transesterification between PBT and PC. On the other hand, f-MSG promoted the crystallization of PBT by heterogeneous nucleation. When the TDDM content was lower than 0.76%, PB-g-MSG particles dispersed in the matrix uniformly, otherwise, agglomeration took place. The change of TDDM content in the PB-g-MSG particles influenced the toughening ability and tensile properties. When the TDDM content was 0.76%, the PBT/PC/PB-g-MSG blend showed the optimum impact toughness and yield strength, which are 908 J/m and 49.4Mpa. Fracture mechanism results indicated that cavitation induced shear yielding occurred in the PBT/PC/PB-g-MSG blend when no TDDM addition for the core-shell particles. With the addition of TDDM, the interfacial strength decreased between the PB-g-MSG core-shell particles and the matrix. So voids appeared due to debonding, which also could promote the shear yielding process.













Similar content being viewed by others

References
He JX, Guo Y, Sun SL, Zhang HX (2015) J Polym Eng 3:247
Jose MRCAS, James T (2006) J Mater Chem 16:237
Kooshki RM, Ghasemi I, Karrabi M, Azizi H (2013) J Vinyl Add Tech 19:203
Lei CH, Chen DH (2008) J Appl Polym Sci 109:1099
DePolo WS, Baird DG (2009) Polym Compos 30:188
Kalkar AK, Siesler HW, Pfeifer F, Wadekar SA (2003) Polymer 44:7251
Bai HY, Zhang Y, Zhang YX, Zhang XF, Zhou W (2005) Polym Test 24:235
Bai HY, Zhang Y, Zhang YX, Zhang XF, Zhou W (2006) J Appl Polym Sci 101:54
Kalhoro MS, Gabrys BJ, Zajac W, King SM, Peiffer (2001) Polymer 42:1679
Wen TT, Guo Y, Song SX, Sun SL, Zhang HX (2015) J Polym Res 22:222
Guo Y, He JX, Zhang XN, Sun SL, Zhang HX (2015) J Macromol Sci B 54:823835
Guo Y, Sun SL, Zhang HX (2014) RSC Adv 4:58880
Lin GP, Lin L, Wang XL, Chen L, Wang YZ (2015) Ind Eng Chem Res 54:1282
Sun SL, Zhang FF, Fu Y, Zhou C, Zhang HX (2013) J Macromol Sci B 2:861
Kuram E, Ozcelik B, Yilmaz F, Timur G, Sahin ZM (2014) Polym Compos 35:2074
Kuram E, Timur G, Ozcelik B, Yilmaz F (2014) Mater Manuf Process 29:1260
Zhang FF, Sun SL, Liu XY, Zhang LX, Zhang HX (2009) E-polymers 77:1
Wu JS, Wang K, Yu DM (2003) J Mater Sci 38:183
Wu JS, Mai YW, Yee AF (2000) J Mater Sci 35:307
Tseng WTW, Lee JS (2000) J Appl Polym Sci 76:1280
Brady AJ, Keskkula H, Paul DR (1994) Polymer 35:3665
Okamoto M, Shinoda Y, Kojima T, Inoue T (1994) Polymer 35:4868
Memon AN (1994) J Appl Polym Sci 54:1059
Gui Y, Sun SL, Han Y (2010) J Appl Polym Sci 115:2386–2393
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51273025, 51272026, and 50803007) and Jilin Provincial Science & Technology Department (20140101104JC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, B., Lv, H., Song, S. et al. Modification of the reactive core-shell particles properties to prepare PBT/PC blends with higher toughness and stiffness. J Polym Res 24, 85 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1250-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1250-3