Abstract
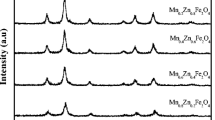
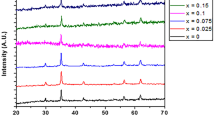
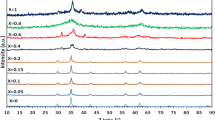
Fe2+-doped manganese ferrite (Mn1−xFexFe2O4, where x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, and 0.6) nanoparticles were synthesized using the co-precipitation method. The structural, morphological, and magnetic properties of the nanoparticles were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy analysis (FESEM), and the vibration sample magnetometer (VSM). The crystallite size and lattice parameter of the samples decreased by increasing the Fe2+-doping concentrations. FESEM study showed the formation of highly agglomerated and isotropic nanoparticles with doping. VSM data revealed the superparamagnetic behavior of nanoparticles with doping. A variation in the saturation magnetization was found; this is directly proportional to the amount of doping for x > 0.2. Low-temperature magnetization studies were carried out at 5 K, revealing an increase in the value of magnetization as well as coercivity due to the freezing of magnetic moments. These results revealedthat the synthesized nanoparticle has different particle sizes and magnetic properties. These nanoparticles have the potential to use in biomedical applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Gao, L., Liu, Z., Yang, Z., Cao, L., Feng, C., Chu, M., Tang, J.: Synthesis and magnetism property of manganese ferrite MnFe2O4 by selective reduction and oxidization roasting process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 508, 145292 (2020)
Akhlaghi, N., Najafpour-Darzi, G.: Manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles: from synthesis to application-a review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 103, 292–304 (2021)
Verma, M., Kumar, A., Singh, K.P., Kumar, R., Kumar, V., Srivastava, C.M., et al.: Graphene oxide-manganese ferrite (GO-MnFe2O4) nanocomposite: one-pot hydrothermal synthesis and its use for adsorptive removal of Pb2+ ions from aqueous medium. J. Mol. Liq. 315, 113769 (2020)
Prado, L.D.L., Hernández, D.C., Bocardo, J.E., López, G.H.: Influence of the heat treatment conditions on the properties of gallium-strontium-substituted manganese ferrites designed for magnetic hyperthermia applications. Ceram. Int. 47(5), 7069–7080 (2021)
Díez-Villares, S., Ramos-Docampo, M.A., da Silva-Candal, A., et al.: Manganese ferrite nanoparticles encapsulated into vitamin E/Sphingomyelin nanoemulsions as contrast agents for high-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 10(21), 2101019 (2021)
Li, Y.K., Cheng, L., Zhang, X.D., Guo, X.: Hierarchically-structured MnFe2O4 nanospheres for highly sensitive detection of NO2. Solid State Ion. 336, 102–109 (2019)
Gürbüz, M.U., Elmacı, G., Ertürk, A.S.: In situ deposition of silver nanoparticles on polydopamine-coated manganese ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and application to the degradation of organic dye pollutants as an efficient magnetically recyclable nanocatalyst. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 35(8), e6284 (2021)
Nonaka, L.H., Almeida, T.S., Aquino, C.B., Domingues, S.H., Salvatierra, R., Souza, V.H.: Crumpled graphene decorated with manganese ferrite nanoparticles for hydrogen peroxide sensing and electrochemical supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3(5), 4859–4869 (2020)
Xiao, Y., Du, J.: Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 8(3), 354–367 (2020)
Islam, K., Haque, M., Kumar, A., et al.: Manganese ferrite nanoparticles (MnFe2O4): size dependence for hyperthermia and negative/positive contrast enhancement in MRI. Nanomaterials 10, 2297 (2020)
Kittel, C.: Introduction to Solid State Physics, Wiley, 7th edition (1995)
Carta, D., Casula, M.F., Mountjoy, G., et al.: Formation and cation distribution in supported manganese ferrite nanoparticles: an X-ray absorption study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10, 3108–3117 (2008)
Arshad, M., Asghar, M., Junaid, M., Warsi, M.F., et al.: Structural and magnetic properties variation of manganese ferrites via Co-Ni substitution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 474, 98–103 (2019)
