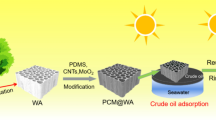
Abstract
Although photothermal materials (PMs) are widely utilized in pure water and seawater, there is less research on the design and preparation of multifunctional photothermal materials with organic dye adsorption and oil displacement properties. In this study, biomass carbon aerogel (BC) was prepared through a simple Ca2+ cross-linking and freeze-drying process. To enhance the antifouling performance of BC, hydrophilic and oleophobic chemical modification was conducted to obtain BC-SP. The contact angle of n-hexadecane can reach to 141.8°, which enable the extensive application of BC-SP in oil-bearing wastewater treatment. Notably, BC-SP exhibited exceptional light absorption efficiency (approximately 95%), excellent heat insulation performance (thermal conductivity 0.0650 W m− 1 K− 1), and rapid water transport capability. Under the irradiation of 1 kW m− 2, the solar energy conversion efficiency can reach to 86.8%. After tested eight cycles, the evaporation efficiency remained relatively stable and can adsorb most organic dyes in dye wastewater. Therefore, the study of BC-SP in this paper may has broad practical application prospects.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Code are available to readers.
References
W. Guan, Y. Guo, Yu, G(2021)Carbon materials for solar water evaporation and desalination. Small 17(48):e2007176
S. Yan, H. Song, Y. Li, J. Yang, X. Jia, S. Wang, Yang, X(2022)Integrated reduced graphene oxide/polypyrrole hybrid aerogels for simultaneous photocatalytic decontamination and water evaporation. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 301:120820
Y. Lu, D. Fan, H. Xu, H. Min, C. Lu, Z. Lin, Yang, X(2020)implementing hybrid energy harvesting in 3D spherical evaporator for solar steam generation and synergic water purification. Solar RRL 4(9):2000232
X. Zeng, W. Cai, S. Fu, X. Lin, Q. Lu, S. Liao, H. Hu, M. Zhang, C. Zhou, X. Wen, Tan S(2022)a novel Janus sponge fabricated by a green strategy for simultaneous separation of oil/water emulsions and dye contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 424(Pt B):127543
Z. Zhang, H. Liu, Z. Kong, M. Fang, M. Wang, Zhu, Y(2022)mushroom-like graphene nanosheets/copper sulfide nanowires foam with Janus-type wettability for solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 5(4):4931–4937
Q. Yang, C. Xu, F. Wang, Z. Ling, Z. Zhang, Fang, X(2019)a high-efficiency and low-cost interfacial evaporation system based on graphene-loaded pyramid polyurethane sponge for wastewater and seawater treatments. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2(10):7223–7232
Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, T. Xiong, H. Qu, J. Koh, D. Nandakumar, J. Wang, Tan, S(2020)manipulating unidirectional fluid transportation to drive sustainable solar water extraction and brine-drenching induced energy generation. Energy Environ. Sci. 13(12):4891–4902
W. Li, X. Tian, X. Li, J. Liu, C. Li, X. Feng, C. Shu, Yu, Z(2022)an environmental energy-enhanced solar steam evaporator derived from MXene-decorated cellulose acetate cigarette filter with ultrahigh solar steam generation efficiency. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 606(Pt 1):748–757
F. Wang, J. Li, W. Bai, C. Wang, Li, A(2021)recent progress on the solar-driven interfacial evaporation based on natural products and synthetic polymers. Solar RRL 5(12):2100475
J. Li, X. Zhou, Y. Jing, H. Sun, Z. Zhu, W. Liang, Li, A(2021)ionic liquid-assisted alignment of corn straw microcrystalline cellulose aerogels with low tortuosity channels for salt-assistance solar steam evaporators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(10):12181–12190
C. Xiao, Q. Hasi, S. Wang, Y. Zhang, H. Li, L. Zhang, L. Chen, Li, A(2022)hollow SiO2 microspheres in-situ doped poly(ionicliquid)s gels as efficient solar steam generators for desalination. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 613:661–670
S. Zhao, L. Chen, C. Zhang, Q. Hasi, L. Zhang, X. Luo, Li, A(2020)functional oil-repellent photothermal materials based on nickel foam for efficient solar steam generation. Sol Energy Mater. Sol Cells 214:110574
J. Chen, B. Li, G. Hu, R. Aleisa, S. Lei, F. Yang, D. Liu, F. Lyu, M. Wang, X. Ge, F. Qian, Q. Zhang, Yin Y(2020)Integrated evaporator for efficient solar-driven interfacial steam generation. Nano Lett. 20(8):6051–6058
Z. Wang, Y. Yan, X. Shen, C. Jin, Q. Sun, Li, H(2019)a wood-polypyrrole composite as a photothermal conversion device for solar evaporation enhancement. J. Mater. Chem. A 7(36):20706–20712
Y. Ding, K. Feng, P. He, N. Liu, L. Hao, J. Gong, R. Niu, Qu, J(2021)a synergistic photothermal and photocatalytic membrane for efficient solar-driven contaminated water treatment. Sustain. Energy Fuels 5(21):5627–5637
C. Xiao, S. Wang, Y. Guo, Y. Zhang, Q. Hasi, Q. Tian, Chen, L(2022)Coffee grounds-doped alginate porous materials for efficient solar steam generation.Langmuir 38(5):1888–1896
