Abstract
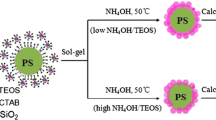
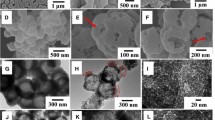
In this study, the emulsifier-free polymerization was employed to prepare polystyrene (PS) latex particles. When the styrene conversion of 80 % was reached, appropriate amounts of methacryl oxypropyl trimethoxy silane (MPS) and divinylbenzene (DVB) were added to the emulsion solution. Emulsion particle surfaces bear silanol functional groups that facilitate the rapid reaction with silica precursor solution, which is formed through the hydrolysis of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and silanol groups of MPS on the emulsion surface. Consequently, a core-shell structure with PS core and silica shell structure was developed. Using extraction and calcination to remove the central polystyrene core, a hollow glass sphere with porous shell structure was obtained. Finally, ascorbic acid was placed and encapsulated in these hollow glass spheres, as inspected by SEM and carbon element mapping images, to examine their controlled release behavior. The cumulative release percentage was analyzed using the Higuchi model, a zero-order model, and a first-order model for kinetic study of release behavior. Results show that the zero order and first order models describe the release kinetics of ascorbic acid equally well for hollow glass spheres.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gole JL, Wang ZL, Dai ZR, Stout J, White M (2003) Colloid Polym Sci 281:673–685
Saito R, Dresselhaus G, Dresselhaus MS (1998) Physical properties of carbon nanotubes. Imperial College Press, London
Devolt MH, Esteve D, Urbina C (1992) Nature 360:547–553
Klein DL, Roth R, Lim AKL, Alivisatos AP, McEuen PL (1997) Nature 389:699–701
Chen J, Hamon MA, Hu H, Chen Y, Rao AM, Eklund PC, Hadden RC (1998) Science 282:95–98
Sousa A, Souza KC, Sousa EMB (2008) Acta Biomater 4:671–679
Ho A, Chang J, Chin W-K, Hsieh HT (2006) J Polym Res 13:285–291
Liu W, Zhang Z (2011) J Polym Res 18:993–1000
Borthakur LJ, Konwer S, Das R, Dolui SK (2011) J Polym Res 18:1207–1215
Xu W, An Q, Hao L, Sun Z, Zhao W (2013) J Polym Res 20:69
Wang W, Jie X, Fei M, Jiang H (2011) J Polym Res 18:13–17
Chen M, Zhou S, Wu L, Xie S, Chen Y (2005) Macromol Chem Phys 206:1896–1902
Tan MN, Park YS (2009) J Ind Eng Chem 15:359–369
Lu Y, McLellan J, Xia Y (2004) Langmuir 20:3464–3470
Deng Z, Chen M, Zhou S, You B, Wu L (2006) Langmuir 22:6403–6407
Yuan J, Wan D, Yang Z (2008) J Phys Chem C 112:17156–17160
Leng W, Chen M, Zhou S, Wu L (2010) Langmuir 26:14271–14275
Tissot I, Reymond JP, Lefebvre F, Bourgeat-Lami E (2002) Chem Mater 14:1325–1331
Ding X, Yu K, Jiang Y, Hari-Bara, Zhang H, Wang Z (2004) Mater Lett 58:3618–3621
Ni KF, Shan GG, Weng ZX, Sheibat-Othman N, Fevotte G (2005) Macromolecules 38:7321–7329
Ni KF, Bourgeat-Lami E, Sheibat-Othman N, Shan G, Fevotte G (2008) Macromol Symp 271:120–128
Chen M, Lu L, Zhou S, You B (2006) Adv Mater 18:801–806
Xu M, Li W, Du M, Shao X, Yin Y, Zhao L, Pu X (2010) Mater Lett 64:931–934
Cao S, Jin X, Yuna X, Wu W, Hu J, Sheng W (2010) J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 48:1332–1338
Lee KC, Wi HA (2010) J Appl Polym Sci 115:3092–3102
Lin HP, Mou CY (2002) Account Chem Res 35:927–935
Chen JF, Ding HM, Wang JX, Shao L (2004) Biomater 25:723–727
Horcajada P, Serre C, Vallet-Reg M, Sebban M, Taulelle F, Ferey G (2006) Angew Chem 45:5974–5978
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the financial support from the Ministry of Economic Affairs of Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, BH., Hsieh, ML., Chen, HY. et al. The preparation of hollow silica spheres with mesoporous shell via polystyrene emulsion latex template and the investigation of ascorbic acid release behavior. J Polym Res 20, 220 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0220-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0220-7