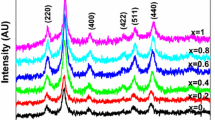
Abstract
In this work, solid solutions of Mn1−x Zn x Fe2O4 (where x = 0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, and 1.0) ferrite nanoparticles were synthesized using the novel combustion method. A powder X-ray diffraction study confirms the formation of spinel-structured Mn1−x Zn x Fe2O4. Unusual increases in the lattice constant were observed from 8.358 to 8.435 Å for Zn substitution. Raman spectra show the change in local environment of tetrahedral and octahedral symmetry. Field emission scanning electron microscopy images show that the prepared samples are nanosized and there is not much difference observed in surface morphology. A magnetic study reveals that the prepared samples exhibit superparamagnetic properties with negligible coercivity and the saturation magnetizations initially increase from 31.12 emu g−1 (x = 0) to 35.48 emu g−1 (x = 0.2) and then decrease for further Zn substitution at 300 K. The zero-field-cooled and field-cooled magnetization studies confirm the superparamagnetic nature of prepared samples, and the observed blocking temperature decreases from 146.05 to 32.3 K. At 20 K, the measured hysteresis loop shows the coercivity and it gradually decreases from 810 to 152 Oe. The obtained results suggest that the prepared superparamagnetic Mn1−x Zn x Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles are a promising candidate material for biomedical applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
17 February 2018
The original article requires minor corrections.
References
Standley, K.J.: Oxide Magnetic Materials. Oxford University Press (1972)
Dionne, G.F.: Magnetic Oxides. Springer (2009)
Goldman, A.: Modern Ferrite Technology. Springer Science & Business Media (2006)
Corot, C., Robert, P., Idée, J.-M., Port, M.: Recent advances in iron oxide nanocrystal technology for medical imaging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 58, 1471–1504 (2006)
Valenzuela, R.: Novel applications of ferrites. Physiother Res Int, 2012 (2012)
Cullity, B.D., Graham, C.D.: Introduction to Magnetic Materials. Wiley (2011)
Snoek, J.L.: New Developments in Ferromagnetic Materials. Elsevier Publishing Company (1949)
Agrafiotis, C., Zaspalis, V.: Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of MnZn-ferrites for inductor applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 283, 364–374 (2004)
Arshak, K., Ajina, A., Egan, D.: Development of screen-printed polymer thick film planner transformer using Mn–Zn ferrite as core material. Microelectron. J. 32, 113–116 (2001)
Waqas, H., Qureshi, A.: Influence of pH on nanosized Mn–Zn ferrite synthesized by sol–gel auto combustion process. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 98, 355–360 (2009)
Masuda, Y., Akiyama, T., Kitaoka, M., Otobe, S., Takei, H.: Development of new ferrite material for deflection yoke core. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers 29, 343–346 (1998)
Keluskar, S., Tangsali, R., Naik, G., Budkuley, J.: High permeability of low loss Mn–Zn ferrite obtained by sintering nanoparticle Mn–Zn ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 305, 296–303 (2006)
Sugimoto, M.: The past, present, and future of ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 269–280 (1999)
Zhang, Z., Xu, L., Liu, C.: Preparation and characterization of composite magnetic photocatalyst MnxZn1−xFe2O4/β- Bi2O3. RSC Advances. 5, 79997–80004 (2015)
Kondo, T., Mori, K., Hachisu, M., Yamazaki, T., Okamoto, D., Watanabe, M., Gonda, K., Tada, H., Hamada, Y., Takano, M., Ohuchi, N., Ichiyanagi, Y.: Alternating current magnetic susceptibility and heat dissipation by Mn1−xZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles for hyperthermia treatment. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 17D157 (2015)
Zhuang, L., Zhang, W., Zhao, Y., Li, D., Wu, W., Shen, H.: Temperature sensitive ferrofluid composed of Mn1−xZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by a modified hydrothermal process. Powder Technol. 217, 46–49 (2012)
Ahmed, M.A., Okasha, N., El-Dek, S.I.: Preparation and characterization of nanometric Mn ferrite via different methods. Nanotechnology 19, 065603 (2008)
Azadmanjiri, J.: Preparation of Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles from chemical sol–gel combustion method and the magnetic properties after sintering. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 353, 4170–4173 (2007)
Rath, C., Anand, S., Das, R., Sahu, K., Kulkarni, S., Date, S., Mishra, N.: Dependence on cation distribution of particle size, lattice parameter, and magnetic properties in nanosize Mn-Zn ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 91, 2211 (2002)
Pemartin, K., Solans, C., Alvarez-Quintana, J., Sanchez-Dominguez, M.: Synthesis of Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles by the oil-in-water microemulsion reaction method. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 451, 161–171 (2014)
Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A., Masoudpanah, S.M.: Effects of pH and citric acid content on the structure and magnetic properties of MnZn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by a sol–gel autocombustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 357, 77–81 (2014)
