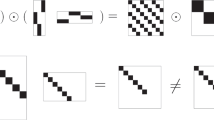Abstract
A wide class of problems involves the minimization of a coercive and differentiable function F on \({\mathbb {R}}^N\) whose gradient cannot be evaluated in an exact manner. In such context, many existing convergence results from standard gradient-based optimization literature cannot be directly applied and robustness to errors in the gradient is not necessarily guaranteed. This work is dedicated to investigating the convergence of Majorization-Minimization (MM) schemes when stochastic errors affect the gradient terms. We introduce a general stochastic optimization framework, called StochAstic suBspace majoRIzation-miNimization Algorithm SABRINA that encompasses MM quadratic schemes possibly enhanced with a subspace acceleration strategy. New asymptotical results are built for the stochastic process generated by SABRINA. Two sets of numerical experiments in the field of machine learning and image processing are presented to support our theoretical results and illustrate the good performance of SABRINA with respect to state-of-the-art gradient-based stochastic optimization methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
A preliminary version of this work has been presented in the conference proceedings [36]. The convergence result was weaker, and stated without proof. The experimental validation was limited to a single, simpler, numerical scenario.
If \(A\preceq B\) and D is a non-necessary square matrix, then \(D^\top A D \preceq D^\top B D\).
Let \(({{\varvec{z}}} _k)_{k\in {\mathbb {N}}}\) a bounded sequence of \({\mathbb {R}} ^N\), verifying \({{\varvec{z}}} _{k+1} - {{\varvec{z}}} _k \underset{k\rightarrow +\infty }{\longrightarrow } 0\). Then the set of cluster points of \(({{\varvec{z}}} _k)_{k\in {\mathbb {N}}}\) is connex.
References
Absil, P.-A., Gallivan, K.A.: Accelerated line-search and trust-region methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(2), 997–1018 (2009)
Akyildiz, Ö.D., Chouzenoux, E., Elvira, V., Míguez, J.: A probabilistic incremental proximal gradient method. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26(8), 1257–1261 (2019)
Allain, M., Idier, J., Goussard, Y.: On global and local convergence of half-quadratic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(5), 1130–1142 (2006)
Atchadé, Y.F., Fort, G., Moulines, E.: On perturbed proximal gradient algorithms. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 18, 1–33 (2017)
Bell, T., Xu, J., Zhang, S.: Method for out-of-focus camera calibration. Appl. Opt. 55(9), 2346–2352 (2016)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Nonlinear Programming, 3rd edn. Athena Scientific, Belmont, Massachusetts (2016)
Bertsekas, D.P., Tsitsiklis, J.N.: Gradient convergence in gradient methods with errors. SIAM J. Optim. 10(3), 627–642 (2000)
Bhatia, R.: Matrix Analysis, vol. 169. Springer (2013)
Bolte, J., Pauwels, E.: Majorization-minimization procedures and convergence of SQP methods for semi-algebraic and tame programs. Math. Oper. Res. 41(2), 442–465 (2016)
Bonnans, J.-F., Gilbert, J.C., Lemaréchal, C., Sagastizábal, C.A.: Numerical Optimization: Theoretical and Practical Aspects. Springer (2006)
Bordes, A., Bottou, L., Gallinari, P.: SGD-QN: careful quasi-Newton stochastic gradient descent. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 10, 1737–1754 (2009)
Bottou, L.: Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In Y. Lechevallier and G. Saporta, (eds.), Proceedings of COMPSTAT 2010, pp. 177–186. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Bottou, L., Curtis, F.E., Nocedal, J.: Optimization methods for large-scale machine learning. Siam Rev. 60(2), 223–311 (2018)
Bouchard, G.: Efficient bounds for the softmax function and applications to approximate inference in hybrid models. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2008), vol. 31. Vancouver, Canada (2008)
Briceño-Arias, L.M., Chierchia, G., Chouzenoux, E., Pesquet, J.-C.: A random block-coordinate Douglas-Rachford splitting method with low computational complexity for binary logistic regression. Comput. Optim. Appl. 72(3), 707–726 (2019)
Byrd, R.H., Hansen, S.L., Nocedal, J., Singer, Y.: A stochastic quasi-Newton method for large-scale optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 26(2), 1008–1031 (2016)
Cadoni, S., Chouzenoux, E., Pesquet, J.-C., Chaux, C.: A block parallel majorize-minimize memory gradient algorithm. In Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 2016), pp. 3194–3198. Phoenix, AZ (2016)
Candes, E.J., Wakin, M.B., Boyd, S.P.: Enhancing sparsity by reweighted \(1\) minimization. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 14(5–6), 877–905 (2008)
Castera, C., Bolte, J., Fevotte, C., Pauwels, E.: An inertial Newton algorithm for deep learning. Technical report, (2019). arxiv:1905.12278
