Abstract
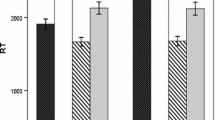
A person who has suffered the total loss of a sensory system has, indirectly, suffered a brain lesion. Semantic and phonologic verbal fluency are used for evaluation of executive function and language. The aim of this study is evaluation and comparison of phonemic and semantic verbal fluency in acquired blinds. We compare 137 blinds and 124 sighted people in verbal fluency task. The tasks were phonemic and semantic verbal fluency test that subjects should be generate as many word as possible in a limited amount of time for a given letter (Phonemic fluency) or a given category (Semantic fluency). Independent T Test was used to comparing blind with sighted. Findings show significant difference between two groups so that that sighted subjects have higher performance in semantic verbal fluency task (p = 0.000). Comparing sighted and blind subjects in phonemic verbal fluency task shows performance in sighted subjects (p = 0.000). Based on this study blinds have lower performance in semantic and phonemic verbal fluency task as a executive function of frontal lobe.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amedi A., Floel A., Knecht S., Zohary E., Cohen L. G. (2004) Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the occipital pole interferes with verbal processing in blind subjects. Nature Neuroscience 7: 1266–1270
Amedi A., Raz N., Pianka P., Malach R., Zohary E. (2003) Early ‘visual’ cortex activation correlates with superior verbal memory performance in the blind. Nature Neuroscience 6: 758–766
Burton H., Snyder A. Z., Conturo T. E., Akbudak E., Ollinger J. M., Raichle M. E. (2002) Adaptive changes in early and late blind: A fMRI study of Braille reading. Journal of Neurophysiology 87: 589–607
Burton H. (2003) Visual cortex activity in early and late blind people. Journal of Neuroscience 23: 4005–4011
Busse A. (2002) Adaptation of dementia screening for vision-impaired older persons: Administration of the mini-mental state examination (MMSE). Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 55: 909–915
Cabeza R., Nyberg L. (2000) Imaging cognition II: An empirical review of 275 PET and fMRI studies. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 12: 1–47
Chomsky N. (1980) Rules and Representations. Columbia University Press, New York
Dickins D. W., Singh K. D., Roberts N., Burns P., Downes J. J., Jimmieson P., Bentall R. P. (2001) An fMRI study of stimulus equivalence. NeuroReport 12: 405–411
Doucet M. E., Guillemot J. P., Lassonde M., Gagne J. P., Leclerc C., Lepore F. (2005) Blind subjects process auditory spectral cues more efficiently than sighted individuals. Experimental Brain Research 160: 194–202
Gaillard W. D., Hertz-Pannier L., Mott S. H., Barnett A. S., LeBihan D., Theodore W. H. (2000) Functional anatomy of cognitive development: fMRI of verbal fluency in children and adults. Neurology 54: 180–185
Goldreich D., Kanics I. M. (2003) Tactile acuity is enhanced in blindness. Journal of Neuroscience 23: 3439–3445
Gougoux F., Zatorre R. J., Lassonde M., Voss P., Lepore F. (2005) A functional neuroimaging study of sound localization: Visual cortex activity performance in early blind individuals. PLoS Biology 3: 27
Gougoux F., Lepore F., Lassonde M., Voss P., Zatorre R. J., Belin P (2004) Neuropsychology: Pitch discrimination in the early blind. Nature 430: 309
Grant A. C., Thiagarajah M. C., Sathian K. (2000) Tactile perception in blind Braille readers: A psychophysical study of acuity and hyperacuity using gratings and dot patterns. Perception & Psychophysics 62: 301–312
Hamilton R. H., Pascual-Leone A., Schlaug G. (2004) Absolute pitch in blind musicians. NeuroReport 15: 803–806
Hotting K., Röder B. (2004) Hearing cheats touch, but less in congenitally blind than in sighted individuals. Psychological Science 15: 60–64
Korten A. E. (1997) A prospective study of cognitive function in the elderly. Psychological Medicine 27: 9191–9930
Kujala T., Alho K., Huotilainen M., Ilmoniemi R.J., Lehtokoski A., Leinonen A. et al (1997) Electrophysiological evidence for cross-modal plasticity in humans with early- and late-onset blindness. Psychophysiology 34: 213–216
Kujala, T., Alho, K., Kekoni, J., Hamalainen, H., Reinikainen K., Salonen O. (1995) Auditory and somatosensory event-related brain potentials in early blind humans. Experimental Brain Research 104: 519–526
Leinonen A., Rinne T., Salonen O., Sinkkonen J., Standertskjold-Nordenstam C. G., Näätänen R. (1997) Electrophysiological evidence for cross-modal plasticity in humans with early and late-onset blindness. Psychophysiology 34: 213–216
