Abstract
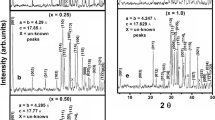
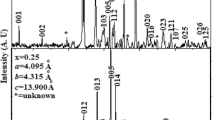
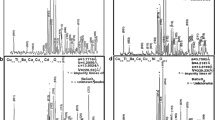
We have synthesized (Cu0.5Tl0.5)Ba2Ca3(Cu4−x Ti x )O12−δ (x = 0, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.0) superconductors by two-step solid-state reaction method at 880 °C. The a-axis length of tetragonal unit cell increases, whereas the c-axis decreases with doping of Ti in the final compound revealed by X-ray diffraction measurements. Moreover, the magnitude of superconductivity suppresses with increased Ti doping. The Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) absorption measurements have shown that the peak position of the apical oxygen modes at 480 and 540 cm −1 remains unchanged, whereas the CuO2/TiO2 planar oxygen modes is softened with increased Ti doping. We explained the softening of planar oxygen mode to be arising due to the difference in the atomic masses of Ti (47.90 amu) and Cu (63.54 amu) atoms. The suppression of superconductivity magnitude is suggested to be originating from an-harmonic oscillations induced by doped Ti atoms which in turn suppress the density of phonon population. These studies show the importance of density of phonon population in mechanism of high- T c superconductivity and hence the electron-phonon interactions. The excess conductivity analyses (FIC) of conductivity data of these samples have shown that with increased Ti doping, the mean field critical temperature T cmf is shifted to lower temperatures. The increase in the coherence length along the c-axis, interlayer coupling, and the Fermi velocity is suggested to be arising from the decrease in the c-axes length. We attribute the suppression in B c, B c1, J c(0), and τ ϕ with Ti doping to the free energy difference between the normal and superconducting state. The idea of suppression in the density of phonon modes induced by Ti doping is supported by excess conductivity analyses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nawazish, A., Khan, A., Javaid, A.A., Khurran, N.H.: Phys. C 425, 90 (2005)
Jergel, M., Conde Gallardo, A., Falcony Guajardo, C., Strbik, V.: upercond. Sci. Technol. 9, 427 (1996)
Ibach, H., Lüth, H.: Solid-state physics: an introduction to theory and experiment. Springer (1993)
Christman, J.R.: Fundamentals of Solid Statem, 1st, p. 215. Wiley (1987)
Khan, N.A., Arif, M.: Physica C 488, 35 (2013)
Mumtaz, M., Khan, N.A., Nawaz, R.: J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 23, 565–569 (2010)
Khan, N. A., Rahim, M.: J. Alloys Compd. 481, 81 (2009)
Rahim, M., Khan, N.A.: J. Alloys Compd. 513, 55 (2011)
Prade, J., Kulkarni, A.D., De Welte, F.W.: Phys. Rev. B 39, 2771 (1989)
Kulkarni, A.D., De Welte, F.W., Prade, J., Schroder, U., Kress, W.: Phys. Rev. B 41, 6409 (1990)
Sato, T., Nakane, H., Mori, N., Yoshizawa, S.: Phys. C 344, 244 (2003)
Ghosh, A.K., Bandyopadhyay, S.K., Barat, P., Sen, P., Basu, A.N.: Phys. C 264, 255 (1996)
Manmeet Kaur, R., Srinibasan, G.K., Mehta, D., Kanjilal, R., Pinto, S.B., Ogale, S., Mohan, V.G.: Phys. C 443, 61 (2006)
Aslamazov, L.G., Larkin, A.L.: Phys. Lett. A 26, 238 (1968)
Lawrence, W.E., Doniach, S.: In: Kanda, E. (ed.) Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Low Temperature Physics, p. 361, Keigaku, Tokyo (1971)
Abu Aly, A.I., Ibrahim, I.H., Awad, R.A., El-Harizy, A.: J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 23, 1325 (2010)
Rojas Sarmiento, M.P., Uribe Laverde, M.A., Vera Lopez, E., Landinez Tellez, D.A., Roa-Rojas, J.: Phys. B 398, 360 (2007)
Ben Azzouz, F., Zouaoui, M., Annabi, M., Ben Salem, M.: Sol. Stat. Phys. C 3, 3048 (2006)
Solovjov, A.L., Dmitriev, V.M., Habermeier, H.-U.: Phys. Rev. B 55, 8551 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, N.A., Abbas, S.Q. & Khan, M.N. Significance of Phonon Modes and Excess Conductivity of (Cu0.5Tl0.5)Ba2Ca3(Cu4−x Ti x )O12−δ (x = 0, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.0) Superconductors. J Supercond Nov Magn 28, 2009–2015 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-2998-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-2998-5