Abstract
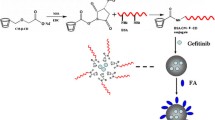
Targeted delivery via surface receptors can significantly improve the therapeutic efficacy and reduce adverse drug reactions. The protein nanocarrier system offers many advantages, including encapsulation in various drugs and molecules and prolonged circulation. Here, the folate receptor-targeted folic acid-conjugated retinoic acid-loaded glutenin nanoparticles (FA-RA-Glu NPs) were successfully synthesised for enhanced delivery of retinoic acid to breast cancer cells (MCF-7). After a complete physico-chemical characterisation of FA-RA-Glu NPs, stability, drug release, release kinetics, cytotoxicity, apoptosis, cell death, and nucleic acid fragmentation were analysed. The results showed that FA-RA-Glu NPs were ⁓185 nm in size, predominantly spherical in shape, crystalline in nature and had a zeta potential of − 3 mV. The RA encapsulation efficiency and loading capacity of Glu NPs were 83.537 ± 3.32% and 9.917 ± 1.68%, respectively. The effects of FA-RA-Glu NPs against MCF-7 cells significantly reduced the number of viable cells and induced apoptosis. The cellular uptake study showed that the FA-RA-Glu NPs had facilitated endocytosis and delivered RA into MCF-7 cells. After treatment with FA-RA-Glu NPs, contracted nuclei and deformed membrane bodies were observed as typical apoptotic morphological changes. The released RA significantly increasing the levels of reactive oxygen species and contributing to the damage of mitochondrial membrane integrity. These results suggest that FA-RA-Glu NPs with facilitated endocytosis and targeted delivery of RA into MCF-7 cells may have significant therapeutic potential for treating breast cancer.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this manuscript.
References
Hejmady S, Pradhan R, Alexander A, Agrawal M, Singhvi G, Gorain B, Tiwari S, Kesharwani P, Dubey SK (2020) Recent advances in targeted nanomedicine as promising antitumor therapeutics. Drug Discov Today 25(12):2227–2244
Yap KM, Sekar M, Fuloria S, Wu YS, Gan SH, Mat Rani NNI, Subramaniyan V, Kokare C, Lum PT, Begum MY (2021) Drug delivery of natural products through nanocarriers for effective breast cancer therapy: a comprehensive review of literature. Int J Nanomed 16:7891–7941
Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer (1997) Cancer, Breast cancer and hormone replacement therapy: collaborative reanalysis of data from 51 epidemiological studies of 52 705 women with breast cancer and 108 411 women without breast cancer. The Lancet 350(9084):1047–1059
Youlden DR, Cramb SM, Dunn NA, Muller JM, Pyke CM, Baade PD (2012) The descriptive epidemiology of female breast cancer: an international comparison of screening, incidence, survival and mortality. Cancer epidemiol 36(3):237–248
Ganesan V, Gurumani V, Kunjiappan S, Panneerselvam T, Somasundaram B, Kannan S, Chowdhury A, Saravanan G, Bhattacharjee C (2018) Optimization and analysis of microwave-assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from Mimosa pudica L. using RSM & ANFIS modeling. J Food Meas Charact 12:228–242
Tang R-Z, Liu Z-Z, Gu S-S, Liu X-Q (2021) Multiple local therapeutics based on nano-hydrogel composites in breast cancer treatment. J Mater Chem B 9(6):1521–1535
Wang X, Zhang H, Chen X (2019) Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist 2(2):141
Vasconcelos MH, Caires HR, Ābols A, Xavier CP, Linē A (2019) Extracellular vesicles as a novel source of biomarkers in liquid biopsies for monitoring cancer progression and drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat 47:100647
Muhammad Mailafiya M, Abubakar K, Danmaigoro A, Musa Chiroma S, Bin Abdul Rahim E, Aris Mohd Moklas M, Abu Bakar Zakaria Z (2019) Cockle shell-derived calcium carbonate (aragonite) nanoparticles: a dynamite to nanomedicine. Appl Sci 9(14):2897
Jung E, Jeong SW, Lee Y, Jeon C, Shin H, Song N, Lee Y, Lee D (2022) Self-deliverable and self-immolative prodrug nanoassemblies as tumor targeted nanomedicine with triple cooperative anticancer actions. Biomaterials 287:121681
Chen M-C, Hsu S-L, Lin H, Yang T-Y (2014) Retinoic acid and cancer treatment. Biomedicine 4(4):22
Perri M, Pingitore A, Cione E, Vilardi E, Perrone V, Genchi G (2010) Proliferative and anti-proliferative effects of retinoic acid at doses similar to endogenous levels in Leydig MLTC-1/R2C/TM-3 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gen Subj 1800(9):993–1001
Yuan M, Yan T-H, Li J, Xiao Z, Fang Y, Wang Y, Zhou H-C, Pellois J-P (2021) Superparamagnetic iron oxide–gold nanoparticles conjugated with porous coordination cages: towards controlled drug release for non-invasive neuroregeneration. Nanomed: Nanotechnol Biol Med 35:102392