Chalvidal, M., Chouzenoux, E.: Block distributed 3MG algorithm and its application to 3D image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 2020), pp. 938–942. Abu Dhabi, UAE (virtual) (2020)
Chang, C.-C., Lin, C.-J.: Libsvm: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2(3), 1–27 (2011)
Chouzenoux, E., Idier, J., Moussaoui, S.: A majorize-minimize strategy for subspace optimization applied to image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(6), 1517–1528 (2010)
Chouzenoux, E., Jezierska, A., Pesquet, J.-C., Talbot, H.: A majorize-minimize subspace approach for \(\ell _2-\ell _0\) image regularization. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 6(1), 563–591 (2013)
Chouzenoux, E., Pesquet, J.-C.: Convergence rate analysis of the majorize-minimize subspace algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(9), 1284–1288 (2016)
Chouzenoux, E., Pesquet, J.-C.: A stochastic majorize-minimize subspace algorithm for online penalized least squares estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65(18), 4770–4783 (2017)
Combettes, P.L., Pesquet, J.-C.: Stochastic approximations and perturbations in forward-backward splitting for monotone operators. Pure Appl. Funct. Anal. 1(1), 13–37 (2016)
Delyon, B., Lavielle, M., Moulines, E.: Convergence of a stochastic approximation version of the EM algorithm. Ann. Stat. 27(1), 94–128 (1999)
Dieuleveut, A., Durmus, A., Bach, F.: Bridging the gap between constant step size stochastic gradient descent and markov chains. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.06386, (2017)
Duchi, J., Hazan, E., Singer, Y.: Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12(7), (2011)
Dudar, V., Chierchia, G., Chouzenoux, E., Pesquet, J.-C., Semenov, V.: A two-stage subspace trust region approach for deep neural network training. In Proceedings of the 25th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2017), Kos Island, Greece (2017)
Duflo, M.: Random iterative models. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Elvira, V., Chouzenoux, E.: Optimized population Monte Carlo. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. (2022)
Ermolie, J. M., Nekrylova, Z.V.: The method of stochastic gradients and its application. In Seminar: Theory of Optimal Solutions. No. 1 (Russian)
Fehrman, B., Gess, B., Jentzen, A.: Convergence rates for the stochastic gradient descent method for non-convex objective functions. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 21, (2020)
Fernandez-Bes, J., Elvira, V., Van Vaerenbergh, S.: A probabilistic least-mean-squares filter. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2015), pp. 2199–2203, Brisbane, Australia (2015)
Fest, J.-B., Chouzenoux, E.: Stochastic majorize-minimize subspace algorithm with application to binary classification. In Proceedings of the 29th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2021), Dublin, Ireland (virtual) (2021)
Florescu, A., Chouzenoux, E., Pesquet, J.-C., Ciuciu, P., Ciochina, S.: A majorize-minimize memory gradient method for complex-valued inverse problems. Signal Process. 103, 285–295 (2014)
Gadat, S.: Stochastic optimization algorithms, non asymptotic and asymptotic behaviour. University of Toulouse (2017)
Gadat, S., Gavra, I.: Asymptotic study of stochastic adaptive algorithm in non-convex landscape. Technical report, (2021). arxiv:2012.05640
Geman, D., Yang, C.: Nonlinear image recovery with half-quadratic regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 4(7), 932–946 (1995)
Gharbi, M., Chouzenoux, E., Pesquet, J.-C., Duval, L.: GPU-based implementations of MM algorithms. Application to spectroscopy signal restoration. In Proceedings of the 29th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2021), Dublin, Ireland (2021)
Gitman, I., Lang, H., Zhang, P., Xiao, L.: Understanding the role of momentum in stochastic gradient methods. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. pp. 9633–9643. (2019)
Huang, Y., Chouzenoux, E., Elvira, V.: Probabilistic modeling and inference for sequential space-varying blur identification. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 7, 531–546 (2021)
Jacobson, M.W., Fessler, J.A.: An expanded theoretical treatment of iteration-dependent Majorize-Minimize algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(10), 2411–2422 (2007)
Kingma, D. P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. Technical report (2014). arxiv:1412.6980
Konečnỳ, J., Liu, J., Richtárik, P., Takáč, M.: Mini-batch semi-stochastic gradient descent in the proximal setting. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 10(2), 242–255 (2015)
Li, C., Chen, C., Carlson, D., Carin, L.: Preconditioned stochastic gradient langevin dynamics for deep neural networks. Technical report (2015). arxiv:1512.07666
Liu, D.C., Nocedal, J.: On the limited memory BFGS method for large scale optimization. Math. Program. 45(1), 503–528 (1989)
