Abstract
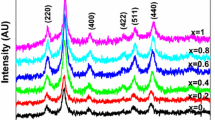
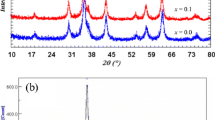
ZnxCu1-xFe2O4 (0.05 ≤ x ≤ 0.85) nanoparticles were synthesized by sol-gel method and were annealed at 500 and 900 °C in air for 3 h. Characterization techniques like XRD, Raman spectroscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometer were used to investigate phase, cation distribution, and magnetic properties. XRD studies showed that all the as-prepared samples are of cubic spinel phase. Tetragonal phase was observed in the samples with x < 0.15 after annealing, whereas all other samples retained cubic phase. Raman spectroscopy showed increase of Zn2+ ions in the tetrahedral site with the increase in Zn2+ concentration in the nanoparticle samples. Cation distribution and magnetic ordering enhanced the magnetization value with increasing x value, and a maximum was observed in the as-prepared and annealed samples. The coercivity decreased with the increase in Zn2+ concentration. The highest magnetization value of 110 emu/g with coercivity of 25 Oe was observed in the present study at 60 K for the sample annealed at 900 °C with x = 0.5. Law of approach to saturation method was adopted to study the magnetic ordering in the nanoparticle samples. The blocking temperature decreased with increase in Zn2+ concentration and annealing temperature. Cation distribution associated magnetic ordering and anisotropy variation with the increasing Zn2+ concentration explains the observed magnetic behavior in these nanoparticle samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sugimoto, M.: The past, present, and future of ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 269–280 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.1999.tb20058.x
Bate, G.: Magnetic recording materials since 1975. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 100, 413–424 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(91)90831-T
Shylesh, S., Schünemann, V., Thiel, W.R.: Magnetically separable nanocatalysts: bridges between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 3428–3459 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200905684
Veiseh, O., Gunn, J.W., Zhang, M.: Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 62, 284–304 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2009.11.002
Lee, J.-H., Huh, Y.-M., Jun, Y., Seo, J., Jang, J., Song, H.-T., Kim, S., Cho, E.-J., Yoon, H.-G., Suh, J.-S., Cheon, J.: Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nat. Med. 13, 95–99 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1467
Lee, J.H., Jang, J.T., Choi, J.S., Moon, S.H., Noh, S.H., Kim, J.W., Kim, J.G., Kim, I.S., Park, K.I., Cheon, J.: Exchange-coupled magnetic nanoparticles for efficient heat induction. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6, 418–422 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.95
Chen, R., Christiansen, M.G., Anikeeva, P.: Maximizing hysteretic losses in magnetic ferrite nanoparticles via model-driven synthesis and materials optimization. ACS Nano. 7, 8990–9000 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn4035266
Lu, A.H., Salabas, E.L., Schüth, F.: Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 1222–1244 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602866
Dong, Y., He, K., Yin, L., Zhang, A.: A facile route to controlled synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles and their environmental catalytic properties. Nanotechnology. 18, 435602 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/43/435602
Masunga, N., Mmelesi, O.K., Kefeni, K.K., Mamba, B.B.: Recent advances in copper ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites synthesis, magnetic properties and application in water treatment: review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7, 103179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103179
Pawar, R.A., Patange, S.M., Shirsath, S.E.: Spin glass behavior and enhanced but frustrated magnetization in Ho3+ substituted Co-Zn ferrite interacting nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 6, 76590–76599 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra12541g
Peddis, D., Cannas, C., Piccaluga, G., Agostinelli, E., Fiorani, D.: Spin-glass-like freezing and enhanced magnetization in ultra-small CoFe2O4nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. 21, 125705 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/21/12/125705
Chinnasamy, C.N., Narayanasamy, A., Ponpandian, N., Chattopadhyay, K., Guérault, H., Greneche, J.-M.: Magnetic properties of nanostructured ferrimagnetic zinc ferrite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 12, 7795–7805 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/12/35/314
Lu, H.M., Zheng, W.T., Jiang, Q.: Saturation magnetization of ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic nanocrystals at room temperature. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 40, 320–325 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/40/2/006
Mlyadai, T., Miyahara, S., Matsuo, Y.: Ferrimagnetic resonance in copper ferrite, I. Cubic-Phase Single Crystal. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 20, 980–984 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.20.980
Alex Goldman: Modern Ferrite Technology. (2006)
Thapa, D., Kulkarni, N., Mishra, S.N., Paulose, P.L., Ayyub, P.: Enhanced magnetization in cubic ferrimagnetic CuFe2O4nanoparticles synthesized from a citrate precursor: the role of Fe2+. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 43, 195004 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/43/19/195004
B.D. Cullity, C.D. Graham.: Introduction to magnetic materials. (2009)
Kulkarni, R.G., Patil, V.U.: Magnetic ordering in Cu-Zn ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. 17, 843–848 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00540382
