Abstract
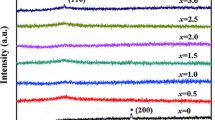
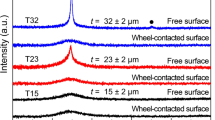
Microstructure and magnetic properties are systematically investigated to figure out what effect does the Cu content have on (Pr0.25Nd0.75)2Fe13.85-xCo0.1Ti0.05CuxB alloys in this work. The experimental result shows the optimal magnetic properties that the remanent magnetization Jr = 1.13 T, the coercivity Hcj = 588.56 kA/m, and the maximum magnetic energy product (BH)max = 260.66 kJ/m3 at the Cu content x = 0.6. However, it shows that Cu addition can promote the formation of the amorphous phase, which is an important reason for the coercivity decrease. Microstructure observation indicates that the reason for the magnetic property decrease is that the hard 2:14:1 magnetic phases and soft α-Fe phases display a state of irregular distribution with Cu content increasing.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article.
References
Kaneko, Y., Kuniyoshi, F., Ishigaki, N.: Proven technologies on high-performance Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets. J. Alloy. Compd. 408–412, 1344–1349 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.04.169
Peng, H., Luo, Y., Dou, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, Z., Yan, W., Xie, J., Yu, D., Diao, S.: Significant coercivity enhancement of Ti doping in Nd-Ce-Fe-B melt spun alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 477, 323–328 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.01.054
Zhang, P., Ma, T., Liang, L., Liu, X., Wang, X., Jin, J., Zhang, Y., Yan, M.: Improved corrosion resistance of low rare-earth Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets by Nd6Co13Cu grain boundary restructuring. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 379, 186–191 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.12.044
Wang, J., Meng, Y., Zhang, H., Tang, H., Lin, R., Sun, C., Wu, C., Xie, F.: The characteristic of crystal growth of Nd-Fe-B cast strips during the rapid solidification process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 396, 283–287 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.08.004
Wan, F., Zhang, Y., Han, J., Liu, S., Liu, T., Zhou, L., Fu, J., Zhou, D., Zhang, X., Yang, J., Yang, Y., Chen, J., Deng, Z.: Coercivity enhancement in Dy-free Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets by using Pr-Cu alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 203910 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4879898
Xu, X.D., Dong, Z.J., Sasaki, T.T., Tang, X., Sepehri-Amin, H., Ohkubo, T., Hono, K.: Influence of Ti addition on microstructure and magnetic properties of a heavy-rare-earth-free Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet. J. Alloy. Compd. 806, 1267–1275 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.289
Matsuura, M., Sugimoto, S., Fukada, T., Goto, R., Tezuka, N.: Effect of Cu addition on coercivity and interfacial state of Nd-Fe-B/Nd-rich thin films. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 200, 82019 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/200/8/082019
X. Chi, Y. Li, X. Han, J. Sun, Y. Zhang, C. Cui, Effect of Cu addition on the structure and magnetic properties of SmCo3.1-xFe0.9CuxB ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 465, 524–530 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.06.049
L. Wang, J. Wang, M. Rong, G. Rao, H. Zhou, Effect of wheel speed on phase formation and magnetic properties of (Nd0.4La0.6)-Fe-B melt-spun ribbons. J. Rare Earths 36, 1179–1183 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.02.013
Hussain, M., Zhao, L.Z., Zhang, C., Jiao, D.L., Zhong, X.C., Liu, Z.W.: Composition-dependent magnetic properties of melt-spun La or/and Ce substituted nanocomposite Nd-Fe-B alloys. Phys. B 483, 69–74 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2015.12.033
Pandian, S., Chandrasekaran, V., Markandeyulu, G., Iyer, K., Rao, K.: Effect of Co, Dy and Ga on the magnetic properties and the microstructure of powder metallurgically processed Nd-Fe-B magnets. J. Alloy. Compd. 364, 295–303 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(03)00541-3
Gholamipour, R., Beitollahi, A., Marghusian, V.K., Ohkubo, T.: Cu effects on coercivity and microstructural features in nanocrystalline Nd-Fe-Co-B annealed melt-spun ribbons. Phys. B 398, 51–54 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2007.04.087
Ma, Q., Hu, Z., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, F., Ju, X., Li, Z., Wang, G., Li, Y.: The effect of Nd8Cu2 alloy on the microstructure and magnetic properties of (Nd, MM)-Fe-B sintered magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 484, 345–349 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.04.028
Zhang, J.S., Zhong, M.L., Zhao, L.Z., Liao, X.F., Zeng, H.X., Zhong, X.C., Yu, H.Y., Zhong, Z.C., Liu, Z.W.: Reducing Dy content by Ce substitution in nanocomposite Nd-Dy-Fe-B/α-Fe alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 766, 1061–1066 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.057
Mc. Zhang, Sc. Zhou, Zc. Wang, Beneficial effects of Cu substitution on the microstructures and magnetic properties of Pr (Fe, Co) B/α-(Fe, Co) nanocomposites. J. Alloys. Compd. 309, 212–218 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(00)01050-1
Peng, H., Luo, Y., Dou, Y., Bai, X., Yan, W., Yu, D., Yang, Y., Diao, S.: Effects of cerium substitution on phase components, microstructures and magnetic properties of Nd-Fe-Ti-B alloy. J. Rare Earths 37, 861–864 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.10.008
Pan, M., Li, Z., Wu, Q., Ge, H., Xu, H.: Study of the role of Ti doping on magnetic properties of some nanocomposite alloys of α-Fe/Nd2Fe14B type. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 471, 457–463 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.097
G.S. Tan, H. Xu, L.Y. Yu, X.H. Tan, Q. Zhang, Y. Gu, X.L. Hou, Study on magnetic properties of (Nd0.8Ce0.2)2-xFe12Co2B (x=0–0.6) alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 437, 7–22 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.04.032
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51761007) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (Grant No. 2021GXNSFDA075009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construe as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled, “Effect of Cu addition on the microstructure and magnetic properties of the Nd-Fe-B melt-spun ribbons”.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Huang, W., Xie, J. et al. Effect of Cu Addition on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of the Nd-Fe-B Melt-Spun Ribbons. J Supercond Nov Magn 34, 3369–3376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05993-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05993-w