Abstract
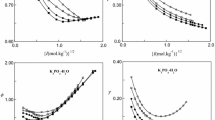
Use has been made of the Pitzer ion-interaction or virial coefficient approach to estimate the pressure dependence of the osmotic and activity coefficients of aqueous solutions of sodium nitrate (NaNO3) up to 423.15 K and 6.0 mol·kg−1 using published volumetric data on NaNO3(aq). In particular, volumetric Pitzer ion-interaction parameters have been evaluated from a mathematical fit of published apparent molar volume data with the appropriate Pitzer equation. The Pitzer parameters were then fitted as a function of temperature and pressure. These results were then used to calculate the change in the osmotic and activity coefficients in going from the state of an initial pressure p1 to one of a final pressure p2. These pressure dependences have been combined with the osmotic and activity coefficient values of NaNO3(aq) at 0.1 MPa or vapor-saturation pressures (psat) obtained from the model of Archer to yield a comprehensive set of thermodynamic parameters for NaNO3(aq) at temperatures from 293.15 K through 423.15 K, at pressures of (5, 10, 15, 20) MPa, and molalities to 6.0 mol·kg−1.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archer, D.G.: Thermodynamic properties of the NaNO3 + H2O system. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 29, 1141–1156 (2000)
Das, B., Pitzer, K.S.: Thermodynamic properties of aqueous potasium sulfate under superambient conditions. J. Solution Chem. 28, 283–289 (1999)
Das, B., Pitzer, K.S.: Thermodynamic properties of aqueous potassium fluoride under superambient conditions. J. Solution Chem. 30, 489–496 (2001)
Abdulagatov, I.M., Azizov, N.D.: Densities and apparent molar volumes of aqueous NaNO3 solutions at temperatures from 292 to 573 K and at pressures up to 30 MPa. J. Solution Chem. 32, 573–599 (2003)
Abdulagatov, I.M., Azizov, N.D.: Densities, apparent molar volumes and viscosities of concentrated aqueous NaNO3 solutions at temperatures from 298 to 607 K and pressures up to 30 MPa. J. Solution Chem. 34, 645–685 (2005)
Peña, M.P., Vercher, E., Martínez-Andreu, A.: Apparent molar volumes of potassium nitrate and sodium nitrate in ethanol + water at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 43, 626–631 (1998)
Johnson, J.W., Oelkers, E.H., Helgeson, H.C.: SUPCRT92: A Software Package for Calculating the Standard Molal Thermodynamic Properties of Minerals, Gases, Aqueous Species, Reactions from 1 to 5000 bars and 0 to 1000 °C. Laboratory of Theoretical Geochemistry, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley (1992)
Robinson, R.A., Stokes, R.H.: Electrolyte Solutions. Butterworths, London (1959)
Rogers, P.S.Z., Pitzer, K.S.: Volumetric properties of aqueous sodium chloride solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 11, 15–81 (1982)
Archer, D.G., Wang, P.: The dielectric constant of water and the Debye–Hückel limiting law slopes. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 19, 371–411 (1990)
Archer, D.G.: Thermofynamic properies of the NaBr + H2O sysyem. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 20, 509–556 (1991)
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support by Presidency University through the Faculty Research and Professional Development Fund (FRPDF) scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pramanik, S., Das, B. Thermodynamic Properties of Aqueous Sodium Nitrate Solutions Under Superambient Conditions. J Solution Chem 48, 167–179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-019-00852-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-019-00852-8