Rana, M.U., Islam, M., Abbas, T.: Cation distribution and magnetic interactions in Zn-substituted CuFe2O4 ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 65, 345–349 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(00)00218-2
Maria, K.H., Choudhury, S., Hakim, M.A.: Structural phase transformation and hysteresis behavior of Cu-Zn ferrites. Int. Nano Lett. 3, 42 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-3-42
Rana, M.U., Ul-Islam, M., Ahmad, I., Abbas, T.: Determination of magnetic properties and Y–K angles in Cu–Zn–Fe–O system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 187, 242–246 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(98)00077-8
Verma, K., Kumar, A., Varshney, D.: Effect of Zn and Mg doping on structural , dielectric and magnetic properties of tetragonal CuFe 2 O 4. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 467–473 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2012.09.015
Hankare, P.P., Kadam, M.R., Patil, R.P., Garadkar, K.M., Sasikala, R., Tripathi, A.K.: Effect of zinc substitution on structural and magnetic properties of copper ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 501, 37–41 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.03.178
Gautam, N., Thirupathi, G., Singh, R.: Effect of Zn-doping on structural and magnetic properties of copper ferrite nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 1731, (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4947753
Atif, M., Nadeem, M., Grössinger, R., Turtelli, R.S.: Studies on the magnetic, magnetostrictive and electrical properties of sol-gel synthesized Zn doped nickel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 5720–5724 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.02.163
Subha, A., Shalini, M.G., Sahu, B., Sahoo, S.C.: Structural transformation and magnetic properties of copper ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 20790–20799 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0221-8
Smit, J., Wijn, H.P.J.: Ferrites. Philips Technical Library, Eindhoven (1959)
Mazen, S.A., Mansour, S.F., Zaki, H.M.: Some physical and magnetic properties of Mg-Zn ferrite. Cryst. Res. Technol. 38, 471–478 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200310059
Cullity, B.D.: Elements of X-ray diffraction. (2014)
Wang, Z., Lazor, P., Saxena, S., Artioli, G.: High-pressure Raman spectroscopic study of spinel (ZnCr2O4). J. Solid State Chem. 165, 165–170 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.2002.9527
Chandramohan, P., Srinivasan, M.P., Velmurugan, S., Narasimhan, S.V.: Cation distribution and particle size effect on Raman spectrum of CoFe2O4. J. Solid State Chem. 184, 89–96 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2010.10.019
Chithra, M., Anumol, C.N., Argish, V., Sahu, B., Sahoo, S.C.: Tailoring magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles by different divalent cation substitution. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 813–822 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7976-1
Chithra, M., Anumol, C.N., Sahu, B., Sahoo, S.C.: Structural and magnetic properties of Zn X Co 1−X Fe 2 O 4 nanoparticles: nonsaturation of magnetization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 424, 174–184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.10.064
Dash, J., Prasad, S., Venkataramani, N., Krishnan, R., Kishan, P., Kumar, N., Kulkarni, S.D., Date, S.K.: Study of magnetization and crystallization in sputter deposited LiZn ferrite thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 86, 3303–3311 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.371206
Kulkarni, P.D., Prasad, S., Venkataramani, N., Krishnan, R., Pang, W., Guha, A., Woodward, R.C., Stamps, R.L.: The high field magnetization in the RF sputter deposited copper ferrite thin films. Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Ferrites, p. 201. [25]. Wiley, San Fr. 2004 (2010)
Sahoo, S.C., Venkataramani, N., Prasad, S., Bohra, M., Krishnan, R.: Stability of nonthermodynamic equilibrium cation distribution frozen during pulsed laser deposition of Co-ferrite thin films. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 98, 889–894 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-009-5471-0
Najmoddin, N., Beitollahi, A., Devlin, E., Kavas, H., Mohseni, S.M., Åkerman, J., Niarchos, D., Rezaie, H., Muhammed, M., Toprak, M.S.: Magnetic properties of crystalline mesoporous Zn-substituted copper ferrite synthesized under nanoconfinement in silica matrix. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 190, 346–355 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.02.033
Sharma, R., Singhal, S.: Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of zinc doped nickel ferrite and their application in photo catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 414, 83–90 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2013.01.015
Haque, M.M., Huq, M., Hakim, M.A.: Effect of Zn 2 + substitution on the magnetic properties of Mg1 - x Zn x Fe 2 O 4 ferrites. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 404, 3915–3921 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2009.07.124
Yafet, Y., Kittel, C.: Antiferromagnetic arrangements in ferrites. Phys. Rev. 87, 290–294 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.87.290
Sumangala, T.P., Mahender, C., Venkataramani, N., Prasad, S.: A study of nanosized magnesium ferrite particles with high magnetic moment. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 382, 225–232 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.01.056
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subha, A., Shalini, M.G., Rout, S. et al. Magnetic Ordering and Enhancement of Magnetization in Zinc-Substituted Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 3577–3586 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05613-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05613-z