Abstract
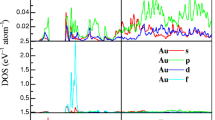
This work is stimulated by the recent developments in the search of novel magnetic materials such as the simple cubic laves phase compounds of yttrium and 3d transition metals with ferromagnetic or exchange enhanced Pauli paramagnetic properties. The ground state electronic structure of the intermetallics was calculated by the full potential linearized augmented plane wave method (FP-LAPW) based on the density functional theory. The suitability of the various approximations LDA and GGA with exchange-correlations (XCs) potentials such as GGA-PBEsol, GGA-WC, etc. on the electronic structure was also investigated. From the calculated band structure and angular-momentum projected density of states (DOS), strong d–d hybridization of electrons at the Fermi level was observed. The Fe-Y and Co-Y coupling is stronger for minority component of Fe/Co d states which leads to formation of negative magnetic moment on Y sites. The magnetic moments were found to be considerably larger than the experimental moments although there is good agreement with methods based on DFT. The Y-TM compounds have mixed chemical bonding character which we have characterized by calculating the Bader charge distributions, electron localization function, as well as the magnetization spin density. High magnetization density is localized on the Fe atoms which imparts ferromagnetism to the more ionic YFe2 system, whereas the shift of electron density and magnetization density towards inter atomic regions imparts exchange enhanced paramagnetic properties in more covalent YCo2 system. In order to study the influence of d-electrons, the temperature-dependent electrical resistivity and thermopower were obtained from the band energies. Magnetism was investigated in terms of enhanced magnetic susceptibility and Sommerfeld term γ obtained from low temperature-specific heats. The dynamical stability of YX2 was investigated by calculating the vibrational phonon modes and phonon density of states. The lowermost frequency modes arise from vibrations of Y–Fe bonds which exhibit structural instability which have been interpreted in terms of electron-phonon coupling. The coupling of magnetic moments with the lattice in YFe2 verifies the magneto-elastic interactions found experimentally.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lange, R.J., Fisher, I.R., Canfield, P.C., Antropov, V.P., Lee, S.J., Harmon, B.N., Lynch, D.W.: Observation of a metamagnetic phase transition in an itinerant 4f system via the magneto-optic Kerr effect Ce(Fe1−x Co x )2. Phys. Rev. B 62, 7084–7092 (2000). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.62.7084
Ritter, C.: Polarized neutron study of the magnetic ordering in the simple alloy YFe2. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter. 1, 2765 (1989). doi:10.1088/0953-8984/1/16/0172
Paolasini, L., Hennion, B., Panchula, A., Myers, K., Canfield, P.: Lattice dynamics of cubic Laves phase ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. B 58, 12125–12133 (1998). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.58.12125
Paolasinia, L., Landerb, G.H.: Iron magnetism in cubic Laves phase itinerant ferromagnets. J. Alloys Compnd. 303–304, 232–238 (2000)
Gratz, E., Bauer, E., Pöllinger, S., Nowotny, H., Burkov, A.T., Vedernikov, M.V.: Thermopower of some rare-earths compounds from 2K-1000 K. J. Phys. Colloques 49, C8-511-C2-512 (1988). doi:10.1051/jphyscol:19888231
Rastogi, A., Hilscher, G., Gratz, E., Pillmayr, N.: Magnetic and transport properties of Ce (Fe1−x Co x )2. J. Phys. Colloques 49, C8-277-C8-278 (1988). doi:10.1051/jphyscol/19888123
Gratz, E., Kottar, A., Lindbaum, A., Mantler, M., Latroche, M., Paul-Boncour, V., Acet, M., Barner, C.L., Holzapfe, W.B., Pacheco, V., Yvon, K.: Temperature- and pressure-induced structural transitions in rare-earth-deficient R1−x Ni2(R = Y, Sm, Gd, Tb) Laves phases. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter. 8, 8351–8361 (1996)
Hauser, R., Bauer, E., Gratz, E.: Pressure-dependent electrical resistivity of RCo2 compounds (R = rare-earth). Phys. Rev. B 57, 2904–2914 (1998). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.57.2904
Dedkov, Y.S., Laubschat, C., Khmelevskyi, S., Redinger, J., Mohn, P., Wienert, M.: Observation of ferromagnetic surface of paramagnetic YCo2. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 100, 072028 (2008). doi:10.1088/1742-6596/100/7/1072028