Gonçalves A, Estevinho BN, Rocha F (2019) Characterization of biopolymer-based systems obtained by spray-drying for retinoic acid controlled delivery. Powder Technol 345:758–765
Öztürk B (2017) Nanoemulsions for food fortification with lipophilic vitamins: production challenges, stability, and bioavailability. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 119(7):1500539
Kunjiappan S, Govindaraj S, Parasuraman P, Sankaranarayanan M, Arunachalam S, Palanisamy P, Mohan UP, Babkiewicz E, Maszczyk P, Vellaisamy S (2020) Design, in silico modelling and functionality theory of folate-receptor-targeted myricetin-loaded bovine serum albumin nanoparticle formulation for cancer treatment. Nanotechnology 31(15):155102
Cui C, Liu W (2021) Recent advances in wet adhesives: adhesion mechanism, design principle and applications. Prog Polym Sci 116:101388
Kianfar E (2021) Protein nanoparticles in drug delivery: animal protein, plant proteins and protein cages, albumin nanoparticles. J Nanobiotechnology 19(1):159
Lindsay MP, Skerritt JH (1999) The glutenin macropolymer of wheat flour doughs: structure–function perspectives. Trends Food Sci Technol 10(8):247–253
Malekzad H, Mirshekari H, Sahandi Zangabad P, Moosavi Basri S, Baniasadi F, Sharifi Aghdam M, Karimi M, Hamblin MR (2018) Plant protein-based hydrophobic fine and ultrafine carrier particles in drug delivery systems. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38(1):47–67
Li F, Qiu C, Li M, Xiong L, Shi Y, Sun Q (2019) Preparation and characterization of redox-sensitive glutenin nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 137:327–336
Prieto C, Talón E, Lagaron J (2021) Room temperature encapsulation of algae oil in water insoluble gluten extract. Food Hydrocoll Health 1:100022
Reddy N, Shi Z, Xu H, Yang Y (2015) Development of wheat glutenin nanoparticles and their biodistribution in mice. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 103(5):1653–1658
Geersing A, de Vries RH, Jansen G, Rots MG, Roelfes G (2019) Folic acid conjugates of a bleomycin mimic for selective targeting of folate receptor positive cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem letters 29(15):1922–1927
Nosrati H, Abbasi R, Charmi J, Rakhshbahar A, Aliakbarzadeh F, Danafar H, Davaran S (2018) Folic acid conjugated bovine serum albumin: an efficient smart and tumor targeted biomacromolecule for inhibition folate receptor positive cancer cells. Int J Biol Macromol 117:1125–1132
Soleymani J, Hasanzadeh M, Somi MH, Jouyban A (2020) The role of nanomaterials on the cancer cells sensing based on folate receptor: analytical approach. TrAC Trends Analyt Chem 125:115834
Scaranti M, Cojocaru E, Banerjee S, Banerji U (2020) Exploiting the folate receptor α in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17(6):349–359
Vinothini K, Rajendran NK, Ramu A, Elumalai N, Rajan M (2019) Folate receptor targeted delivery of paclitaxel to breast cancer cells via folic acid conjugated graphene oxide grafted methyl acrylate nanocarrier. Biomed Pharmacother 110:906–917
Norton N, Youssef B, Hillman DW, Nassar A, Geiger XJ, Necela BM, Liu H, Ruddy KJ, Polley M-YC, Ingle JN (2020) Folate receptor alpha expression associates with improved disease-free survival in triple negative breast cancer patients. NPJ Breast Cancer 6(1):4
Akbarian A, Ebtekar M, Pakravan N, Hassan ZM (2020) Folate receptor alpha targeted delivery of artemether to breast cancer cells with folate-decorated human serum albumin nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 152:90–101
Rana A, Bhatnagar S (2021) Advancements in folate receptor targeting for anti-cancer therapy: a small molecule-drug conjugate approach. Bioorg Chem 112:104946
Rajeshkumar RR, Pavadai P, Panneerselvam T, Deepak V, Pandian SRK, Kabilan SJ, Vellaichamy S, Jeyaraman A, Kumar ASK, Sundar K (2023) Glucose-conjugated glutenin nanoparticles for selective targeting and delivery of camptothecin into breast cancer cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02480-y
Elzoghby AO, Samy WM, Elgindy NA (2012) Albumin-based nanoparticles as potential controlled release drug delivery systems. J control release 157(2):168–182
Kunjiappan S, Sankaranarayanan M, Kumar BK, Pavadai P, Babkiewicz E, Maszczyk P, Glodkowska-Mrowka E, Arunachalam S, Pandian SRK, Ravishankar V (2020) Capsaicin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: design, biodistribution, in silico modeling and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation. Nanotechnology 32(9):095101
