Abstract
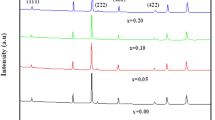
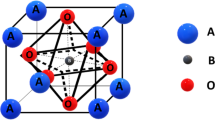
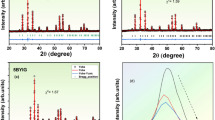
The conversion of waste heat into electrical energy plays a key role in our current challenge to develop alternative energy technologies to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. Thermoelectric (TE) materials are the first choice to handle this subject. In TE materials, cobaltites are the material of interest, due to their nontoxic properties. Cobaltites exhibits large TE power, low resistivity, and relatively small thermal conductivity at room temperature. TE material (BiCa2−x R x CoO y ) where R is for rare earth like Nd, (x = 0.0, 0.2) was synthesized in nanoregime by simplified sol–gel method. Simplified sol–gel method was chosen because it gives maximum phase purity and tunable parameters for desired properties. The mechanism used to enhance thermoelectric properties is to reduce thermal conductivity of the material and increase electrical conductivity of the material using nanostructures. Material characterizations were done for structural studies using X-ray diffraction (XRD). XRD revealed monoclinic crystal structure. Temperature-dependent electrical conductivity showed an increase with increase in temperature. Thermal conductivity was also measured. Both electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity decrease as a result of neodymium doping which enhanced its importance as thermoelectric material. The different parameters were correlated to understand the conduction mechanism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chena, Z.G., Hana, G., Yanga, L., Cheng, Zoua, J.: Prog. Nat. Sci. 22, 535 (2012)
Terasaki, I., Sasago, Y., Uchinokura, K.: Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 56, 685 (1997)
Lambert, S., Leligny, H., Grebille, D.: J. Solid State Chem. 160, 322 (2001)
He, J., Liu, Y.: J. Mater. Res. 26, 1762 (2011)
Pelloquin, D., Hébert, S., Maignan, A., Raveau, B.: Solid State Sci. 6, 167 (2004)
Luo, X.G., Jing, Y.C., Chen, H., Chen, X.H.: J. Cryst. Growth 308, 309 (2007)
Rowe, D.M. (ed.).: Thermoelectrics Handbook Macro to Nano. Taylor & Francis group, London New York (2006)
Nasir, S., Saleemi, A.S., Fatima-tuz-Zahra, Anis-ur-Rehman, M.: J. Alloys Compd. 572, 170 (2013)
Baba, S., Sato, H., Huang, L., Uritani, A., Funahashi, R., Akedo, J.: J. Alloys Compd. 589, 56 (2014)
Fergus, J.W.: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 525 (2012)
Anis-ur-Rehman, M., Maqsood, A.: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 35, 2040 (2002)
Zhang, F.P., Zhang, X., Lu, Q.M., Zhang, J.X., Liu, Y.Q., Zhang, G.Z.: Solid State Sci. 13, 1443 (2011)
Moon, Ji.W., Masuda, Y., Seo, W.S., Koumoto, K.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 85, 70 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, F., Munir, A., Saqib, M. et al. Introducing Rare Earth Dopants for Controlled Conductivity in Thermoelectric Cobaltites. J Supercond Nov Magn 28, 961–964 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2735-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2735-5