Shultz, M., Allsbrook, M., Carpenter, E.: Control of the cation occupancies of MnZn ferrite synthesized via reverse micelles. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 09M518 (2007)
Arulmurugan, R., Jeyadevan, B., Vaidyanathan, G., Sendhilnathan, S.: Effect of zinc substitution on Co–Zn and Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 288, 470–477 (2005)
Cullity, B.D., Stock, S.R.: Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, New York (2001)
Aslibeiki, B.: Nanostructural, magnetic and electrical properties of Ag doped Mn-ferrite nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 14, 1659–1664 (2014)
Gul, I.H., Ahmed, W., Maqsood, A.: Electrical and magnetic characterization of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrite synthesis by co-precipitation route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 270–275 (2008)
Syue, M.-R., Wei, F.-J., Chou, C.-S., Fu, C.-M.: Magnetic and electrical properties of Mn–Zn ferrites synthesized by combustion method without subsequent heat treatments. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 07A324 (2011)
Tang, Z.X., Chen, J.P., Sorensen, C.M., Klabunde, K.J., Hadjipanayis, G.C., Tang, et al.: Reply. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3114–3114 (1992)
Gopalan, E.V., Al-Omari, I., Malini, K., Joy, P., Kumar, D.S., Yoshida, Y., Anantharaman, M.: Impact of zinc substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of chemically derived nanosized manganese zinc mixed ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 1092–1099 (2009)
Shannon, R., Gumerman, P., Chenavas, J.: Effect of octahedral distortion on mean mn3+-o distances. Mineralogical Soc Amer 1130 17th St Nw Suite 330, 714–716 (1975). DC 20036
Shebanova, O.N., Lazor, P.: Raman spectroscopic study of magnetite (FeFe2O4): a new assignment for the vibrational spectrum. J. Solid State Chem. 174, 424–430 (2003)
White, W.B., DeAngelis, B.A.: Interpretation of the vibrational spectra of spinels. Spectrochim. Acta A: Mol. Spectrosc. 23, 985–995 (1967)
Diodati, S., Pandolfo, L., Caneschi, A., Gialanella, S., Gross, S.: Green and low temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline transition metal ferrites by simple wet chemistry routes. Nano Res. 7, 1027–1042 (2014)
Xu, Y., Sherwood, J., Qin, Y., Holler, R.A., Bao, Y.: A general approach to the synthesis and detailed characterization of magnetic ferrite nanocubes. Nanoscale 7, 12641–12649 (2015)
Sekulić, D., Lazarević, Z., Jovalekić, Č., Rečnik, A., Romčević, M., Hadžić, B., Romčević, N.: The comparative study of the structural and the electrical properties of the nano spinel ferrites prepared by the soft mehanochemical synthesis. Sci. Sinter. 46, 235–245 (2014)
Tang, Z.X., Sorensen, C.M., Klabunde, K.J., Hadjipanayis, G.C.: Size-dependent Curie temperature in nanoscale MnFe2O4 particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 3602–3605 (1991)
Zheng, M., Wu, X.C., Zou, B.S., Wang, Y.J.: Magnetic properties of nanosized MnFe2O4 particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 183, 152–156 (1998)
Chen, J., Sorensen, C., Klabunde, K., Hadjipanayis, G., Devlin, E., Kostikas, A.: Size-dependent magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 fine particles synthesized by coprecipitation. Phys. Rev. B 54, 9288 (1996)
Kodama, R.H., Berkowitz, A.E., McNiff, J.E.J., Foner, S.: Surface spin disorder in NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 394–397 (1996)
Neel, L.: Magnetic properties of ferrites: ferrimagnetism and antiferromagnetism. Ann. Phys. 3, 137–198 (1948)
Néel, L.: Antiferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism. Proc. Phys. Soc. London, Sect. A 65, 869 (1952)
Smith, J., Wijin, H.P.J.: Ferrites. Wiley, New York (1959)
Lu, A.-H., Salabas, E.L., Schüth, F.: Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 1222–1244 (2007)
Liu, C., Zou, B., Rondinone, A.J., Zhang, Z.J.: Reverse micelle synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic MnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanocrystallites. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 1141–1145 (2000)
Ali, M.B., El Maalam, K., El Moussaoui, H., Mounkachi, O., Hamedoun, M., Masrour, R., Hlil, E., Benyoussef, A.: Effect of zinc concentration on the structural and magnetic properties of mixed Co–Zn ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by sol/gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 398, 20–25 (2016)
Murugesan, C., Chandrasekaran, G.: Impact of gd3+ substitution on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 5, 73714–73725 (2015)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Central Instrumentation Facility, Pondicherry University, and DST-FIST, Government of India, for funding the facilities utilized in the present work and the Center for Nano Science and Technology for providing XRD measurement. C.M. thanks UGC, New Delhi, India, for the financial assistance in the form of the Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship (RGNF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4607-x.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murugesan, C., Chandrasekaran, G. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Mn1−x Zn x Fe2O4 Ferrite Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 29, 2887–2897 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3604-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3604-1