Loizou, N., Richtárik, P.: Momentum and stochastic momentum for stochastic gradient, newton, proximal point and subspace descent methods. Comput. Optim. Appl. 77(3), 653–710 (2020)
Mairal, J.: Stochastic majorization-minimization algorithms for large-scale optimization. Technical report (2013). arxiv:1306.4650
Marnissi, Y., Chouzenoux, E., Benazza-Benyahia, A., Pesquet, J.-C.: Majorize-minimize adapted Metropolis–Hastings algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 68, 2356–2369 (2020)
Meyer, P.-A.: Martingales and stochastic integrals I, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2006)
Miele, A., Cantrell, J.: Study on a memory gradient method for the minimization of functions. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 3(6), 459–470 (1969)
Moulines, E., Bach, F.: Non-asymptotic analysis of stochastic approximation algorithms for machine learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Systems, vol. 24, (2011)
Nesterov, Y.E.: A method for solving the convex programming problem with convergence rate \(O(1/k^2)\). Dokl. akad. nauk Sssr 269, 543–547 (1983)
Nocedal, J., Wright, S.: Numerical optimization. Springer (2006)
Ostrowski, A. N.: Solutions of equations in Euclidean and Banach spaces. Academic Press, (1973)
Pereyra, M., Schniter, P., Chouzenoux, E., Pesquet, J.-C., Tourneret, J.-Y., Hero, A.O., McLaughlin, S.: A survey of stochastic simulation and optimization methods in signal processing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 10(2), 224–241 (2015)
Repetti, A., Wiaux,Y.: A forward-backward algorithm for reweighted procedures: application to radio-astronomical imaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2020), pp. 1434–1438. (2020)
Richardson, E., Herskovitz, R., Ginsburg, B., Zibulevsky, M.: Seboost-boosting stochastic learning using subspace optimization techniques. Technical report (2016). arxiv:1609.00629
Robbins, H., Monro, S.: A stochastic approximation method. Ann. Math. Stat. pp. 400–407 (1951)
Robbins, H., Siegmund, D.: A convergence theorem for non negative almost supermartingales and some applications. In Optimizing Methods in Statistics, pp. 233–257. Academic Press, (1971)
Robini, M.C., Zhu, Y.: Generic half-quadratic optimization for image reconstruction. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 8(3), 1752–1797 (2015)
Rosasco, L., Villa, S., Vu, B.: Convergence of stochastic proximal gradient algorithm. Appl. Math. Optim. 82, 891–917 (2020)
Ruder, S.: An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms. Technical report (2016). arxiv:1609.04747
Sghaier, M., Chouzenoux, E., Pesquet, J.-C., Muller, S.: A novel task-based reconstruction approach for digital breast tomosynthesis. Med. Image Anal. 77, 102341 (2022)
Shi, Z.-J., Shen, J.: Convergence of supermemory gradient method. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 24(1), 367–376 (2007)
Sonneveld, P.: CGS: A fast Lanczos-type solver for nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 10(1), 36–52 (1989)
Sun, Y., Babu, P., Palomar, D.P.: Majorization-minimization algorithms in signal processing, communications, and machine learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65(3), 794–816 (2016)
Sutskever, I., Martens, J., Dahl, G., Hinton, G.: On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning (ICML 2013), pp. 1139–1147, Atlanta, USA (2013)
Tieleman, T., Hinton, G.: RMSProp: divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude. COURSERA Neural Netw. Mach. Learn. 4(2), 26–31 (2012)
Yuan, Y.-X.: Subspace techniques for nonlinear optimization, In R. Jeltsch, D. Li and I.H. Sloan, (eds.), Some Topics in Industrial and Applied Mathematics (Series in Contemporary Applied Mathematics CAM 8), pp. 206–218, Higher Education Press, Beijing, (2007)
Zhang, Z., Kwok, J.T., Yeung, D.-Y.: Surrogate maximization/minimization algorithms and extensions. Mach. Learn. 69, 1–33 (2007)
Zibulevsky, M.: SESOP-TN: combining sequential subspace optimization with truncated newton method. Technical report (2008). http://www.optimization-online.org/DB_FILE/2008/09/2098.pdf
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jean-Christophe Pesquet (Univ. Paris Saclay, France) and Matthieu Terris (Heriot-Watt University, UK) for initial motivations and thoughtful discussions.
Funding
This research work received funding support from the European Research Council Starting Grant MAJORIS ERC-2019-STG-850925.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by Nguyen Dong Yen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chouzenoux, E., Fest, JB. SABRINA: A Stochastic Subspace Majorization-Minimization Algorithm. J Optim Theory Appl 195, 919–952 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-022-02122-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-022-02122-y