Abstract
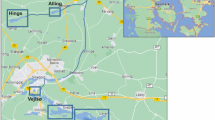
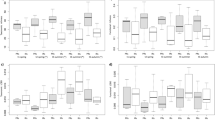
We investigated how the history of local disturbances in a watershed can influence the regional coherence of ecosystem properties in lakes that have similar morphometry and climatic conditions. We measured sedimentary δ13C, δ15N, C:N and %BSiO2 in Sooke Lake Reservoir (SOL) and Shawnigan Lake (SHL), which are located within 4 km of each other on Vancouver Island, Canada. SOL is an impounded lake whose watershed has been fully protected over the last century, although the lake level has been raised 3 times via impoundment during this period. SHL has a similar limnological regime, but the surrounding watershed has been developed extensively for residential uses. We investigated how a pulse disturbance regime in SOL (i.e. repeated dam raising) and a press disturbance regime in SHL (i.e. persistent development) influenced the variability of paleoindicators in each system over time. We found that these contrasting disturbance regimes reduced the regional temporal coherence of aquatic productivity between the two lakes (indicated by %BSiO2), but did not influence the regional coherence of nutrient status or the main carbon sources of the lakes (indicated by %C, %N and δ13C). In contrast, an indicator of the sources and cycling of nitrogen (δ15N) showed increased coherence. Local disturbances also affected the variability of the paleoindicators within each system over time. In SOL, impoundments led to both declines (%N, δ15N) and increases (δ13C) in the variability of paleoindicators. In SHL, persistent watershed development led to lower variability of two paleoindicators (%N, %BSiO2). Overall, our data suggest that local disturbances can influence the %BSiO2 and C:N ratio of lake sediments, but are less likely to alter the regional coherence of %C, %N and δ13C between lakes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller RC (1994) Bioturbation and remineralization of sedimentary organic matter: effects of redox oscillation. Chem Geol 114:331–345. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(94)90062-0
Appleby PG (2001) Chronostratigraphic techniques in recent sediments. In: Last WM, Smol JP (eds) Tracking environmental change using lake sediments. Volume 1: basin analysis, coring, and chronological techniques. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 171–203
Appelby PG, Oldfield F (1978) The calculation of lead-210 dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment. Catena 5:1–18. doi:10.1016/S0341-8162(78)80002-2
Barraclough CL (1995) Paleolimnological elucidation of the historical water quality of SOL Reservoir, Victoria, British Columbia, by diatom stratigraphic analysis. M. Sc. Thesis, University of Victoria, Victoria, British Columbia, Canada
Bender EA, Case TJ, Gilpin ME (1984) Perturbation experiments in community ecology: theory and practice. Ecology 65:1–13. doi:10.2307/1939452
Bradbury JP, Van Metre PC (1997) A land-use and water-quality history of White Rock Lake reservoir, Dallas, Texas, based on paleolimnological analyses. J Paleolimnol 17:227–237. doi:10.1023/A:1007923829759
Cairns J Jr (1995) Urban runoff in an integrated landscape context. In: Herricks EE (ed) Stormwater runoff and receiving systems. Lewis, Chelsea, pp 9–20
Carpenter SR, Brock WA (2006) Rising variance: a leading indicator of ecological transition. Ecol Lett 9:311–318. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00877.x
Carpenter SR, Caraco NF, Correll DL, Howarth RW, Sharply AN, Smith VH (1998) Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol Appl 8:559–568. doi:10.1890/1051-0761(1998)008[0559:NPOSWW]2.0.CO;2
Chmura GL, Santos A, Pospelova V, Spasojevic Z, Lam R, Latimer JS (2004) Response of three paleo-primary production proxy measures to development of an urban estuary. Sci Total Environ 320:225–243. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.08.003
Conley DJ, Malone TC (1992) Annual cycle of dissolved silicate in Chesapeake Bay: implications for the production and fate of phytoplankton biomass. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 81:121–128. doi:10.3354/meps081121
Conley DJ, Schelske CL (2001) Biogenic silica. In: Smol JP, Birks HJB, Last WM (eds) Tracking environmental changes using lake sediments. Vol. 3: terrestrial, algal, and siliceous indicators. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 281–293
Cottingham KL, Rusak JA, Leavitt PR (2000) Increased ecosystem variability and reduced predictivity following fertilization: evidence from paleolimnology. Ecol Lett 3:340–348. doi:10.1046/j.1461-0248.2000.00158.x
