Abstract
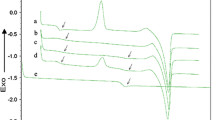
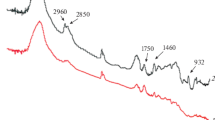
The Fourier transform infrared results suggest that the carboxylic acid groups of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) molecules react with the epoxy groups of molecules of Ethylene Glycidyl Methacrylate Copolymer (EGMC) during the reactive extrusion processes of PLAxEGMCy specimens. The tensile and tear strength values of PLAxEGMCy blown-film specimens in machine and transverse directions improve significantly, and reach their maximal values as their EGMC contents approach an optimum value of 6 wt.%. The melt shear viscosity values of PLAxEGMCy resins, measured at varying shear rates, are significantly higher than those of the PLA resin, and increase consistently with their EGMC contents. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) of PLA and PLAxEGMCy specimens reveal that the percentage crystallinity, peak melting temperature, and onset re-crystallization temperature values of PLAxEGMCy specimens reduce gradually as their EGMC contents increase. In contrast, the glass transition temperatures of PLAxEGMCy specimens increase gradually in conjunction with their EGMC contents. Demarcated porous morphology with several connected fungi-decomposed cavities was found on the surfaces of the PLAxEGMCy specimens after being buried for specific amounts of time, in which the sizes of the fungi-decomposed cavities found on the surfaces of buried PLAxEGMCy specimens reduce significantly as their EGMC contents increase. Further DMA and morphological analysis of PLAxEGMCy specimens reveal that the EGMC molecules are compatible with PLA molecules at EGMC contents equal to or less than 2 wt.% because no phase-separated EGMC droplets and tan δ transitions were found on fracture surfaces and tan δ curves of PLAxEGMCy specimens, respectively. The possible reasons for these remarkable properties of the PLA/EGMC specimens are proposed in this study.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meinander K, Niemi M, Hakola JS, Selin JF (1997) Macromol Symp 1123:147
Rashkov I, Manolova N, Li SM, Espartero JL, Vert M (1996) Macromolecules 29:50
Chen XH, McCarthy SP, Gross RA (1997) Macromolecules 30:4295
Maglio G, Migliozzi A, Palumbo R (2003) Polymer 44:369
Chon D, Hotovely-Salomon A (2005) Polymer 46:2068
Choi NS, Kim SH, Cho KY, Park JK (2002) J Appl Polym Sci 86:1892
Na YH, He Y, Shuai X, Kikkawa Y, Doi Y, Inoue Y (2002) Biomacromolecules 3:1179
Blűmm E, Owen AJ (1995) Polymer 36:4077
Zhang LL, Deng XM, Zhao SJ, Huang ZTJ (1997) Appl Polym Sci 65:1849
Focarete ML, Scandola M, Dobrzynski P, Kowalczuk M (2002) Macromolecules 35:8472
Zhang LL, Xiong CD, Deng XM (1996) Polymer 37:235
Nijenhuis AJ, Colstee E, Grijpma DW, Pennings A (1996) J Polymer 37:5849
Wang L, Ma W, Gross RA, McCarthy SP (1998) Polym Degrad Stab 59:161
Groeninckx G, Maglio G, Malinconico M, Migliozzi A (2001) Polymer 42:831
Chen CC, Chueh JY, Tseng H, Huang HM, Lee SY (2003) Biomaterials 24:2297
Gajria AM, Dave V, Gross RA (1996) Polymer 37:437
Koyama N, Doi Y (1997) Polymer 38:1589
Ohkoshi I, Abe H, Doi Y (2000) Polymer 41:5985
Park JW, Im SS (2002) J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 40:931
Park JW, Im SS (2002) J Appl Polym Sci 86:647
Yeh JT, Chai WL, Huang CY, Chen KN (2009) Appl Polym Sci 112:2757
Yeh JT, Tsou CH, Huang CH, Chen KN, Wu CS, Chai WL (2010) J Appl Polym Sci 116:680
Yeh JT, Tsou CH, Lu W, Li YM, Xiao HW, Huang CH, Chen KN, Wu CS, Chai WL (2010) J Polymer Sci: Part B: Polymer Phys 48:913
Fischer EW, Sterzel HJ, Wegner G, Kolloid ZZ (1973) Polymer 251:980
Wool RP, Raghavan D, Wagner GD, Billieux SJ (2000) Appl Polym Sci 77:1643
Goheen SM, Wool RP (1991) J Appl Polym Sci 42:2691
Rezgui F, Swistek M, Hiver JM, G’Sell C, Sadoun T (2005) Polymer 46:7370
Martin O, Averous L (2001) Polymer 42:6209
Fischer EW, Sterzel HJ, Wegner G, Koloid ZZ (1973) Polymer 251:980
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their appreciation to the Department of Industrial Technology, Ministry of Economic Affairs (95-EC-17-A-11-S1-057, 96-EC-17-A-11-S1-057, 97-EC-17-A-11-S1-057 and 99-EC-17-A-11-S1-155) and 99-2622-E-011-003-CC3 for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, Jt., Tsou, Ch., Li, Ym. et al. The compatible and mechanical properties of biodegradable poly(Lactic Acid)/ethylene glycidyl methacrylate copolymer blends. J Polym Res 19, 9766 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-011-9766-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-011-9766-4