Abstract
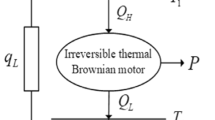
We model a Brownian heat engine as a Brownian particle that hops in a periodic ratchet potential where the ratchet potential is coupled with a linearly decreasing background temperature. We show that the efficiency of such Brownian heat engine approaches the efficiency of endoreversible engine \(\eta =1-\sqrt{{T_{c}/T_{h}}}\) [23]. On the other hand, the maximum power efficiency of the engine approaches \(\eta ^{MAX}=1-({T_{c}/T_{h}})^{1\over 4}\). It is shown that the optimized efficiency always lies between the efficiency at quasistatic limit and the efficiency at maximum power while the efficiency at maximum power is always less than the optimized efficiency since the fast motion of the particle comes at the expense of the energy cost. If the heat exchange at the boundary of the heat baths is included, we show that such a Brownian heat engine has a higher performance when acting as a refrigerator than when operating as a device subjected to a piecewise constant temperature. The role of time on the performance of the motor is also explored via numerical simulations. Our numerical results depict that the time t and the external load dictate the direction of the particle velocity. Moreover, the performance of the heat engine improves with time. At large t (steady state), the velocity, the efficiency and the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator attain their maximum value. Furthermore, we study the effect of temperature by considering a viscous friction that decreases exponentially as the background temperature increases. Our result depicts that the Brownian particle exhibits a fast unidirectional motion when the viscous friction is temperature dependent than that of constant viscous friction. Moreover, the efficiency of this motor is considerably enhanced when the viscous friction is temperature dependent. On the hand, the motor exhibits a higher performance of the refrigerator when the viscous friction is taken to be constant.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hänggi, P., Marchesoni, F., Nori, F.: Brownian motors. Ann. Phys. 14, 51 (2005). (Leipzig)
Hänggi, P., Marchesoni, F.: Artificial Brownian motors: Controlling transport on the nanoscale. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 387 (2009)
Hondou, T., Sekimoto, k: Stochastic energetics. Phys. Rev. E 62, 6021 (2000)
Marin, A.G., Sancho, J.M.: Tight coupling in thermal Brownian motors. Phys. Rev. E 74, 062102 (2006)
Li, N., Zhan, F., Hänggi, P., Li, B.: Shuttling heat across one-dimensional homogenous nonlinear lattices with a Brownian heat motor. Phys. Rev. E 80, 011125 (2009)
Li, N., Hänggi, P., Li, B.: Ratcheting heat flux against a thermal bias. Europhys. Lett. 84, 40009 (2008)
Zhan, F., Li, N., Kohler, S., Hänggi, P.: Molecular wires acting as quantum heat ratchets. Phys. Rev. E 80, 061115 (2009)
Büttiker, M.: Transport as a consequence of state-dependent diffusion. Z. Phys. B 68, 161 (1987)
van Kampen, N.G.: Relative stability in nonuniform temperature. IBM J. Res. Dev. 32, 107 (1988)
Landauer, R.: Motion out of noisy states. J. Stat. Phys. 53, 233 (1988)
Landauer, R.: Inadequacy of entropy and entropy derivatives in characterizing the steady state. Phys. Rev. A 12, 636 (1975)
Landauer, R.: Stability and relative stability in non-linear systems. Helv. Phys. Acta 56, 847 (1983)
Reimann, P., Bartussek, R., Häussler, R., Hänggi, P.: Brownian motors driven by temperature oscillations. Phys. Lett. A 215, 26 (1996)
Asfaw, M., Bekele, M.: Current, maximum power and optimized efficiency of a Brownian heat engine. Eur. Phys. J. B 38, 457 (2004)
Asfaw, M., Bekele, M.: Energetics of a simple microscopic heat engine. Phys. Rev. E 72, 056109 (2005)
Asfaw, M., Bekele, M.: Exploring the operation of a tiny heat engine. Phys. A 384, 346 (2007)
Matsuo, M., Sasa, S.: Stochastic energetics of non-uniform temperature systems. Phys. A 276, 188 (1999)
Derènyi, I., Astumian, R.D.: Efficiency of Brownian heat engines. Phys. Rev. E 59, R6219 (1999)
Derènyi, I., Bier, M., Astumian, R.D.: Generalized efficiency and its application to microscopic engines. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 903 (1999)
Sancho, J.M., Miguel, M.S., Dürr, D.: Adiabatic elimination for systems of Brownian particles with nonconstant damping coefficients. J. Stat. Phys. 28, 291 (1982)
Ai, B.Q., Xie, H.Z., Wen, D.H., Liu, X.M., Liu, L.G.: Heat flow and efficiency in a microscopic engine. Eur. Phys. J. B 48, 101 (2005)
Asfaw, M.: Effect of thermal inhomogeneity on the performance of a Brownian heat engine. Eur. Phys. J. B 86, 189 (2013)
Curzon, F.L., Ahlborn, B.: Efficiency of a Carnot engine at maximum power output. Am. J. Phys. 43, 22 (1975)
Asfaw, M.: Exact analytical thermodynamic expressions for a Brownian heat engine. Phys. Rev. E 89, 012143 (2014)
Asfaw, M., Duki, S.F.: The effect of temperature dependence of viscosity on a Brownian heat engine. Eur. Phys. J. B 88, 322 (2015)
Benjamin, R., Kawai, R.: Inertial effects in Bttiker-Landauer motor and refrigerator at the overdamped limit. Phys. Rev. E 77, 051132 (2008)
Benjamin, R.: Stochastic energetics of a Brownian motor and refrigerator driven by non-uniform temperature. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 28, 1450055 (2014)
Reineck, P.Christoph, Wienken, J., Braun, D.: Thermophoresis of single stranded DNA. Electrophoresis 31, 279 (2010)
Reynolds, O.: On the theory of lubrication and Its application to Mr. Beauchamp tower’s experiments, including an experimental determination of the viscosity of Olive Oil. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 177, 157 (1886)
Sekimoto, K.: Kinetic characterization of heat bath and the energetics of thermal ratchet models. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 66, 1234 (1997)
Sekimoto, K.: Langevin equation and thermodynamics. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 130, 17 (1998)
Matsuo, M., Sasa, Shin-ichi: Stochastic energetics of non-uniform temperature systems. Phys. A 276, 188 (2000)
Esposito, M., Lindenberg, k, Van den Broeck, C.: Universality of efficiency at maximum power. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 130602 (2009)
Sheng, S., Tu, Z.C.: Constitutive relation for nonlinear response and universality of efficiency at maximum power for tight-coupling heat engines. Phys. Rev. E 91, 022136 (2015)
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Mulu Zebene for her constant encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taye, M.A. Irreversible Brownian Heat Engine. J Stat Phys 169, 423–440 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-017-1869-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-017-1869-9