Lezak M. D. (1995) Neuropsychological Assessment 3 edn. New York, Oxford
Linn R. T. (1995) The dpreclinical caseT of probable Alzheimer’s disease A-13 year prospective study of the Framingham cohort. Archives of Neurology 52: 485–490
Liotti M., Ryder K., Woldorff M.G. (1998) Auditory attention in the congenitally blind: Where, when and what gets reorganized?. NeuroReport 9: 1007–1012
Martin A., Wiggs C. L., Lalonde F., Mack C. (1994) Word retrieval to letter and semantic sues: A double association in normal subjects using interference tasks. Neuropsychologia 32: 1487–1494
Merabet L., Rizzo J., Amedi A., Somers D., Pascual-Leone A. (2005) What blindness can tell us about seeing again: Merging neuroplasticity and neuroprostheses. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 6: 71–77
Muchnik C., Efrati M., Nemeth E., Malin M., Hildesheimer M. (1991) Central auditory skills in blind and sighted subjects. Scandinavian Audiology 20: 19–23
Noppeney U., Friston K. J., Price C. J. (2003) Effects of visual deprivation on the organization of the semantic system. Brain 126: 1620–1627
Press, D. Z., Casement, M. D., Moo, L. R., & Alsop, D. C. (2004). Imaging phonological and semantic networks with fMRI. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. Viewer/Itinerary Planner. No. 80.13.
Ravnkilde B., Videbech P., Rosenberg R., Gjedde A., Gade A. (2002) Putative tests of frontal lobe function: A PET-study of brain activation during Stroop’s test and verbal fluency. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 24: 534–547
Reischies F. M., Geiselmann B. (1997) Age-related cognitive decline and vision impairment affecting the detection of dementia syndrome in old age. British Journal of Psychiatry 171: 449–451
Riedel-Heller S.G., Busse A., Anfermeyer M.C. (1997) Are cognitively impaired individuals adequately represented in community surveys? Recruitment challenges and strategies to facilitate participation in community surveys of older adults. A review. European Journal of Epidemiology, 16: 827–835
Roder B., Stock O., Bien S., Neville H., Rosler F. (2002) Speech processing activates visual cortex in congenitally blind humans. The European Journal of Neuroscience 16: 930–936
Röder B., Rösler F., Hennighausen E., Nacker F. (1996) Event related potentials during auditory and somatosensory discrimination in sighted and blind human subjects. Brain Research Cognitive Brain Research 4: 77–93
Röder B., Rösler F., Neville H. J. (1999a) Effects of interstimulus interval on auditory event-related potentials in congenitally blind and normally sighted humans. Neuroscience letters 264: 53–56
Röder B., Rösler F., Spence C. (2004) Early vision impairs tactile perception in the blind. Current Biology 14: 121–124
Röder B., Teder-Salejarvi W., Sterr A., Rösler F., Hillyard S. A., Neville H. J. (1999b) Improved auditory spatial tuning in blind humans. Nature 400: 162–166
Sterr A., Muller M. M., Elbert T., Rockstroh B., Pantev C., Taub E. (1998) Perceptual correlates of changes in cortical representation of fingers in blind multifinger Braille readers. Journal of Neuroscience 18: 4417–4423
Stevens A. A., Weaver K. (2005) Auditory perceptual consolidation in early-onset blindness. Neuropsychologia 43: 1901–1910
Theoret H., Merabet L., Pascual-Leone A. (2004) Behavioral and neuroplastic changes in the blind: Evidence for functionally relevant cross-modal interactions. Journal of Physiology, Paris 98(1-3): 221–233
Uhlmann R. F., Pearlman R. A. (1991) Perceived quality of life and preferences for life-sustaining treatment in older adults. Archives of Internal Medicine 151: 495–497
Van Boven R., Hamilton R., Kaufman T., Keenan J. P., Pascual-Leone A. (2000) Tactile spatial resolution in blind Braille readers. Neurology 54: 2030–2046
Voss P., Lassonde M., Gougoux F., Fortin M., Guillemot J. P., Lepore F. (2004) Early- and late-onset blind individuals show supra-normal auditory abilities in far-space. Current Biology 14: 1734–1738
Warren D. H. (1994) Blindness and children: An individual differences approach. Cambridge University Press, New York
Yabe T., Kaga K. (2005) Sound lateralization test in adolescent blind individuals. NeuroReport 16: 939–942
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nejati, V., Asadi, A. Semantic and Phonemic Verbal Fluency in Blinds. J Psycholinguist Res 39, 235–242 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-009-9136-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-009-9136-0