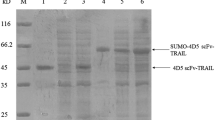
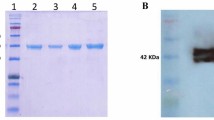
Abstract
Along with all cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgery, targeting therapy is a new treatment manner. Immunotoxins are new recombinant structures that kill cancer cells by targeting specific antigens. Immunotoxins are composed of two parts: toxin moiety, which disrupts protein synthesis process, and antigen binding moiety that bind to antigens on the surface of cancer cells. Glypican 3 (GPC3) is an oncofetal antigen on the surface of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. In this study, truncated Diphtheria toxin (DT389) was fused to humanized scFv YP7 by one, two and three repeats of GGGGS linkers (DT389-(GGGGS)1-3YP7). In-silico and experimental investigation were performed to find out how many repeats of linker between toxin and scFv moieties are sufficient. Results of in-silico investigations revealed that the difference in the number of linkers does not have a significant effect on the main structures of the immunotoxin; however, the three-dimensional structure of two repeats of linker had a more appropriate structure compared to others with one and three linker replications. In addition, with enhancing the number of linkers, the probability of protein solubility has increased. Generally, the bioinformatics results of DT389-(GGGGS)2-YP7 structure showed that expression and folding is suitable; and YP7 scFv has appropriate orientation to bind GPC3. The experimental investigations indicated that the fusion protein was expressed as near to 50% soluble. Due to the high binding affinity of YP7 scFv and the proven potency of diphtheria in inhibiting protein synthesis, the proposed DT389-(GGGGS)2-YP7 immunotoxin is expected to function well in inhibiting HCC.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR (2019) A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0186-y
Parvin S, Sedighian H, Sohrabi E, Mahboobi M, Rezaei M, Ghasemi D et al (2021) Prediction of genes involved in lung cancer with a systems biology approach based on comprehensive gene information. Biochem Genet 60(4):1253–1273
Sohrabi E, Moslemi M, Rezaie E, Nafissi N, Khaledi M, Afkhami H et al (2021) The tissue expression of MCT3, MCT8, and MCT9 genes in women with breast cancer. Genes Genomics 43(9):1065–1077
Li N, Gao W, Zhang Y-F, Ho M (2018) Glypicans as cancer therapeutic targets. Trends Cancer 4(11):741–754
Nakano K, Ishiguro T, Konishi H, Tanaka M, Sugimoto M, Sugo I et al (2010) Generation of a humanized anti-glypican 3 antibody by CDR grafting and stability optimization. Anticancer Drugs 21(10):907–916
Hashemi Yeganeh H, Heiat M, Kieliszek M, Alavian SM, Rezaie E (2021) DT389-YP7, a recombinant immunotoxin against glypican-3 that inhibits hepatocellular cancer cells: an in vitro study. Toxins 13(11):749
Heiat M, Hashemi Yeganeh H, Alavian SM, Rezaie E (2021) Immunotoxins immunotherapy against hepatocellular carcinoma: a promising prospect. Toxins 13(10):719
Potala S, Sahoo SK, Verma RS (2008) Targeted therapy of cancer using diphtheria toxin-derived immunotoxins. Drug Discovery Today 13(17–18):807–815
Williams D, Parker K, Bacha P, Bishai W, Borowski M, Genbauffe F et al (1987) Diphtheria toxin receptor binding domain substitution with interleukin-2: genetic construction and properties of a diphtheria toxin-related interleukin-2 fusion protein. Protein Eng Des Sel 1(6):493–498
Rezaie E, Mohammadi M, Sakhteman A, Bemani P, Ahrari S (2018) Application of molecular dynamics simulations to design a dual-purpose oligopeptide linker sequence for fusion proteins. J Mol Model 24(11):313
Mohammadi M, Rezaie E, Sakhteman A, Zarei N (2020) A highly potential cleavable linker for tumor targeting antibody-chemokines. J Biomol Str Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1841025
Keshtvarz M, Mahboobi M, Kieliszek M, Miecznikowski A, Sedighian H, Rezaei M et al (2021) Engineering of cytolethal distending toxin B by its reducing immunogenicity and maintaining stability as a new drug candidate for tumor therapy; an in silico study. Toxins 13(11):785
Chen X, Zaro JL, Shen W-C (2013) Fusion protein linkers: property, design and functionality. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(10):1357–1369
Wang Z, Wei M, Zhang H, Chen H, Germana S, Huang CA et al (2015) Diphtheria-toxin based anti-human CCR4 immunotoxin for targeting human CCR4+ cells in vivo. Mol Oncol 9(7):1458–1470
Zheng Q, Wang Z, Zhang H, Huang Q, Madsen JC, Sachs DH et al (2017) Diphtheria toxin-based anti-human CD 19 immunotoxin for targeting human CD 19+ tumors. Mol Oncol 11(5):584–594
Liger D, van der Spek JC, Gaillard C, Cansier C, Murphy JR, Leboulch P et al (1997) Characterization and receptor specific toxicity of two diphtheria toxin-related interleukin-3 fusion proteins DAB389–mIL-3 and DAB389–(Gly4Ser) 2-mIL-3. FEBS Lett 406(1–2):157–161
Rezaie E, Amani J, Pour AB, Hosseini HM (2020) A new scfv-based recombinant immunotoxin against EPHA2-overexpressing breast cancer cells; High in vitro anti-cancer potency. Eur J Pharmacol 870:172912
Gao W, Tang Z, Zhang Y-F, Feng M, Qian M, Dimitrov DS et al (2015) Immunotoxin targeting glypican-3 regresses liver cancer via dual inhibition of Wnt signalling and protein synthesis. Nat Commun 6(1):1–12
Fleming BD, Ho M (2020) Development of glypican-3 targeting immunotoxins for the treatment of liver cancer: an update. Biomolecules 10(6):934