X. Liu, D.D. Mishra, X. Wang, H. Peng, Hu, C(2020)towards highly efficient solar-driven interfacial evaporation for desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 8(35): 17907–17937
F. Wang, D. Wei, Y. Li, T. Chen, P. Mu, H. Sun, Z. Zhu, W. Liang, Li, A(2019)Chitosan/reduced graphene oxide-modified spacer fabric as a salt-resistant solar absorber for efficient solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 7(31):18311–18317
L. Chen, M. Xia, J. Du, X. Luo, L. Zhang, Li, A(2020)superhydrophilic and oleophobic porous architectures based on basalt fibers as oil-repellent photothermal materials for solar steam generation. ChemSusChem 13(3):493–500
W. Li, M.C. Tekell, Y. Huang, K. Bertelsmann, M. Lau, Fan, D(2018)synergistic high-rate solar steaming and mercury removal with MoS2/C @ polyurethane composite sponges. Adv. Energy Mater. 8(32):1802108
M. Xia, J. Wei, Z. Han, Q. Tian, C. Xiao, Q.-M. Hasi, Y. Zhang, Chen, L(2022)an integrated solar absorber with salt-resistant and oleophobic based on PVDF composite membrane for solar steam generation. Mater. Today Energy 25:100959
L. Chen, X. Mu, Y. Guo, H. Lu, Y. Yang, C. Xiao, Hasi Q(2022)MXene-doped kapok fiber aerogels with oleophobicity for efficient interfacial solar steam generation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 626:35–46
P. Mu, W. Bai, Y. Fan, Z. Zhang, H. Sun, Z. Zhu, W. Liang, Li, A(2019)conductive hollow kapok fiber-PPy monolithic aerogels with excellent mechanical robustness for efficient solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 7(16):9673–9679
Z. Yu, P. Wu, Biomimetic MXene-polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel with vertically aligned channels for highly efficient solar steam generation. Adv. Mater. Technol. 5(6), 2000065 (2020)
Z. Xiong, Y. Zhu, Z. Wang, Y. Chen, H. Yu, (2021)tree-inspired ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires‐based multifunctional aerogel with vertically aligned channels for continuous flow catalysis, water disinfection, and solar energy‐driven water purification. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32(9):2106978
D. Li, S. Chen, R. Huang, C. Xue, P. Li, Y. Li, Q. Chang, H. Wang, N. Li, S. Jia, S. Hu, J. Yang, (2021)Photothermal, photocatalytic, and anti-bacterial Ti-Ag-O nanoporous powders for interfacial solar driven water evaporation. Ceram. Int. 47(14):19800–19808
S. Zhao, M. Xia, Y. Zhang, Q. Hasi, J. Xu, Chen, L(2021)novel oil-repellent photothermal materials based on copper foam for efficient solar steam generation. Sol Energy Mater. Sol Cells 225:111058
J. Yang, Z. Zhang, X. Xu, X. Zhu, X. Men, Zhou X(2012)superhydrophilic-superoleophobic coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 22(7):2834
Q. Hasi, Y. Guo, S. Wang, J. Yu, Z. Han, C. Xiao, Y. Zhang, Chen, L(2022)conjugated microporous polymer-coated sponges for effectively removal of oils and trace aromatic pollutions in water. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 139(31):e52731
H. Qin, T. Hu, Y. Zhai, N. Lu, Aliyeva, J(2020)the improved methods of heavy metals removal by biosorbents: a review. Environ. Pollut 258:113777
H. Zhang, X. Song, J. Zhang, Y. Liu, H. Zhao, J. Hu, Zhao, J(2022)performance and mechanism of sycamore flock based biochar in removing oxytetracycline hydrochloride. Bioresour Technol. 350:126884
X. Sheng, H. Shi, L. Yang, P. Shao, K. Yu, Luo X(2021)rationally designed conjugated microporous polymers for contaminants adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 750:141683
L. Chen, J. Wei, Q. Tian, Z. Han, L. Li, S. Meng, Hasi Q(2021)dual-functional graphene oxide-based photothermal materials with aligned channels and oleophobicity for efficient solar steam generation. Langmuir 37(33):10191–10199
K. Xu, Q. Hasi, X. Mu, C. Xiao, Y. Zhang, X. Jiang, J. Xu, L. Chen, A. Li, )lipophilic, nanocellulose based macroporous sponge loaded with mixed microorganisms for efficient elimination of petroleum hydrocarbon pollution in water. Cellulose. 29(11), 6161–6179 (2022)
W. Li, W. Feng, S. Wu, W. Wang, D. Yu, Sep. Purif. Technol. 292, 120989 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors are supported by the Talent Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project of Lanzhou (Grant No. 2022-RC-16), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22365026), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 31920230167).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shun Lu synthesized the materials and performed sample characterization. Qi Tian and Xiaotong Mu conducted the experiment. Jiale Yu, Qimeige Hasi and Yuhan Zhang performed data analysis and theoretical investigation. Chaohu Xiao and Lihua Chen participated in experimental scheme design and revised the manuscript. The manuscript was written by all the authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, S., Xiao, C., Tian, Q. et al. Superhydrophilic and oleophobic porous aerogel based on biomass carbon for solar-dirven interfacial evaporation. J Porous Mater (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-024-01606-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-024-01606-8