Abstract
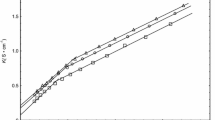
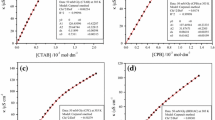
The power-time curves of the micelle formation process were determined at four temperatures for a cationic surfactant [cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB)] in a non-aqueous solvent [N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF)] by titration microcalorimetry. From the data of the minimum of the titration point and the area of the power-time curves, values of their CMC and ΔH θm were obtained. Values of ΔG θm and ΔS θm were also calculated according to standard thermodynamic relations. For the cationic surfactant CTAB, the relationships involving the carbon numbers of the alcohols, the alcohol’s concentration, and the temperature on the CMC, and also the thermodynamic functions for micellization are discussed. For systems containing an identical concentration of various alcohols, values of the CMC, ΔH θm and ΔS θm increased whereas those of ΔG θm decreased with increasing temperature. For systems containing identical alcohol concentrations at the same constant temperature, values of the CMC, ΔH θm ,ΔG θm and ΔS θm decreased with increasing carbon number of the alcohol. For systems containing the same alcohol at the same temperature, the CMC and ΔG θm values increased whereas ΔH θm and ΔS θm decreased with increasing alcohol concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evans, D.F., Miller, D.D.: Organized Solutions, pp. 33–45. Marcel Dekker, New York (1992)
Nakano, T., Sugihara, G., Nakashima, T., Yu, S.: Thermodynamic study of mixed hydrocarbon/fluorocarbon surfactant system by conductometric and fluorimetric techniques. Langmuir 18, 8777–8785 (2002). doi:10.1021/la020370w
Wang, X., Li, Y., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Ye, J., Yan, H.: Interaction of cationic Gemini surfactants with hydrophobically modified poly(acrylamides) studied by fluorescence and microcalorimetry. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 12850–12855 (2005). doi:10.1021/jp050651n
Li, Y., Reeve, J., Wang, Y., Thomas, R.K., Wang, J., Yan, H.: Microcalorimeitric study on micellization of nonionic surfactants with a benzene ring or adamntane in their hydrophobic chains. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 16070–16074 (2005). doi:10.1021/jp0523874
Akhter, M.S.: Effect of solubilization of alcohols on critical micelle concentration of non-aqueous micelle solution. Colloids Surf. A, Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 157, 203–210 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0927-7757(99)00089-8
Akhter, M.S., Sadeq, M., Lawi, A.: Influence of alcohols on the critical micelle concentration of non-aqueous micelle solution. Colloids Surf. A, Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 164, 247–255 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0927-7757(99)00341-6
Akhter, M.S., Sadeq, M., Lawi, A.: The effect of organic additives on critical micelle concentration of non-aqueous micelle solution. Colloids Surf. A, Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 175, 311–320 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0927-7757(00)00671-3
Liu, H., Lin, R., Zhang, H.: Enthalpic interactions of amino acids with glucose aqueous solutions at 298.15 K. J. Solution Chem. 32, 977–985 (2003). doi:10.1023/B:JOSL.0000017062.76672.4a
Liu, H., Lin, R., Zhang, H.: Enthalpies of dilution and enthalpies of mixing of amino-acids with sucrose in aqueous solution at 298.15 K. J. Solution Chem. 35, 679–688 (2006). doi:10.1007/s10953-006-9018-0
Zhang, H.-L., Kong, Z., Yan, Y.-M., Li, G.-Z., Yu, L.: Microcalorimetric study of the influence of alcohols on the critical micelle concentration and thermodynamic functions of non-aqueous micelle solutions at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 53, 327–330 (2008). doi:10.1021/je700195r
Xiu-Fang, Y., Wu, L.-L., Zhang, H.-L.: Microcalorimetric study on the formation of reversed micelle in P 204Li organic phase. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 3, 263–266 (2000)
Myers, D.: Surfaces, Interface, and Colloids: Principles and Application, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (1999)
Li, G.-Z., Rong, G.: Theory of Latex Emulsion and Application, pp. 81–86. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (1995)
Attwood, D., Florence, A.T.: Surfactant systems—Their Chemistry, Pharmacy and Biology, pp. 105–117. Chapman and Hall, London (1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Hl., Zhu, Y., Zhang, K. et al. Studies on the CMC and Thermodynamic Functions of a Cationic Surfactant in DMF/Long-Chain Alcohol Systems Using a Microcalorimetric Method. J Solution Chem 38, 187–198 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-008-9365-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-008-9365-0