Abstract
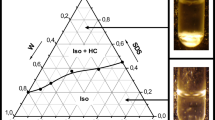
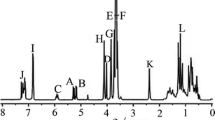
The solid-state complexes of a flexible polymer, polyacrylamide (PAA), and an amphiphilic surfactant, dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid (DBSA), have been investigated. Complexation between PAA and DBSA occurred via proton transfer from DBSA to the carbonyl group in PAA, giving rise to a “supramolecular comb-like polymer” with ionic bonding. The mesomorphic phase in the complexes was identified by the birefringent patterns under polarized optical microscopy. Wide angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) revealed that the complexes microphase separated into a lamellar morphology consisting of alternating polar and nonpolar layers with the long period of ca. 3 nm. As the composition x (the average number of DBSA molecules bound with a PAA repeating unit) ≥ 0.7, the SAXS profiles were characterized by a major scattering peak associated with the flat lamellar structure. Multiple scattering peaks were observed at lower degree of complexation (x ≤ 0.6), which were ascribed to the formation of undulated lamellae that organized into a macrolattice with the diffraction patterns observable by SAXS. Preliminary assignments of the lattice planes suggested that the lobes of the undulated lamellae organized into body centered cubic (bcc) or simple cubic (sc) types of unit cell. The glass transition temperature of the polar layers in PAA(DBSA) complexes increased with increasing degree of complexation owing to the stiffening of polymer chains. Complexation with DBSA also enhanced the thermal stability of PAA, where the thermal decomposition temperature can be raised by as much as 35 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Antonietti, J. Conrad and A. Thunemann, Macromolecules, 27, 6007(1994).
M. Antonietti, C. Burger and J. Effing, Adv. Mater., 7, 751 (1995).
O. Ikkala, J. Ruokolainen, G. ten Brinke, M. Torkkeli and R. Serimaa, Macromolecules, 28, 7088 (1995).
J. Ruokolainen, J. Tanner, G. ten Brinke, O. Ikkala, M. Torkkeli and R. Serimaa, Macromolecules, 28, 7779 (1995).
E. A. Ponomarenko, A. J. Waddon, K. N. Bakeev, D. A. Tirrell and W. J. Macknight, Macromolecules, 29, 4340 (1996).
C. K. Ober and G. Wegner, Adv. Mat., 8, 17 (1997).
J. Ruokolainen, J. Tanner, O. Ikkala, G. ten Brinke and E. L. Thomas, Macromolecules, 31, 3532(1998).
J. Ruokolainen, R. Makinen, M. Torkkeli, T. Makela, R. Serimaa, G. ten Brinke and O. Ikkala, Science, 280, 557 (1998).
S. Ujiie, S. Takagi and M. Sato, High Perform. Polym., 10, 139 (1998).
H.-L. Chen and M.-S. Hsiao, Macromolecules, 32, 2967 (1999).
G. H. Fredrickson, Macromolecules, 26, 2825 (1993).
M. Antonietti, C. Burger, M. A. Micha and M. Weissenberger, Macromol. Chem. Phys., 200, 150 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HL., Chang, MN. Supramolecular structure of the solid-state complexes of polyacrylamide and dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid. J Polym Res 6, 231–236 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-006-0092-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-006-0092-1