Michalska M, Wolf P (2015) Pseudomonas exotoxin A: optimized by evolution for effective killing. Front Microbiol 6:963
Wang C, Gao W, Feng M, Pastan I, Ho M (2017) Construction of an immunotoxin, HN3-mPE24, targeting glypican-3 for liver cancer therapy. Oncotarget 8(20):32450
Zhang Y-F, Ho M (2016) Humanization of high-affinity antibodies targeting glypican-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep 6(1):1–11
Lee GR, Heo L, Seok C (2016) Effective protein model structure refinement by loop modeling and overall relaxation. Proteins 84:293–301
Magnan CN, Randall A, Baldi P (2009) SOLpro: accurate sequence-based prediction of protein solubility. Bioinformatics 25(17):2200–2207
Zeng P, Li H, Lu P-H, Zhou L-N, Tang M, Liu C-Y et al (2017) Prognostic value of CD146 in solid tumor: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 7(1):1–7
Gao W, Kim H, Feng M, Phung Y, Xavier CP, Rubin JS et al (2014) Inactivation of Wnt signaling by a human antibody that recognizes the heparan sulfate chains of glypican-3 for liver cancer therapy. Hepatology 60(2):576–587
Ahmad ZA, Yeap SK, Ali AM, Ho WY, Alitheen NBM, Hamid M (2012) scFv antibody: principles and clinical application. Clin Dev Immunol 2012(8):980250
Liu TF, Cohen KA, Ramage JG, Willingham MC, Thorburn AM, Frankel AE (2003) A diphtheria toxin-epidermal growth factor fusion protein is cytotoxic to human glioblastoma multiforme cells. Can Res 63(8):1834–1837
Rezaie E, Bidmeshki Pour A, Amani J, Mahmoodzadeh HH (2020) Bioinformatics predictions, expression, purification and structural analysis of the PE38KDEL-scfv immunotoxin against EPHA2 receptor. Int J Pept Res Ther 26(2):979–996
Idicula-Thomas S, Balaji PV (2007) Protein aggregation: a perspective from amyloid and inclusion-body formation. Curr Sci 92:758–767
Idicula-Thomas S, Balaji PV (2007) Correlation between the structural stability and aggregation propensity of proteins. In Silico Biol 7(2):225–237
Wriggers W, Chakravarty S, Jennings PA (2005) Control of protein functional dynamics by peptide linkers. Biopolymers 80(6):736–746
Keshtvarz M, Salimian J, Yaseri M, Bathaie SZ, Rezaie E, Aliramezani A et al (2017) Bioinformatic prediction and experimental validation of a PE38-based recombinant immunotoxin targeting the Fn14 receptor in cancer cells. Immunotherapy 9(5):387–400
Xun S, Jiang F, Wu Y-D (2015) Significant refinement of protein structure models using a residue-specific force field. J Chem Theory Comput 11(4):1949–1956
Saito Y, Kitagawa W, Kumagai T, Tajima N, Nishimiya Y, Tamano K et al (2019) Developing a codon optimization method for improved expression of recombinant proteins in actinobacteria. Sci Rep 9(1):1–10
Kolb P, Ferreira RS, Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK (2009) Docking and chemoinformatic screens for new ligands and targets. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20(4):429–436
Sousa SF, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ (2006) Protein–ligand docking: current status and future challenges. Proteins 65(1):15–26
Kuntz ID, Blaney JM, Oatley SJ, Langridge R, Ferrin TE (1982) A geometric approach to macromolecule-ligand interactions. J Mol Biol 161(2):269–288
Dyson MR, Shadbolt SP, Vincent KJ, Perera RL, McCafferty J (2004) Production of soluble mammalian proteins in Escherichia coli: identification of protein features that correlate with successful expression. BMC Biotechnol 4(1):32
Canaves JM, Page R, Wilson IA, Stevens RC (2004) Protein biophysical properties that correlate with crystallization success in Thermotoga maritima: maximum clustering strategy for structural genomics. J Mol Biol 344(4):977–991
Goh C-S, Lan N, Douglas SM, Wu B, Echols N, Smith A et al (2004) Mining the structural genomics pipeline: identification of protein properties that affect high-throughput experimental analysis. J Mol Biol 336(1):115–130
Gräslund S, Nordlund P, Weigelt J, Hallberg BM, Bray J, Gileadi O et al (2008) Protein production and purification. Nat Methods 5(2):135
Jevševar S, Gaberc-Porekar V, Fonda I, Podobnik B, Grdadolnik J, Menart V (2005) Production of nonclassical inclusion bodies from which correctly folded protein can be extracted. Biotechnol Prog 21(2):632–639
Li Y, Chen Z (2008) RAPD: a database of recombinantly-produced antimicrobial peptides. FEMS Microbiol Lett 289(2):126–129
Ventura S (2005) Sequence determinants of protein aggregation: tools to increase protein solubility. Microb Cell Fact 4(1):1–8
Funding
This work was supported by the NIMAD: National institute for medical research development (Grant No. 983134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH, MH, and EH designed the chimeric protein for the article. HH and EH assessed the chimeric protein through various bioinformatics softwares and drafted the early version of the manuscript. HH, MH, and EH evaluated and discussed the software and the results. EH and MH provided comments on the manuscript and contributed to editing of the manuscript. MA received the grant for the current study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Research Involving Human and Animal Participants
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi Yeganeh, H., Heiat, M., Alavian, S.M. et al. A New Combination: Anti Glypican-3 scFv and Diphtheria Toxin with the Best Flexible Linker. Protein J 41, 527–542 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-022-10074-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-022-10074-5