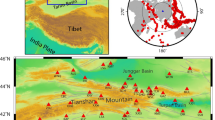
Abstract
Variations in crustal thickness in the Zagros determined by joint inversion of P wave receiver functions (RFs) and Rayleigh wave group and phase velocity dispersion. The time domain iterative deconvolution procedure was employed to compute RFs from teleseismic recordings at seven broadband stations of INSN network. Rayleigh wave phase velocity dispersion curves were estimated employing two-station method. Fundamental mode Rayleigh wave group velocities for each station is taken from a regional scale surface wave tomographic imaging. The main variations in crustal thickness that we observe are between stations located in the Zagros fold and thrust belt with those located in the Sanandaj–Sirjan zone (SSZ) and Urumieh–Dokhtar magmatic assemblage (UDMA). Our results indicate that the average crustal thickness beneath the Zagros Mountain Range varies from ∼46 km in Western and Central Zagros beneath SHGR and GHIR up to ∼50 km beneath BNDS located in easternmost of the Zagros. Toward NE, we observe an increase in Moho depth where it reaches ∼58 km beneath SNGE located in the SSZ. Average crustal thickness also varies beneath the UDMA from ∼50 km in western parts below ASAO to ∼58 in central parts below NASN. The observed variation along the SSZ and UDMA may be associated to ongoing slab steepening or break off in the NW Zagros, comparing under thrusting of the Arabian plate beneath Central Zagros. The results show that in Central Iran, the crustal thickness decrease again to ∼47 km below KRBR. There is not a significant crustal thickness difference along the Zagros fold and thrust belt. We found the same crystalline crust of ∼34 km thick beneath the different parts of the Zagros fold and thrust belt. The similarity of crustal structure suggests that the crust of the Zagros fold and thrust belt was uniform before subsidence and deposition of the sediments. Our results confirm that the shortening of the western and eastern parts of the Zagros basement is small and has only started recently.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbassi A, Nasrabadi A, Tatar M, Yamini-Fard F, Abbassi MR, Hatzfeld D, Priestley K (2010) Crustal velocity structure in the southern edge of the Central Alborz (Iran). J Geodyn 49:68–78
Afsari N, Sodoudi F, TaghizadehFarahmand F, Ghassemi MR (2011) Crustal structure of Northwest Zagros (Kermanshah) and Central Iran (Yazd and Isfahan) using teleseismic Ps converted phases. J Seismol 15(2):341–353
Agard P, Omrani J, Jolivet L, Mouthereau F (2005) Convergence history across Zagros (Iran): constraints from collisional and earlier deformation. Int J Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s00531-005-0481-4
Agard P, Omrani J, Jolivet L, Whitechurch H, Vrielynck B, Spakman W, Monié P, Meyer B, Wortel R (2011) Zagros orogeny: a subduction-dominated process. In: Lacombe O, Grasemann B, Simpson G (eds) Geodynamic Evolution of the Zagros. Geol Mag 692–725
Aki K, Richard PG (2002) Quantitative Seismology. Freeman, San Francisco
Alavi M (1994) Tectonics of the Zagros orogenic belt of Iran: new data and interpretations. Tectonophysics 229:211–238
Alavi M (2004) Regional stratigraphy of the Zagros fold-thrust belt of Iran and its proforeland evolution. Am J Sci 304:1–20
Allen M., Jackson JA, Walker R., 2004. Late Cenozoic reorganization of the Arabia–Eurasia collision and the comparison of short-term and long-term deformation rates. Tectonics 23. doi:10.1029/2003TC001530.
