Abstract
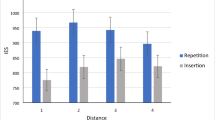
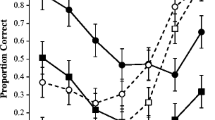
This paper examines evidence for a nonlexical influence on children’s repetition of real words. We investigate the extent to which two computational models of auditory repetition can simulate the performance of 68 children aged between 5 and 11 years-old when they are attempting to repeat familiar words. Both computational accounts were derived from Foygel and Dell’s (J Mem Lang 43:182–216, 2000) semantic-phonological model of picture-naming. Results showed that a dual-route model in which a lexical and a nonlexical route work together to repeat familiar words (Hanley et al. in Cogn Neuropsychol 21:147–158, 2004) provided an accurate simulation of children’s repetition, whereas Foygel and Dell (J Mem Lang 43:182–216, 2000) single lexical-route model under-predicted performance. The only exception was the repetition performance of 5 year-old children, which was over-predicted by the dual-route model. It is argued that at 5 years of age, some children have available both a lexical and a nonlexical repetition route but the output of the two routes does not summate when real words are being repeated. Some young children may lack the attentional skills that would enable them to co-ordinate the activity of the lexical and nonlexical repetition routes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel S., Huber W., Dell G. S. (2009) Connectionist diagnosis of lexical disorders in aphasia. Aphasiology 23: 1–26
Adams A. M., Gathercole S. E. (1995) Phonological working memory and speech production in pre-school children. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 38: 403–414
Baddeley A. D., Gathercole S. E., Papagno C. (1998) The phonological loop as a language learning device. Psychological Review 105: 158–173
Baron R., Hanley J. R., Dell G., Kay J. M. (2008) Testing single and dual-route computational models of auditory repetition with new data from six aphasic patients. Aphasiology 22: 62–76
Betts J., McKay J., Maruff P., Anderson V. (2006) The development of sustained attention in children: The effect of age and task load. Child Neuropsychology 12: 205–221
Budd M.-J., Hanley J. R., Griffiths Y. (2011) Simulating children’s retrieval errors in picture naming: A test of Foygel & Dell’s (2000) semantic/phonological model of speech production. Journal of Memory & Language 64: 74–87
Dell G. S., Martin N., Schwartz M. F. (2007) A case-series test of the interactive two-step model of lexical access: Predicting word repetition from picture naming. Journal of Memory and Language 56: 490–520
Dell G. S., Schwartz M. F., Martin N., Saffran E. M., Gagnon D. A. (1997) Lexical access in aphasic and nonaphasic speakers. Psychological Review 104: 801–838
Foygel D., Dell G. S. (2000) Models of impaired lexical access in speech production. Journal of Memory and Language 43: 182–216
Gathercole S. E. (1995) Is nonword repetition a test of phonological memory or long-term knowledge? It all depends on the nonwords. Memory and Cognition 23: 83–94
Gathercole S. E., Adams A.-M. (1993) Phonological working memory in very young children. Developmental Psychology 29: 770–778
Gathercole S. E., Baddeley A. D. (1989) Evaluation of the role of phonological short-term memory in the development of vocabulary in children: A longitudinal study. Journal of Memory and Language 28: 200–213
Gathercole S. E., Baddeley A. D. (1990) Phonological memory deficits in language-disordered children: Is there a causal connection?. Journal of Memory and Language 29: 336–360
Gupta P., Tisdale J. (2009) Does phonological short-term memory causally determine vocabulary learning? Toward a computational resolution of the debate. Journal of Memory and Language 61: 481–502
Hanley J. R., Dell G. A., Kay J., Baron R. (2004) Evidence for the involvement of a nonlexical route in the repetition of familiar words; A comparison of single and dual-route models of auditory repetition. Cognitive Neuropsychology 21: 147–158
Hanley J. R., Kay J., Edwards M. (2002) Imageability effects and phonological errors: Implications for models of auditory repetition. Cognitive Neuropsychology 19: 193–206
Hillis A., Carramazza A. (1991) Mechanisms for accessing lexical representations for output: Evidence from a category specific semantic deficit. Brain and Language 40: 106–144
Jescheniak J. D., Hahne A., Hoffman S., Wagner V. (2006) Phonological activation of category co-ordinates during speech planning is observable in children but not in adults: Evidence for cascaded processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory & Cognition 32: 373–386
Jones G., Gobet F., Pine J.M. (2008) Computer simulations of developmental change: The contributions of working memory and long-term knowledge. Cognitive Science: A Multidisciplinary Journal 32: 1148–1176
McNeil M. R., Odell K. H., Tseng C.-H. (1991) Towards the integration of resource allocationinto a general theory of aphasia. Clinical Aphasiology 20: 21–40
Murray L. L. (2000) The effects of varying attentional demands on the word retrieval skills of adults with aphasia, right hemisphere brain damage, or no brain damage. Brain and Language 72: 40–72
Nation K., Marshall M., Snowling M. J. (2001) Phonological and semantic contributions to children’s picture naming skill: Evidence from children with developmental reading disorders. Language and Cognitive Processes 16: 241–259
Nozari N., Kittredge A. K., Dell G. S., Schwartz M. F. (2010) Naming and repetition in aphasia: Steps, routes and frequency effects. Journal of Memory and Language 63: 541–559
Petry M. C., Crosson B., Gonzalez-Rothi L. J., Bauer R. M., Schauer C. A. (1994) Selective attention and aphasia in adults: Preliminary findings. Neuropsychologia 32: 1397–1408
Piaget J. (1952) The origins of intelligence in children. Basic Books, New York
Roelofs A. (2008) Dynamics of the attentional control of word retrieval: Analyses of response time distributions. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 137: 303–323
Schwartz M. F., Dell G. S., Martin N., Gahl S., Sobel P. (2006) A case-series test of the interactive two step model of lexical access: Evidence from picture naming. Journal of Memory and Language 54: 228–264
Service E. (1992) Phonology, working memory, and foreign language learning. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 45: 21–50
Stemberger J. M. (1989) Speech errors in early child language production. Journal of Memory and Language 28: 164–188
Vance M., Stackhouse J., Wells B. (2005) Speech production skills in children aged 3–7 years. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 40: 29–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Budd, MJ., Hanley, J.R. & Nozari, N. Evidence for a Non-Lexical Influence on Children’s Auditory Repetition of Familiar Words. J Psycholinguist Res 41, 253–266 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-011-9189-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-011-9189-8