Abstract
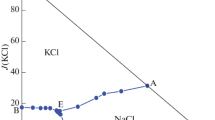
Phase equilibria of the quaternary NaCl–NaBr–Na2SO4–H2O system at 323 K were studied by the isothermal dissolution equilibrium method. The solubilities of salts and densities of saturated solutions were determined. Solid solutions [Na(Cl, Br)] were found in the experiments. The phase diagram of the quaternary system has no invariant point, but has one univariant curve at the boundary of Na(Cl, Br) and Na2SO4 crystallization fields. The experimental results show that an increase of the NaBr concentration is accompanied by an obvious increase of the solution density and the decrease of the solubilities of NaCl and Na2SO4.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, Y.T., Cao, S.X.: Rare gasfield brines rich in potassium and boron was found in the west of Sichuan Basin. Chin. Geol. (China) 28(7), 45–47 (2001)
Lin, Y.T.: Geochemical characteristics and exploitation assessment of the underground water of a gas field in Western Sichuan. Natural Gas Industry (China) 20(5), 9–14 (2000)
Harvie, C., Weare, J.H.: The prediction of mineral solubilities in natural waters: The Na–K–Mg–Ca–Cl–SO4–H2O system from zero to high concentration at 25°C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 44, 981–997 (1980)
Harvie, C., Møller, N., Weare, J.H.: The prediction of mineral solubilities in natural waters: The Na–K–Mg–Ca–H–Cl–SO4–OH–HCO3–CO3–CO2–H2O system from zero to high concentration at 25°C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 48, 723–751 (1984)
Møller, N.: The predietion of mineral solubilities in natural waters: A chemical model for the Na–Ca–Cl–SO4–H2O system, to high temperature and concentration. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 821–837 (1988)
Christov, C., Møller, N.: A chemical equilibrium model of solution behavior and solubility in the H–Na–K–Ca–OH–Cl–HSO4–SO4–H2O system to high concentration and temperature. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 68, 3717–3739 (2004)
Felmy, A.R., Weare, J.H.: The prediction of borate mineral equilibria in nature waters: application to Searles Lake. Califomia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 2271–2783 (1986)
Weng, Y.B., Wang, J.K., Yin, Q.X., Wang, Y.F.: Solid–liquid equilibria in the ternary system NaCl–NaBr–H2O. Petrochem. Tech. (China) 36(4), 358–361 (2007)
Weng, Y.B., Wang, Y.F., Wang, J.K., Yin, Q.X.: Phase diagram of the ternary system K + , Cl–, Br––H2O at 298 K, 313 K and 333 K. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. (China) 21(4), 695–698 (2007)
Tang, Z.X., Zhang, F.X., Guo, Z.Z., Huang, J.Y.: Study on the systems consisting of water and lithium and potassium halides in salt lake and bittern resources IV: the ternary systems NH4I–LiI–H2O. LiI–LiBr–H2O and NH4Br–LiBr–H2O at 298.2 K. J. Salt Lake Res. (China) 1(3), 9–12 (1993)
Sang, S.H., Yin, H.A., Ni, S.N., Zhang, C.J.: A study on the equilibrium solubilities of salts and properties of solutions in the ternary system K2B4O7–KBr–H2O at 298 K. J. Chengdu Univ. Tech. (Sci. Tech. Edition) (China) 33, 414–416 (2006)
Sang, S.H., Yu, H.Y.: Na2B4O7–NaBr–H2O—study on the phase equilibrium of Na2B4O7–NaBr–H2O ternary system at 298 K. Sea-Lake Salt. Chem. Ind. (China) 35(2), 4–6 (2006)
Sang, S.H., Sun, M.L., Li, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, K.J.: A study on the phase equilibria of the quaternary system Na+ K+//Br−SO4 2−–H2O at 323 K. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. (China) 27(5), 845–849 (2011)
Zeng, X.X., Sang, S.H., Wang, D., Zhang, J.J.: Theoretical calculation of phase equilibria in reciprocal quaternary system Na+ K+//Br− SO4 2−–H2O at 323 K. Chem. Eng. (China) 40(5), 32–35 (2012)
Sun, M.L., Sang, S.H., Li, H., Zhao, X.Y.: Study on the phase equilibria in ternary system NaBr–Na2SO4–H2O at 323 K. Chem. Eng. (China) 38(7), 67–70 (2010)
Wang, D., Sang, S.H., Zeng, X.X., Ning, H.Y.: The phase equilibria of quaternary system KCl–KBr–K2SO4–H2O at 323 K. Petrochem. Tech. (China) 40(3), 285–288 (2011)
Ning, H.Y., Sang, S.H., Wang, D., Zeng, X.X.: Study on the phase equilibria in quaternary system NaB4O7–NaBr–Na2SO4–H2O at 348 K. Chem. Eng. (China) 40(4), 27–30 (2012)
Christov, C.: An isopiestic study of aqueous NaBr and KBr at 50°C: chemical equilibrium model of solution behavior and solubility in the NaBr–H2O, KBr–H2O and Na–K–Br–H2O systems to high concentration and temperature. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 71, 3557–3569 (2007)
Christov, C.: Isopiestic investigation of the osmotic coefficients of MgBr2(aq) and study of bromide salts solubility in the (m 1KBr + m 2MgBr2)(aq) system at T = 323.15 K. Thermodynamic model of solution behaviour and (solid + liquid) equilibria in the MgBr2(aq), and (m 1KBr + m 2MgBr2)(aq) systems to high concentration and temperature. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 43, 344–353 (2011)
Christov, C.: Temperature variable chemical model of bromide–sulfate solution interaction parameters and solid–liquid equilibria in the Na–K–Ca–Br–SO4–H2O system. CALPHAD 36, 71–81 (2012)
Christov, C.: Study of bromide salts solubility in the (m 1NaBr + m 2MgBr2)(aq) system at T = 323.15 K, Thermodynamic model of solution behavior and solid–liquid equilibria in the (Na + K + Mg + Br + H2O) system to high concentration and temperature. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 47, 335–340 (2012)
Christov, C.: Isopiestic investigation of the osmotic coefficients of aqueous CaBr2 and study of bromide salt solubility in the NaBr–CaBr2–H2O system at 50 °C: Thermodynamic model of solution behavior and solid–liquid equilibria in the CaBr2–H2O, and NaBr–CaBr2–H2O systems to high concentration and temperature. CALPHAD 35, 42–53 (2011)
Christov, C.: Study of bromide salts solubility in the (m 1KBr + m 2CaBr2)(aq) system at T = 323.15 K. Thermodynamic model of solution behaviour and (solid + liquid) equilibria in the ternaries (m 1KBr + m 2CaBr2)(aq), and (m 1MgBr2 + m 2CaBr2)(aq), and in the quinary (Na + K + Mg + Ca + Br + H2O) systems to high concentration and temperature. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 55, 7–22 (2012)
Silcock., H.L.: Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds, Ternary and Multicomponent Systems of Inorganic Substances, Vol. 3 (Part 2), pp. 1051–1055. Oxford Pergamon Press, UK (1979)
Acknowledgments
We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions. This work was supported by Open Funds (PLC201001, PLC201204) of State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation (Chengdu University of Technology), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40973047, 41172118), the Specialized Research Fund (20125122110015) for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China, and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, China (D2012403010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sang, SH., Cui, RZ., Hu, JW. et al. Measurements of the Solid–Liquid Equilibria in the Quaternary System NaCl–NaBr–Na2SO4–H2O at 323 K. J Solution Chem 42, 1633–1640 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-013-0061-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-013-0061-3