Abstract
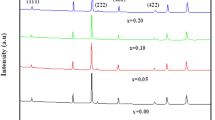
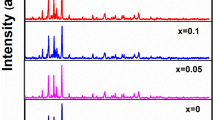
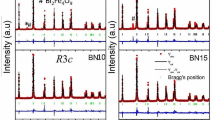
Ba1−xRexCo2ZnxFe16−xO27 (Re = La, Nd, Pr; x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2) hexaferrites were prepared by a sol–gel auto-combustion method and sintering at 1250 °C for 2 h. The effects of rare-earth (RE) substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of the hexaferrites were investigated. XRD patterns of the samples revealed crystallization of pure W-type hexaferrite phase in all samples, except for Nd–Zn (x = 0.2) sample, which contained a minor M-type phase in addition to the major W-type phase. The saturation magnetization did not change appreciably with RE–Zn substitution, although the magnetic measurements revealed slight improvement with Pr–Zn substitution. However, the magnetocrystalline anisotropy field (Ha) increased significantly with RE–Zn substitution, recording a maximum increase up to 9.23 kOe compared with 6.30 kOe for the unsubstituted sample. The results indicated the possibility of tuning the anisotropy field, and consequently, the ferromagnetic resonance frequency, to frequency ranges appropriate for desired microwave applications. The thermomagnetic curves revealed spin reorientation transitions below 300 °C, and magnetic phase transition in the range at 461–481 °C, which was associated with the Curie temperature of the W phase. In addition, the weak magnetic phase transition in the temperature range of 505–516 °C was associated with Co-rich impurity magnetic phase, with enhanced superexchange interactions in Co-rich regions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smit, J., Wijn, H.P.J.: Ferrites. Wiley, New York (1959)
Chikazumi, S.: Physics of ferromagnetism 2e, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2009)
Pullar, R.C.: Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 1191–1334 (2012)
Mahmood, S.H.: Ferrites with high magnetic parameters. In: Mahmood, S.H., Abu-Aljarayesh, I. (eds.) Hexaferrite permanent magnetic materials, pp. 111–152. Materials Research Forum LLC, Millersville (2016)
Mahmood, S.H., Bsoul, I.: Tuning the magnetic properties of M-type hexaferrites. In: Jotania, R.B., Mahmood, S.H. (eds.) Magnetic oxides and composites, pp. 49–100. Materials Research Forum LLC, Millersville (2018)
Harris, V.G., Geiler, A., Chen, Y., Yoon, S.D., Wu, M., Yang, A., Chen, Z., He, P., Parimi, P.V., Zuo, X.: Recent advances in processing and applications of microwave ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2035–2047 (2009)
Özgür, Ü., Alivov, Y., Morkoç, H.: Microwave ferrites, part 2: passive components and electrical tuning. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20, 911–952 (2009)
Mahmood, S.H.: High performance permanent magnets. In: Mahmood, S.H., Abu-Aljarayesh, I. (eds.) Hexaferrite permanent magnetic materials, pp. 47–73. Materials Research Forum LLC, Millersville (2016)
Mahmood, S.H.: Permanent magnet applications. In: Mahmood, S.H., Abu-Aljarayesh, I. (eds.) Hexaferrite permanent magnetic materials, pp. 153–165. Materials Research Forum LLC, Millersville (2016)
Abu-Aljarayesh, I.: Magnetic recording. In: Mahmood, S.H., Abu-Aljarayesh, I. (eds.) Hexaferrite permanent magnetic materials, pp. 166–181. Materials Research Forum LLC, Millersville (2016)
Stergiou, C., Litsardakis, G.: Preparation and magnetic characterization of Co2-W strontium hexaferrites doped with Ni and La. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2362–2368 (2011)
Khan, I., Sadiq, I., Ashiq, M.N.: Role of Ce–Mn substitution on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of W-type strontium hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 8042–8046 (2011)
Zi, Z., Dai, J., Liu, Q., Liu, H., Zhu, X., Sun, Y.: Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of W-type Ba (ZnxCo1− x)2Fe16O27 hexaferrite platelets. Journal of Applied Physics. 109, 07E536 (2011)
Zou, H., Li, S., Zhang, L., Yan, S., Wu, H., Zhang, S.: M. Tian, determining factors for high performance silicon rubber microwave absorbing materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1643–1651 (2011)
Huang, X., Chen, J., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Zhang, Q.: A new microwave absorber based on antimony-doped tin oxide and ferrite composite with excellent electromagnetic match. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 506, 347–350 (2010)
Wu, Y., Ong, C., Lin, G., Li, Z.: Improved microwave magnetic and attenuation properties due to the dopant V2O5 in W-type barium ferrites. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 39, 2915 (2006)
A. Pasko, F. Mazaleyrat, M. Lobue, V. Loyau, V. Basso, M. Küpferling, C. Sasso, L. Bessais: Magnetic and structural characterization of nanosized BaCoxZn2−xFe16O27 hexaferrite in the vicinity of spin reorientation transition, in: Journal of Physics: conference series, IOP Publishing, pp. 012045 2011
