Abstract
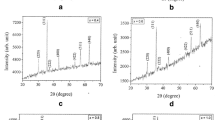
The present work deals with the synthesis and characterizations of magnesium-substituted cobalt ferrite (Co 1−x Mg x Fe 2 O 4; x = 0.00, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.00) nanoparticles by sol-gel auto combustion method. X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques were used for the characterization of the prepared samples. The magnetic properties were studied through pulse field hysteresis loop technique at room temperature. The XRD patterns of all the samples show the reflection which belongs to the cubic spinel structure. The XRD analysis confirmed the single-phase formation of spinel structure for the present ferrite system. Various structural parameters such as tetrahedral ionic radius (r A), the octahedral ionic radius (r B), theoretical lattice constant (a th), hopping length (L A and L B), tetrahedral bond length (d AL), octahedral bond length (d BL), tetra edge (d AE) and octa edge (d BE) were calculated from the XRD data. The variation of these structural parameters in magnesium composition has been studied. The M-H curves recorded at room temperature exhibit a typical hysteresis loop indicating that the sample exhibits a magnetic nature, which decreases with an increase in Mg content x. The large coercivity (H c) values indicate a nanocrystalline nature of the present samples. The coercivity, saturation magnetization, remanence magnetization, and magneton number decreases with an increase in Mg content x.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Standley, K.J.: Oxide magnetic materials, 2nd edition (1972)
Sato Turtello, R., Duong, G.V., Nunes, W., Grpssinger, R., Knobel, M.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 339 (2008)
Hannour, A., Vincent, D., Kahlouche, F., Tchangoulian, A., Neveu, S., Dupuis, V.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 353, 29–33 (2014)
Murdock, E.S., Simmons, R.F., Davidson, R.: IEEE Trans. Magn. 5(2), 3078–3083 (1992)
Okuno, S.N., Hashimoto, S., Inomata, K.: J. Appl. Phys. 71, 5926–5929 (1992)
Raut, A.V., Barkule, R.S., Shengule, D.R., Jadhav, K.M.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 358–359, 87–92 (2014)
Shinde, S.S., Jadhav, K.M.: J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 17, 849–851 (1998)
Birajdar, D.S., Devatwal, U.N., Jadhav, K.M.: J. Mater. Sci. 37, 1443–1448 (2002)
Karimi, Z., Mohammadifar, Y., Shokrollahi, H., KhamenehAsl, Sh., Yousefi, Gh., Karimi, L.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 361, 150–156 (2014)
Modi, K.B., Rangolia, M.K., Chhantbar, M.C., Joshi, H.H.: J. Mater. Sci. 41, 22 (2006)
Pradeep, A., Priyadharsini, P., Chandrasekaran, G.: J. Alloys Compd. 509, 39173923 (2011)
Vasambekar, P.N., Kolekar, C.B., Vaingankar, A.S.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 186, 333 (1998)
Mathew, D.S., Juang, R.S.: Chem. Eng. J. 129, 51 (2007)
Vinayak, V., Khirade, P.P., Birajdar, S.D., Alange, R.C., Jadhav, K.M.: J Supercond Nov Magn. doi:10.1007/s10948-015-3159-6
Pornprasertsuk, R., Yuwapttanawong, C., Permkittikul, S., Tungtidtham, T.: Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 13(10), 1813–1819 (2012)
Thankachan, S., Jacob, B.P., Xavier, S., Mohammed, E.M.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 348, 140–145 (2013)
Pandit, A.A., Shitre, A.R., Shengule, D.R., Jadhav, K.M.: J. Mater. Sci. 40(2) (2005)
Waldron, R.A.: Ferrites: an introduction for microwave engineers (1961)
Hafner, S., Laves, F.Z.: Krist. 115, 331 (1961)
Kurmude, D.V., Shinde, A.B., Pandit, A. A., Kale, C.M., Shengule, D.R., Jadhav, K.M.: J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. doi:10.1007/s10948-014-2943-z
Pradeep, A., Priyadharsini, P., Chandrasekaran, G.: J. Alloys Compd. 509, 39173923 (2011)
Vasambekar, P.N., Kolekar, C.B., Vaingankar, A.S.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 186, 333 (1998)
Mathew, D.S., Juang, R.S.: Chem. Eng. J. 129, 51 (2007)
Wells, S., Ramana, C.V.: Ceram. Int. 39, 9549 (2013)
Lin, X.M., Sorensen, C.M., Klabunde, K.J., Hadjipanayis, G.C.: Langmuir 14, 7140 (1998)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to IIT Mumbai for providing X-ray diffraction facility and Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, for FTIR and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) characterization facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinayak, V., Khirade, P.P., Birajdar, S.D. et al. Structural, Microstructural, and Magnetic Studies on Magnesium (Mg2+)-Substituted CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 29, 1025–1032 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3348-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3348-3