Rezaei, M., Mirkazemi, S.M., Alamolhoda, S.: The role of PVA surfactant on magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel hydrothermal method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 34, 1397–1408 (2021)
Liu, G., Dai, B., Ren, Y., Zhang, W.: Rapid synthesis and characterization of spinel manganese ferrite nanopowder by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. Results Phys. 26, (2021)
Yousuf, M.A., Baig, M.M., Waseem, M., et al.: Low cost micro-emulsion route synthesis of Cr-substituted MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 45, 22316–22323 (2019)
Singh, G., Sudeshna Chandra, S.: Electrochemical performance of MnFe2O4 nano-ferrites synthesized using thermal decomposition method. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 43, 4058–4066 (2018)
Almahri, A.: The solid-state synthetic performance of bentonite stacked manganese ferrite nanoparticles: adsorption and photo-Fenton degradation of MB dye and antibacterial applications. J. Market. Res. 17, 2935–2949 (2022)
Debnath, S., Deb, K., Saha, B., et al.: X-ray diffraction analysis for the determination of elastic properties of zinc-doped manganese spinel ferrite nanocrystals (Mn0.75Zn0.25Fe2O4), along with the determination of ionic radii, bond lengths, and hopping lengths. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 134, 105–114 (2019)
Kumar, D.R., Lincoln, C.A., Ravinder, D., et al.: Structural, morphological, luminescence, magnetic, and electrical transport properties of zinc-doped MnFe2O4 nanomaterials. Appl. Phys. A 126, 705 (2020)
Noor, A., Akhtar, M.N., Khan, S.N., et al.: Synthesis, morphological and electromagnetic evaluations of Ca doped Mn spinel nanoferrites for GHz regime applications. Ceram. Int. 46, 13961–13968 (2020)
Naik, A.B., Naik, P.P., Hasolkar, S.S., et al.: Structural, magnetic and electrical properties along with antifungal activity & adsorption ability of cobalt doped manganese ferrite nanoparticles synthesized using combustion route. Ceram. Int. 46, 21046–21055 (2020)
Deshmukh, V.V, Nagaswarupa, H.P., Raghavendra, N.: Development of Co-doped MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for electrochemical supercapacitors. Ceram. Int. 46, 10268–10273 (2021)
Sun, Y., Zhou, J., Dan Liu, D., et al.: Enhanced catalytic performance of Cu-doped MnFe2O4 magnetic ferrites: tetracycline hydrochloride attacked by superoxide radicals efficiently in a strong alkaline environment. Chemosphere 297, 134154 (2022)
Al-Mokdad, F., Sayed Hassan, R., Awad, R.: Physical and dielectric properties of MnFe2O4 doped by Mo. Curr. Nanomater. 4, 125–136 (2019)
Sinha, A., Abhigyan Dutta, A.: Structural, optical, and electrical transport properties of some rare-earth- doped nickel ferrites: a study on effect of ionic radii of dopants. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 145, 109534 (2020)
Karaagac, O., Köçkar, H.: The effects of temperature and reaction time on the formation of manganese ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 2567–2574 (2020)
Patterson, L.: The Scherrer formula for X-Ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56, 979–982 (1939)
Jain, R., Luthra, V., Gokhale, G.: Probing influence of rare earth ions (Er3+, Dy3+ and Gd3+) on structural, magnetic and optical properties of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 456, 179–185 (2018)
Ikram, S., Jacob, J., Mehboob, K., et al.: Role of rare earth metal ions doping on structural, electrical, magnetic, and dielectric behavior of spinel ferrites: a comparative study. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 34, 1833–1842 (2021)
Ghosh, M.P., Sharma, S., Harendra Kumar Satyapal, H.K., et al.: Tuning the microstructural, optical and superexchange interactions with rare earth Eu doping in nickel ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 241, 122383 (2020)
Can, Wu., C., Xu, Y., Xu, S., et al.: Enhanced adsorption of arsenate by spinel zinc ferrite nano particles: effect of zinc content and site occupation. J. Environ. Sci. 79, 248–255 (2019)
Nakai, T., Toba, K., Yamamoto, H., et al.: Creep and stress relaxation behaviour for natural cellulose crystal of wood cell wall under uniaxial tensile stress in the fiber direction. J. Wood Sci. 64, 745–750 (2018)
Anita Luthra, V.: Tweaking electrical and magnetic properties of Al–Ni co-doped ZnO nanopowders. Ceram. Int. 40, 14927–14932 (2014)