Paoluzi, A., Licci, F., Moze, O., Turilli, G., Deriu, A., Albanese, G., Calabrese, E.: Magnetic, Mössbauer, and neutron diffraction investigations of W-type hexaferrite BaZn2−xCoxFe16O27 single crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 63, 5074–5080 (1988)
Xu, J., Zou, H., Li, H., Li, G., Gan, S., Hong, G.: Influence of Nd3+ substitution on the microstructure and electromagnetic properties of barium W-type hexaferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 490, 552–556 (2010)
S.H. Mahmood, Q. Al-Shiab, I. Bsoul, Y. Maswadeh, A. Awadallah, Structural and magnetic properties of (Mg, Co)2W hexaferrites, arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.08581, (2017)
Tang, J., Liu, X., Rehman, K.M.U., Li, D., Li, M., Yang, Y.: Microstructure and characterization of W-type hexaferrite Ba1− xLaxFe22+Fe163+O27 prepared by solid state method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 452, 354–359 (2018)
Huang, X., Zhang, J., Wang, H., Yan, S., Wang, L., Zhang, Z.: Er3+-substituted W-type barium ferrite: preparation and electromagnetic properties. Journal of Rare Earths. 28, 940–943 (2010)
Wang, L., Song, J., Zhang, Q., Huang, X., Xu, N.: The microwave magnetic performance of Sm3+ doped BaCo2Fe16O27. J. Alloys Compd. 481, 863–866 (2009)
J. Rodriguez-Carvajal: Recent developments of the program FULLPROF. IUCR Newsletter 26, 12 (2001)
Mahmood, S.H., Al Sheyab, Q., Bsoul, I., Mohsen, O., Awadallah, A.M.: Structural and magnetic properties of Ga-substituted Co2-W hexaferrites. Current Applied Physics. 18, 2590–2598 (2018)
Awadallah, A., Mahmood, S.H., Maswadeh, Y., Bsoul, I., Awawdeh, M., Mohaidat, Q.I., Juwhari, H.: Structural, magnetic, and Mossbauer spectroscopy of Cu substituted M-type hexaferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 74, 192–201 (2016)
Collomb, A., Wolfers, P., Obradors, X.: Neutron diffraction studies of some hexagonal ferrites: BaFe 12O19, BaMg2-W and BaCo2-W. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 62, 57–67 (1986)
Shannon, R.D.: Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallographica A. 32, 751–767 (1976)
Warren, B.E.: X-ray Diffraction. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1969)
Awadallah, A., Mahmood, S.H., Maswadeh, Y., Bsoul, I., Aloqaily, A.: Structural and magnetic properties of vanadium doped M-type barium hexaferrite (BaFe12-xVxO19). IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng. 92, 012006 (2015)
Mahmood, S.H., Awadallah, A., Maswadeh, Y., Bsoul, I.: Structural and magnetic properties of Cu-V substituted M-type barium hexaferrites. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng. 92, 012008 (2015)
Rezlescu, L., Rezlescu, E., Popa, P., Rezlescu, N.: Fine barium hexaferrite powder prepared by the crystallisation of glass. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 193, 288–290 (1999)
Cullity, B.D., Graham, C.D.: Introduction to magnetic materials, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken (2011)
Grӧssinger, R.: A critical examination of the law of approach to saturation I. Fit procedure. Phys. Status Solidi A. 66, 665–674 (1981)
Hessien, M., Rayan, D., Mahmoud, M., Alhadhrami, A., Rashad, M.: Controlling the structural, microstructure and magnetic properties of barium W-type hexaferrite elaborated using tartaric acid precursor strategy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 9771–9779 (2018)
Guo, F., Wu, X., Ji, G., Xu, J., Zou, L., Gan, S.: Synthesis and properties investigation of non-equivalent substituted W-type hexaferrite. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 411–420 (2014)
Ahmad, M., Grössinger, R., Kriegisch, M., Kubel, F., Rana, M.: Characterization of Sr-substituted W-type hexagonal ferrites synthesized by sol–gel autocombustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 332, 137–145 (2013)
Iqbal, M.J., Khan, R.A., Mizukami, S., Miyazaki, T.: Tailoring of structural, electrical and magnetic properties of BaCo2W-type hexaferrites by doping with Zr–Mn binary mixtures for useful applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2137–2144 (2011)
Jing, W., Hong, Z., Shuxin, B., Ke, C., Changrui, Z.: Microwave absorbing properties of rare-earth elements substituted W-type barium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 312, 310–313 (2007)
Tsutaoka, T., Koga, N.: Magnetic phase transitions in substituted barium ferrites BaFe12− x(Ti0. 5Co0. 5)xO19 (x = 0–5). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 325, 36–41 (2013)
Mahmood, S.H., Zaqsaw, M.D., Mohsen, O.E., Awadallah, A., Bsoul, I., Awawdeh, M., Mohaidat, Q.I.: Modification of the magnetic properties of Co2Y hexaferrites by divalent and trivalent metal substitutions. Solid State Phenom. 241, 93–125 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dmour, M.K., Al-Hwaitat, E.S., Bsoul, I. et al. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Ba1−xRexCo2ZnxFe16−xO27 W-Type Hexaferrites Prepared by Sol–Gel Auto-Combustion. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 473–482 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05213-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05213-6