CRD (Capital Region District) (1999) Strategic plan for water management. Vol. 3: watershed management. Capital Region District, British Columbia
Davies JM, Nowlin WH, Mazumder A (2004) Temporal changes in nitrogen and phosphorus codeficiency of plankton in lakes of coastal and interior British Columbia. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 61:1538–1551. doi:10.1139/f04-092
DeAngelis DL, Waterhouse JC (1987) Equilibrium and nonequilibrium concepts in ecological models. Ecol Monogr 571:1–21. doi:10.2307/1942636
Douglas TA, Chamberlain CP, Blum JD (2002) Land use and geologic controls on the major elemental and isotopic (δ15N and 87Sr/86Sr) geochemistry of the Connecticut River watershed, USA. Geology 189:19–34. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00047-5
Edgington ES (1987) Randomization tests. Marc Dekker Inc, New York
Finney BP, Gregory-Eaves I, Sweetman J, Douglas MSV, Smol JP (2000) Impacts of climatic change and fishing on Pacific salmon abundances over the past 300 years. Science 290:795–799. doi:10.1126/science.290.5492.795
Friedli H, LöTscher H, Oeschger H, Siegenthaler U, Stauffer B (1986) Ice core record of the 13C/12C ratio of atmospheric CO2 in the past two centuries. Nature 324:237–238. doi:10.1038/324237a0
Fry B (1991) Stable isotope diagrams of freshwater food webs. Ecology 72(6):2293–2297. doi:10.2307/1941580
Gaedeke A, Sommer U (1986) The influence of the frequency of periodic disturbances on the maintenance of phytoplankton diversity. Oecologia 71:25–28. doi:10.1007/BF00377315
Glazebrook HS, Robertson AI (1999) The effect of flooding the flood timing on leaf litter breakdown rates and nutrient dynamics in a river red gum (Eucalyptus camaldulensis) forest. J Ecol 24:625–635
Hecky RE, Kilham P (1988) Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: a review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnol Oceanogr 33(4):796–822
Hilborn R, Mangel M (1997) The ecological detective: confronting models with data. Monographs in population biology, vol 28. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Jeppesen E, Sondergaard M, Kronvang B, Jensen JP, Svendsen LM, Lauridsen TL (1999) Lake and catchment management in Denmark. Hydrobiologia 395(396):419–432. doi:10.1023/A:1017071602549
Kaushal SS, Lewis WM Jr, McCutchan JH Jr (2006) Land use change and nitrogen enrichment of a rocky mountain watershed. Ecol Appl 16:299–312. doi:10.1890/05-0134
Kliza D, Telmer K (2001) Phase I: lake sediment studies in the vicinity of the Horne smelter in Rouyn-Noranda, Quebec. GSC-Open File D2952, Geological Survey of Canada, Natural Resources Canada, 18 pp + annx
Kratz TK, Frost TM, Magnuson JJ (1987) Inferences from spatial and temporal variability in ecosystems: long-term zooplankton data from lakes. Am Nat 129:830–846. doi:10.1086/284678
Lake JL, McKinney RA, Osterman FA, Pruell RJ, Kiddon J, Ryba SA et al (2001) Stable nitrogen isotopes as indicators of anthropogenic activities in small freshwater systems. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58:870–878. doi:10.1139/cjfas-58-5-870
Langhans AD, Tockner K (2005) The role of timing, duration, and frequency of inundation in controlling leaf litter decomposition in a river-floodplain ecosystem (Tagliamento, northeastern Italy). Oecologia 147:501–509. doi:10.1007/s00442-005-0282-2
Larmola T, Alm J, Juutinen S, Saarnio S, Martikainen PJ, Silvola J (2004) Floods can cause large interannual differences in littoral net ecosystem productivity. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1896–1906
Lehmann MF, Bernasconi SM, Barbieri A, McKenzie JA (2002) Preservation of organic matter and alteration of its carbon and nitrogen isotope composition during simulated and in situ early sedimentary diagenesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:3573–3584. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00968-7
MacKay DK (1966) Characteristics of river drainage and runoff in Canada. Geogr Bull 8:219–227
Magnuson JJ, Benson BJ, Kratz TK (1990) Temporal coherence in the limnology of a suite of lakes in Wisconsin, USA. Freshw Biol 23:145–159. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.1990.tb00259.x
Mariotti A (1983) Atmospheric nitrogen is a reliable standard for natural l5N abundance measurements. Nature 303:685–687. doi:10.1038/303685a0
Meyers PA (1994) Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter. Chem Geol 114:289–302. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(94)90059-0
Meyers PA, Ishiwatari R (1993) Lacustrine organic geochemistry—an overview of indicators of organic matter sources and diagenesis in lake sediments. Org Geochem 20:867–900. doi:10.1016/0146-6380(93)90100-P