Rueden, C. T., Schindelin, J., Hiner, M.C., et al.: ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. Rueden et al. BMC Bioinformat. 18, 529 (2017)
Sharma, R., Thakur, P., Kumar, M., et al.: Enhancement in A-B super-exchange interaction with Mn2+ substitution in Mg-Zn ferrites as a heating source in hyperthermia applications. Ceram. Int. 43, 13661–13669 (2017)
Ansari, M.M.N., Khan, S., Ahmad, N.: Effect of R3+ (R = Pr, Nd, Eu and Gd) substitution on the structural, electrical, magnetic and optical properties of Mn-ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 465, 81–87 (2018)
Kombaiah, K., Vijaya, J.J., Kennedy, L.J., et al.: A green approach: synthesis, characterization and opto-magnetic properties of MgxMn1−xFe2O4 spinel nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 10321–10329 (2017)
Kadam, A.B., Mande, V.K., Kadam, S.B., et al.: Influence of gadolinium (Gd3+) ion substitution on structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of cobalt ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 840, 55669 (2020)
Anu, K., Hemalatha, J.: Magnetic and electrical conductivity studies of zinc doped cobalt ferrite nanofluids. J. Mol. Liq. 284, 445–453 (2019)
Moyer, J.A., Vaz, C.A.F., Arena, D.A., et al.: Magnetic structure of Fe-doped CoFe2O4 probed by x-ray magnetic spectroscopies. Phys. Rev. B 84, 054447 (2011)
Panda, R.K., Muduli, R., Jayarao, G., et al.: Effect of Cr3+ substitution on electric and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 669, 19–28 (2016)
Jain, R., Luthra, V., Gokhale, S.: Dysprosium doping induced shape and magnetic anisotropy of Fe3-xDyxO4 (x=0.01–0.1) nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 414, 111–115 (2016)
Abraime, B., Mahmoud, A. , Boschini, F., et al.: Tunable maximum energy product in CoFe2O4 nanopowder for permanent magnet application. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 467, 129–134.40 (2018)
Icten, O., Erdem Tundemir, B., Tuncdemir, Mergen, H.: Design and development of gold-loaded and boron-attached multicore manganese ferrite nanoparticles as a potential agent in biomedical applications. ACS Omega 7, 20195–20203 (2022)
Batoo, K.M., Raslan, E.H., Yang, Y., et al.: Structural, dielectric and low temperature magnetic response of Zn doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. AIP Adv. 9, 055202 (2019)
Abdellatif-Youssef, M., Etter, M., Fromme, P., et al.: Extended properties of magnetic spins of zinc ferrite nanoparticles in the THz frequency range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 525, 167574 (2021)
Aslibeiki, B.: Nanostructural, magnetic and electrical properties of Ag doped Mn-ferrite nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 14, 1659–1664 (2014)
Poudel, T.P., Rai, B.K., Yoon, S., et al.: The effect of gadolinium substitution in inverse spinel nickel ferrite: structural, magnetic, and Mössbauer study. J. Alloy. Compd. 802, 609–619 (2019)
Kozlovskiy, A.L., Zdorovets, M.V.: Effect of doping of Ce4+/3+ on optical, strength and shielding properties of (0.5-x)TeO2–0.25MoO-0.25Bi2O3-xCeO2 glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 263, 124444 (2021)
Zeb, F., Shoaib Khan, M., Nadeem, K., et al.: Reduced surface spin disorder in ZrO2 coated γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 284–286, 69–74 (2018)
Abraime, B., Mahmoud, A., Boschini, F., et al.: Tunable maximum energy product in CoFe2O4 nanopowder for permanent magnet application. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 467, 129–134 (2018)
Noshahi, N.A., Nadeem, K., Kamran, M.: Role of Mn doping on magnetic properties of multiferroic NiCr2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 47, 10643–10649 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Sudha Gulati: conceptualization, synthesis, analysis, and review. Dr. Richa Jain: investigation, analysis, writing, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gulati, S., Jain, R. Structural, Morphological, and Magnetic Properties of Fe2+-Substituted Mn Ferrite Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. J Supercond Nov Magn 36, 1373–1383 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-023-06570-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-023-06570-z