Cyrot, M., Lavagna, M.: Density of states and magnetic properties of rare earth compounds. J. Phys. 40, 763–771 (1979). doi:10.1051/jphys:01979004008076300
Yamada, H., Inoue, J., Terao, K., Kanda, S., Shimizu, M.: Electronic structure and magnetic properties of YM2 compounds (M = Mn, Fe, Co and Ni). J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 14, 1943–1960 (1984). doi:10.1088/0305-4608/14/8/023
Mohammad, F.Z., Yehia, S., Aly, S.H.: A DFT-based study of the magnetic, electronic and elastic properties of YFe2. Int. J. Phys. Appl. 2, 135–148 (2010)
Yanez-Terrazas, E., Gallegos-Orozco, V., Matutes-Aquino, J.A., Ochoa-Lara, M.T., Espinosa-Magana, F.: Electronic structure of YFe2 by EELS and ab initio calculations. Ad. Mat. Res 68, 89–95 (2009). doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.68.89
Coehoorn, R.: Calculated electronic structure and magnetic properties of Y-Fe compounds. Phys. Rev. B 39, 13072 (1989). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.39.13072
Eriksson, O., Johansson, B., Brooks, M.S.S., Skriver, H.L.: Electronic structure and magnetic properties of selected lanthanide and actinide intermetallic Laves phase alloys. Phys. Rev. B 40, 9519–9527 (1989). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.40.9519
Becker C., Hafner J.: Structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of Fe-Y alloys. Phys. Rev. B 50, 3913–3929 (1994). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.50.3913
Inoue, J., Shimizu, M.: Electronic structure and magnetic properties of amorphous YCo2. J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 15, 1525–1536 (1985). doi:10.1088/0305-4608/15/7/011
Chioncel, L., Burzo, E., Tetean, R., Pop, V.: Electronic structure of Y(Co x Ni1−x )2 compounds. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 417, 29–37 (2004). doi:10.1080/15421400490478641
Nakada, K., Shimizu, H., Yamada, H.: Fermi surfaces of YFe2and YNi2. Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 329–333, 129–1130 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0921-4526(02)02470-5
Moulay, N., Rached, H., Rabah, M., Benalia, S., Rache, D., Reshak, A.H., Benkhettou, N., Ruterana, P.: First-principles calculations of the elastic, and electronic properties of YFe2, NiFe2 and YNiFe4 intermetallic compounds. Compt. Mat. Sci. 73, 56–64 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.02.010
Gaidukova, I.Y., Markosyan, A.S.: d-magnetism instability in R-Co intermetallic compounds. J. Sci.: Adv. Mat. Devices 1, 105–112 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.jsamd.2016.06.008
Blaha P., Schwarz K., Madsen G.K.H., Kuasnicka D., Luitz J.: WIEN2k, an augmented plane wave+ local orbitals program for calculating crystal properties, K. Schwartz Technical Universitat, Wien, Australia, ISBN 3-9501031-1 (2001)
Kresse, G., Hafner, J.: ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys.Rev.B 47, 558 (1993). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.47.558
Kresse, G., Hafner, J.: ab initio molecular-dynamics simulation of the liquid-metal-amorphous-semiconductor transition in germanium. Phys. Rev. B 49, 14251 (1994). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB941.49.14251
Kresse, G., Furthmüller, J.: Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mat. Sci. 6, 15 (1996). doi:10.1016/0927-0256(96)00008-0
Kresse, G., Furthmüller,J.: Efficient iterative schemes for ab-initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169 (1996). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169
Parlinski, K., Li, Z.Q., Kawazoe, Y.: First principles determination of the soft mode in cubic ZrO2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 4063–4072 (1997). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.4063
Madsen, G.K.H., Singh, D.J.: BoltzTraP. A code for calculating band-structure dependent quantities. Comp. Phys. Comm. 175, 67–71 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.cpc.2006.03.007
Acknowledgments
We are thankful for financial assistance (Grant no. 2011/371/29/BRNS/1782) provided by BRNS, Mumbai. We are also thankful to Prof. Blaha for Wien2K code and Prof. Kress for VASP code.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, R., Sharma, Y. Magnetism in Yttrium Intermetallics: Ab Initio Study. J Supercond Nov Magn 30, 1003–1018 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3890-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3890-7