Nowlin WH, Davies JM, Nordin RN, Mazumder A (2004) Effects of water level fluctuations and short-term climate variation on thermal and stratification regimes of a British Columbia reservoir and lake. J Lake Reserv Manag 20:91–109
Patoine A, Leavitt PR (2006) Century-long synchrony of fossil algae in a chain of Canadian prairie lakes. Ecology 87:1710–1721. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1710:CSOFAI]2.0.CO;2
Peterson BJ, Fry B (1987) Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 18:293–320. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.18.110187.001453
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing (version 2.6.2). R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Reynolds CS (1984) The ecology of freshwater phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rosenmeier MF, Brenner M, Kenney WF, Whitmore TJ, Taylor CM (2004) Recent eutrophication in the southern basin of Lake Petén Itźa, Guatemala: human impact on a large tropical lake. Hydrobiologia 511:161–172. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000014038.64403.4d
Rosenzweig ML (1971) Paradox of enrichment: destabilization of exploitation ecosystems in ecological time. Science 171:385–387. doi:10.1126/science.171.3969.385
Rusak JA, Yan ND, Somers KM, McQueen DJ (1999) The temporal coherence of zooplankton population abundances in neighboring north-temperate lakes. Am Nat 153:46–58. doi:10.1086/303147
Schindler DW, Fee EJ, Ruszczynski T (1978) Phosphorus input and its consequences for phytoplankton standing crop and production in the experimental lakes area and in similar lakes. J Fish Res Board Can 35:190–196
Sollins P, Spycher G, Glassman CA (1984) Net nitrogen mineralization from light fraction and heavy fraction forest soil organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 16:31–37. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(84)90122-6
Spafard MA, Nowlin WH, Davies JM, Mazumder A (2002) A morphometric atlas of selected lakes in southern British Columbia: Vancouver Island, Saltspring Island, and the Kooteney region. University of Victoria Press, Victoria
SPSS Inc (2008) SPSS 15.0 for Windows. SPSS Inc., Chicago
Teranes JL, Bernasconi SM (2000) The record of nitrate utilization and productivity limitation provided by δ15N values in lake organic matter—a study of sediment trap and core sediments from Bladeggersee, Switzerland. Limnol Oceanogr 45:801–813
Tilman D, Sterner RW (1984) Invasions of equilibria: tests of resource competition using two species of algae. Oecologia 61:197–200. doi:10.1007/BF00396760
Tilman D, Knops J, Wedin D, Reich P, Ritchie M, Siemann E (1997) The influence of functional diversity and composition on ecosystem processes. Science 277:1300–1302. doi:10.1126/science.277.5330.1300
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JMH (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment. Nature 441:629–632. doi:10.1038/nature04742
Tuller SE (1979) Climate, chap 4. In: Forward CN (ed) Vancouver Island, Land of contrasts. University of Victoria, Victoria, pp 71–91
Underwood AJ (1991) Beyond BACI: experimental designs for detecting human environmental impacts on temporal variations in natural populations. Aust J Mar Freshwater Res 42:569–587. doi:10.1071/MF9910569
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall Inc., Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, USA
Zhu Z, Nordin R, Mazumder A (2007) Soil and vegetation as the determinants of lake nitrogen concentrations in forested watersheds in British Columbia, Canada. Ecol Indic 8:431–441. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2007.04.006
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Simon Thomson and Shane Edmison for helping with sediment core collection, Sergei Verenitch, Shapna Mazumder and Jutta Kolhi for laboratory analysis, and Rick Espie and Christopher Lowe for editorial correction and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments that markedly improved the paper. This research was supported by an NSERC CGSD to Biplob Das, an NSERC CGSM to Anita Narwani, an NSERC IRC to Asit Mazumder, and by partnership support from CRD Water Services to Asit Mazumder.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biplob Das and Anita Narwani contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, B., Narwani, A., Matthews, B. et al. Anthropogenic disturbance history influences the temporal coherence of paleoproductivity in two lakes. J Paleolimnol 42, 167–181 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-008-9269-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-008-9269-4