Ammon GJ (1991) The isolation of receiver effects from teleseismic P waveforms. Bull Seismol Soc Am 81:2504–2510
Ammon CJ, Randall GE, Zandt G (1990) On the non-uniqueness of receiver function inversions. J Geophys Res 95:15303–15318
Berberian F, Berberian M (1981) Tectonoplutonic episodes in Iran. In: Gupta HK, Delany FM (eds) Zagros–Hindu Kush–Himalaya Geodynamic Evolution. American Geophysical Union, Washington, pp 5–32
Berberian M, King GCP (1981) Towards a paleogeography and tectonic evolution of Iran. Can J Earth Sci 18
Berberian F, Muir ID, Pankhurst RJ, Berberian M (1982) Late Cretaceous and early Miocene Andean-type plutonic activity in Northern Makran and Central Iran. J Geol Soc Lond 139:605–614
Bird P (1978) Finite element modeling of lithosphere deformation: the Zagros collision orogeny. Tectonophysics 50:307–336
Bird P, Toksoz MN, Sleep NH (1975) Thermal and mechanical models of continent–continent convergence zones. J Geophys Res 32:4405–4416
Chang SJ, van der Lee S, Flanagan MP, Bedle H, Marone F, Matzel EM, Pasyanos ME, Rodgers AJ, Romanowicz B, Schmid C (2010) Joint inversion for three-dimensional S velocity mantle structure along the Tethyan margin. J Geophys Res 115, B08309. doi:10.1029/2009jb007204
Davoudzadeh M, Lammerer B, Weber-Diefenbach K (1997) Paleogeography, stratigraphy, and tectonics of the tertiary of Iran, Neues Jahrb. Geol Palaeontol Abh 205:33–67
Dehghani GA, Makris J (1984) The gravity field and crustal structure of Iran. N Jb Geol Palaontol Agh 168:215–229
Engdahl ER, Jackson JA, Myers SC, Bergman EA, Priestley K (2006) Relocation and assessment of seismicity in the Iran region. Geophys J Int 167:761–778
Giese P, Makris J, Akashe B, Rower P, Letz H, Mostaanpour M (1983) Seismic crustal studies in southern Iran between the Central Iran and Zagros belt. Geol Surv Iran 51:71–89
Golonka J (2004) Plate tectonic evolution of the southern margin of Eurasia in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic. Tectonophysics 381:235–273
Hatzfeld D, Tatar M, Priestley K, Ghafory-Ashtiany M (2003) Seismological constraints on the crustal structure beneath the Zagros Mountain belt (Iran). Geophys J Int 155:403–410
Hatzfeld D, Authemayou C, van der Beek P, Bellier O, LAVE’ J, Oveisi B, Tatar M, Tavakoli F, Walpersdorf A, Yamini-Fard F (2010) The kinematics of the Zagros Mountains (Iran). Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 330:19–42
Herrin E, Goforth T (1977) Phase-matched filters: application to the study of Rayleigh waves. Bull Seismol Soc Am 67:1259–1275
Herrmann RB, Ammon CJ (2003) Computer programs in seismology, Version 3.20, Surface waves, Receiver functions and Crustal structure, Saint Louis University, Penn State University
Jackson JA (1980) Reactivation of basement faults and crustal shortening in orogenic belts. Nature 283:343–346
Jackson J, McKenzie D (1984) Active tectonics of the Alpine–Himalayan Belt between western Turkey and Pakistan. Geophys J Roy Astron Soc 77:185–264
Julia J, Ammon CJ, Herrmann RB, Correig AM (2000) Joint inversion of receiver function and surface-wave dispersion observations. Geophys J Int 143:99–112
Langston CA (1979) Structure under Mount Rainier, Washington. The inferred from teleseismic body waves. J Geophys Res 84:4749–4762
Levshin AL, Ratnikova L, Berger J (1992) Peculiarities of surface-wave propagation across Central Eurasia. Bull Seismol Soc Am 82:2464–2493
Ligorria JP, Ammon CJ (1999) Iterative deconvolution and receiver function estimation. Bull Seismol Soc Am 89:1395–1400
Maggi A, Jackson JA, Priestley K, Baker C (2000) A reassessment of focal depth distributions in southern Iran, the Tien Shan, and northern India: Do earthquakes really occur in the continental mantle? Geophys J Int 143:629–661
Moghadam HS, Stern RJ, Rahgoshay M (2010) The Dehshir ophiolite (central Iran): geochemical constraints on the origin and evolution of the Inner Zagros ophiolite belt. Geol Soc Am Bull 122(9–10):1516–1547. doi:10.1130/ b30066.1
Molinaro M, Zeyen H, Laurencin X (2005) Lithospheric structure beneath the south-eastern Zagros Mountains, Iran: recent slab break-off? Terra Nova 17:1–6
Mouthereau F, Lacombe O, Vergés J (2012) Building the Zagros collisional orogen: timing, strain distribution, and the dynamics of Arabia/Eurasia plate convergence. Tectonophysics 532–535:27–60
Ni J, Barazangi M (1986) Seismotectonics of the Zagros continental collision zone and a comparison with the Himilayas. J Geophys Res 91(B8):8205–8218
Ozalaybey S, Savage MK, Sheehan AF, Louie JN, Brune JN (1997) Shear-wave velocity structure in the northern basin and range province from the combined analysis of receiver functions and surface waves. Bull Seismol Soc Am 87:183–199