Baskararaj S, Panneerselvam T, Govindaraj S, Arunachalam S, Parasuraman P, Pandian SRK, Sankaranarayanan M, Mohan UP, Palanisamy P, Ravishankar V (2020) Formulation and characterization of folate receptor-targeted PEGylated liposome encapsulating bioactive compounds from Kappaphycus alvarezii for cancer therapy. 3 Biotech 10:1–18
Yang R, An Y, Miao F, Li M, Liu P, Tang Q (2014) Preparation of folic acid-conjugated, doxorubicin-loaded, magnetic bovine serum albumin nanospheres and their antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomed. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S67210
Kunjiappan S, Theivendran P, Baskararaj S, Sankaranarayanan B, Palanisamy P, Saravanan G, Arunachalam S, Sankaranarayanan M, Natarajan J, Somasundaram B (2019) Modeling a pH-sensitive Zein-co-acrylic acid hybrid hydrogels loaded 5-fluorouracil and rutin for enhanced anticancer efficacy by oral delivery. 3 Biotech 9:1–20
Hassanpour M, Jafari H, Sharifi S, Rezaie J, Lighvan ZM, Mahdavinia GR, Gohari G, Akbari A (2021) Salicylic acid-loaded chitosan nanoparticles (SA/CTS NPs) for breast cancer targeting: synthesis, characterization and controlled release kinetics. J Mol Struct 1245:131040
Lazzari S, Moscatelli D, Codari F, Salmona M, Morbidelli M, Diomede L (2012) Colloidal stability of polymeric nanoparticles in biological fluids. J Nanopart Res 14:1–10
Mohan UP, Sriram B, Panneerselvam T, Devaraj S, MubarakAli D, Parasuraman P, Palanisamy P, Premanand A, Arunachalam S, Kunjiappan S (2020) Utilization of plant-derived Myricetin molecule coupled with ultrasound for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles against breast cancer. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 393:1963–1976
Attallah OA, Shetta A, Elshishiny F, Mamdouh W (2020) Essential oil loaded pectin/chitosan nanoparticles preparation and optimization via Box-Behnken design against MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines. RSC Adv 10(15):8703–8708
Mohan Viswanathan T, Krishnakumar V, Senthilkumar D, Chitradevi K, Vijayabhaskar R, Rajesh Kannan V, Senthil Kumar N, Sundar K, Kunjiappan S, Babkiewicz E (2022) Combinatorial delivery of gallium (III) nitrate and curcumin complex-loaded hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for breast cancer treatment. Nanomaterials 12(9):1472
Kunjiappan S, Theivendren P, Sankaranarayanan M, Somasundaram B, Subbarayan S, Arunachalam S, Parasuraman P, Sivakumar V, Murugan I, Baskararaj S (2019) Design, graph theoretical analysis and bioinformatic studies of proanthocyanidins encapsulated ethyl cellulose nanoparticles for effective anticancer activity. Biomed Phys Eng Exp 5(2):025004
Cimini A, D’Angelo B, Das S, Gentile R, Benedetti E, Singh V, Monaco AM, Santucci S, Seal S (2012) Antibody-conjugated PEGylated cerium oxide nanoparticles for specific targeting of Aβ aggregates modulate neuronal survival pathways. Acta biomater 8(6):2056–2067
Gijsens A, Derycke A, Missiaen L, De Vos D, Huwyler J, Eberle A, de Witte P (2002) Targeting of the photocytotoxic compound AlPcS4 to Hela cells by transferrin conjugated PEG-liposomes. Int J Cancer 101(1):78–85
Sahtout AH, Hassan M, Shariff M (2001) DNA fragmentation, an indicator of apoptosis, in cultured black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon infected with white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). Dis Aquat Org 44(2):155–159
Alizadeh F, Bolhassani A, Khavari A, Bathaie SZ, Naji T, Bidgoli SA (2014) Retinoids and their biological effects against cancer. Int Immunopharmacol 18(1):43–49
Napoli JL (2016) Functions of intracellular retinoid binding-proteins, the biochemistry of retinoid signaling II: the physiology of vitamin A-uptake, transport. Metabolism Signal. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-0945-1_2
Kunjiappan S, Pavadai P, Vellaichamy S, Ram Kumar Pandian S, Ravishankar V, Palanisamy P, Govindaraj S, Srinivasan G, Premanand A, Sankaranarayanan M (2021) Surface receptor-mediated targeted drug delivery systems for enhanced cancer treatment: a state-of-the-art review. Drug Dev Res 82(3):309–340
Dimov N, Kastner E, Hussain M, Perrie Y, Szita N (2017) Formation and purification of tailored liposomes for drug delivery using a module-based micro continuous-flow system. Sci Rep 7(1):12045
Chowdhury A, Kunjiappan S, Panneerselvam T, Somasundaram B, Bhattacharjee C (2017) Nanotechnology and nanocarrier-based approaches on treatment of degenerative diseases. Inter Nano Lett 7:91–122
Stevison F, Jing J, Tripathy S, Isoherranen N (2015) Role of retinoic acid-metabolizing cytochrome P450s, CYP26, in inflammation and cancer. Adv Pharmacol 74:373–412
Clark HW, Sees KL, Nathan JA (1988) Clinical and legal aspects of nonphysician prescription of vitamins, amino acids, and other nutritional supplements. J Psychoact Drugs 20(3):355–374
N. Capurso, Development of a nanoparticulate drug delivery vehicle for retinoic acid, (2011).
Mohan S, Oluwafemi OS, Kalarikkal N, Thomas S, Songca SP (2016) Biopolymers–application in nanoscience and nanotechnology. Recent Adv Biopolymers 1(1):47–66
Reddy MSB, Ponnamma D, Choudhary R, Sadasivuni KK (2021) A comparative review of natural and synthetic biopolymer composite scaffolds. Polymers 13(7):1105
Kalimuthu AK, Pandian SRK, Pavadai P, Panneerselvam T, Kabilan SJ, Sankaranarayanan M, Ala C, Kunjiappan S (2023) Drug delivery applications of exopolysaccharides from endophytic bacteria Pseudomonas otitidis from Tribulus terrestris L. J Polym Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-02848-4
Moore TL, Rodriguez-Lorenzo L, Hirsch V, Balog S, Urban D, Jud C, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Lattuada M, Petri-Fink A (2015) Nanoparticle colloidal stability in cell culture media and impact on cellular interactions. Chem Soc Rev 44(17):6287–6305
Li Y, Kröger M, Liu WK (2015) Shape effect in cellular uptake of PEGylated nanoparticles: comparison between sphere, rod, cube and disk. Nanoscale 7(40):16631–16646
Gregoriou Y, Gregoriou G, Yilmaz V, Kapnisis K, Prokopi M, Anayiotos A, Strati K, Dietis N, Constantinou AI, Andreou C (2021) Resveratrol loaded polymeric micelles for theranostic targeting of breast cancer cells. Nanotheranostics 5(1):113
Honary S, Zahir F (2013) Effect of zeta potential on the properties of nano-drug delivery systems-a review (Part 2). Trop J Pharm Res 12(2):265–273
He C, Hu Y, Yin L, Tang C, Yin C (2010) Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31(13):3657–3666
Tavakol S, Hoveizi E, Kharrazi S, Tavakol B, Karimi S, Rezayat Sorkhabadi SM (2017) Organelles and chromatin fragmentation of human umbilical vein endothelial cell influence by the effects of zeta potential and size of silver nanoparticles in different manners. Artif Cells, Nanomed, Biotechnol 45(4):817–823
Kayani Z, Bordbar A-K, Firuzi O (2018) Novel folic acid-conjugated doxorubicin loaded β-lactoglobulin nanoparticles induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother 107:945–956
Kunjiappan S, Panneerselvam T, Somasundaram B, Arunachalam S, Sankaranarayanan M, Parasuraman P (2018) Preparation of liposomes encapsulated epirubicin-gold nanoparticles for tumor specific delivery and release. Biomed Phys Eng Express 4(4):045027
Cai J, Yang J, Jones D (1998) Mitochondrial control of apoptosis: the role of cytochrome c. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 1366(1–2):139–149
Acknowledgements
RRR thanks to Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education for the university research fellowship.
Funding
SK gratefully acknowledge the Management of Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education for Seed Money Grant (KARE/VC/R&D/SMPG/2021–2022/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, resources, writing review & editing; RRR, PP, SRKP, ASKK writing-original draft, formal analysis, investigation; TP, SJK, PM, EB conceptualization, writing, investigation and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval was not required for this research.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
The authors give the consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajeshkumar, R.R., Pavadai, P., Panneerselvam, T. et al. Enhanced Delivery of Retinoic Acid to Breast Cancer Cells by Folate Receptor-Targeted Folic Acid-Conjugated Glutenin Nanoparticles for Promising Treatment of Breast Cancer. J Polym Environ (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03107-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-03107-2