Paul A, Kaviani A, Hatzfeld D, Vergne J, Mokhtari M (2006) Seismological evidence for crustal-scale thrusting in the Zagros mountain belt (Iran). Geophys J Int 166:227–237
Paul A, Kaviani A, Hatzfeld D, Tatar M, Priestley K (2010) Seismic imaging of thelithospheric structure of the Zagros Mountain belt (Iran). J Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 330:5–18
Pedersen HA, Coutant O, Deschamps A, Soulage M, Cotte N (2003) Measuring surface wave phase velocities beneath smallbroad-band arrays: tests of an improved algorithmand application to the French Alps. Geophys J Int 154:903–912
Rapine R, Tilmann F, West M, Ni J (2003) Crustal structure of Northern and Southern Tibet from surface wave dispersion analysis. J Geophys Res 108:doi: 10.1029/2001JB000445
Rham D (2009) The crustal structure of the Middle East.Ph.D. thesis, University of Cambridge Library, Cambridge, UK
Shapiro NM, Singh SK (1999) A systematic error in estimating surface wave group-velocity dispersion curves and a procedure for its correction. Bull Seismol Soc Am 89:1138–1142
Simmons NA, Myers SC, Johannesson G (2011) Global-scale P wave tomography optimized for prediction of teleseismic and regional travel times for Middle East events: 2. Tomographic inversion. J Geophys Res 116: (B04305). doi:10.1029/2010jb007969
Snyder DB, Barazangi M (1986) Deep crustal structure and flexure of the Arabian Plate beneath the Zagros collisional mountain belt as inferred from gravity observations. Tectonics 5:361–373
Stocklin J (1968) Structural history and tectonics of Iran: a review. Am Assoc Petrol Geol Bull 52:1229–1258
Stöcklin J (1974) Possible ancient continental margins in Iran. In: Burke C and Drake C (eds) Geology of Continental Margins. New York, 873–877
Stoneley R (1981) The geology of the Kuh-e Dalneshin area of Southern Iran, and its bearing on the evolution of Southern Tethys. J Geol Soc Lond 138:509–526
Tatar M, Hatzfeld D, Ghafory-Ashtiany M (2004) Tectonics of the Central Zagros (Iran) deduced from microearthquakes seismicity. Geophys J Int 156:255–266
Tatar M, Hatzfeld D, Moradi AS, Paul A (2005) The 2003 December 26 Bam earthquake (Iran), Mw 6.6, aftershock sequence. Geophys J Int 163:90–105
Tezel T, Erduran M, Alptekin O (2007) Crustal shear wave velocity structure of Turkey by surface wave dispersion analysis. Ann Geophys 50:177–190
Vergés J, Goodarzi MH, Emami H, Karpuz R, Efstatiou J, Gillespie P (2011) Multiple detachment folding in Pusht-e Kuh Arc, Zagros. Role of mechanical stratigraphy. In: McClay, K., Shaw, J., Suppe, J. (eds) Thrust Fault Related Folding: AAPG Memoir, 94: 69–94. Chapter 4
Vernant P, Nilforoushan F, Hatzfeld D, Abbassi M, Vigny C, Masson F, Nankali H, Martinod J, Ashtiani A, Bayer R, Tavakoli F, Chery J (2004) Present-day crustal deformation and plate kinematics in the Middle East constrained by GPS measurements in Iran and northern Oman. Geophys J Int 157:381–398
Walker RT, Andalibi MJ, Gheitanchi MR, Jackson JA, Karegar S, Priestley K (2005) Seismological and field observations from the 1990 November 6 Furg (Hormozgan) earthquake: a rare case of surface rupture in the Zagros Mountains of Iran. Geophys J Int 163:567–579. doi:10.1111/ j.1365-246X.2005.02731.x
Walpersdorf A et al (2006) Difference in the GPS deformation pattern of North and Central Zagros (Iran). Geophys J Int 167:1077–1088. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03147.x
Wessel P, Smith W (1995) New version of the Generic Mapping Tool release. Eos Trans AGU 76:329
Wiener N (1949) Extrapolation, Interpolation, and Smoothing of Stationary Time Series. Wiley, New York
Yamini-Fard F, Hatzfeld D, Tatar M, Mokhtari M (2006) Microearthquake seismicity at the intersection between the Kazerun fault and the Main Recent Fault (Zagros, Iran). Geophys J Int 166:186–196. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.02891.x
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Iranian National Seismic Network (INSN) for kindly providing the teleseismic recordings of their broadband stations. This research is supported by the International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IIEES) under research project 5327 entitled “Lithosphere structure of Iranian plateau using receiver functions and surface waves analysis”. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions and comments. We used the computer programs in seismology (Herrmann and Ammon 2003) for data processing and GMT(Wessel and Smith, 1995) for plotting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatar, M., Nasrabadi, A. Crustal thickness variations in the Zagros continental collision zone (Iran) from joint inversion of receiver functions and surface wave dispersion. J Seismol 17, 1321–1337 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-013-9394-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-013-9394-z