Abstract
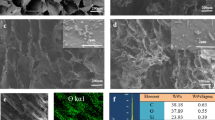
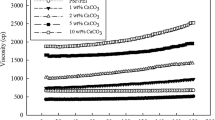
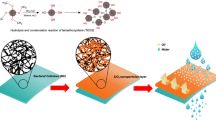
In this study, pure cellulose acetate (CA) and rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) seed shell activated carbon (RSSAC) blended CA membranes were fabricated by the phase-inversion technique. Results indicate that the composite membranes exhibit increased water content, porosity and pore size. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) images reveal that no pores visibly found at the surface of membrane. The atomic force microscopic images (AFM) indicate an decreased squared average roughness (Rq) of membrane upto 1 wt% of RSSAC additives. Filtration experiments were conducted to evaluate the performance of membranes for the chemical oxygen demand (COD) and waste engine oil removal efficiency. The results evince that the COD and waste engine oil removal efficiency of composite membrane increased than the pure CA membrane, which is due to the attraction of hydrocarbon towards the composite membrane. Further, in comparison with pure CA, the antifouling properties of the composite membranes were found to be significantly improved.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li J, Liu Q, Liu Y, Xie J (2017) Development of electro-active forward osmosis membranes to remove phenolic compounds and reject salts. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 3(1):139–146. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00275G
Zhu Y, Wang D, Jiang L, Jin J (2014) Recent progress in developing advanced membranes for emulsified oil/water separation. NPG Asia Mater 6(5):e101. https://doi.org/10.1038/am.2014.23
Ahmad AL, Majid MA, Ooi BS (2011) Functionalized PSf/SiO2 nanocomposite membrane for oil-in-water emulsion separation. Desalination 268:266–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.017
Mansourizadeh A, Azad AJ (2014) Preparation of blend polyethersulfone/cellulose acetate/polyethylene glycol asymmetric membranes for oil–water separation. J Polym Res 21(375):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0375-x
Velu S, Rambabu K, Muruganandam L (2014) Development, characterization and application studies of cellulose acetate–activated carbon blend ultra filtration membranes. IJCRGG 6(1):565–577
Zhou J, Chen J, He M, Yao J (2016) Cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals: preparation and characterization. J Appl Polym Sci 133:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43946
Mukherjee R, De S (2016) Preparation, characterization and application of powdered activated carbon–cellulose acetate phthalate mixed matrix membrane for treatment of steel plant effluent. Polym Adv Technol 27:444–459. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.3690
Rana D, Scheier B, Narbaitz RM, Matsuura T, Tabe S, Jasim SY, Khulbe KC (2012) Comparison of cellulose acetate (CA) membrane and novel CA membranes containing surface modifying macromolecules to remove pharmaceutical and personal care product micropollutants from drinking water. J Membr Sci 409:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.04.005
Savova D, Apak E, Ekinci E, Yardim F, Petrov N, Budinova T, Razvigorova M, Minkova V (2001) Biomass conversion to carbon adsorbents and gas. Biomass Bioenergy 21(2):133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0961-9534(01)00027-7
Ioannidou O, Zabaniotou A (2007) Agricultural residues as precursors for activated carbon production—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 11(9):1966–2005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2006.03.013
Abduh MY, Manurung R, Heeres HJ (2017) Techno-economic analysis for small scale production of rubber seed oil and biodiesel in Palangkaraya, Indonesia. J Clean Energy Technol 5(4):268–273. https://doi.org/10.18178/jocet.2017.5.4.381
Deng J, Xiong T, Wang H, Zheng A, Wang Y (2016) Effects of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin on the structure and morphology of porous carbons. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(7):3750–3756. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00388
Bagheri S, Julkapli NM (2016) Effect of hybridization on the value-added activated carbon materials. Int J Ind Chem 7(3):249–264
Imanah JE, Okieimen FE (2003) Rheological and mechanical properties of natural rubber reinforced with agricultural byproduct. J Appl Polym Sci 90(13):3718–3722. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.13058
Osabohien E, Egboh SHO (2007) Cure characteristics and physico-mechanical properties of natural rubber filled with the seed shells of cherry (Chrysophyllum albidum). J Appl Environ Manag 11(2):43–48. https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v11i2.54983
Khalil HPS, Jawaid M, Firoozian P, Rashid U, Islam A, Akil HM (2013) Activated carbon from various agricultural wastes by chemical activation with KOH: preparation and characterization. J Biobased Mater 7(6):708–714. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbmb.2013.1379
Rengaraj S, Moon SH, Sivabalan R, Arabindoo B, Murugesan V (2002) Removal of phenol from aqueous solution and resin manufacturing industry wastewater using an agricultural waste: rubber seed coat. J Hazard Mater 89:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00308-9
Hameed BH, Daud FBM (2008) Adsorption studies of basic dye on activated carbon derived from agricultural waste: Hevea brasiliensis seed coat. Chem Eng J 139(1):48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.07.089
Liou TH (2010) Development of mesoporous structure and high adsorption capacity of biomass-based activated carbon by phosphoric acid and zinc chloride activation. Chem Eng J 158(2):129–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.12.016
Bai H, Zhou Y, Wang X, Zhang L (2012) The permeability and mechanical properties of cellulose acetate membranes blended with polyethylene glycol 600 for treatment of municipal sewage. Procedia Environ Sci 16:346–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.10.049
Shoba B, Jeyanthi J, Vairam S (2020) Synthesis, characterization of cellulose acetate membrane and application for the treatment of oily wastewater. Environ Technol 41(12):1590–1605. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1543353
Kumar A, Jena HM (2016) Preparation and characterization of high surface area activated carbon from Fox nut (Euryale ferox) shell by chemical activation with H3PO4. Results Phys 6:651–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2016.09.012
Senthilkumar ST, Senthilkumar B, Balaji S, Sanjeeviraja C, Kalai Selvan R (2011) Preparation of activated carbon from sorghum pith and its structural and electrochemical properties. Mater Res Bull 46(3):413–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2010.12.002
Isahak WNRW, Hisham MWM, Yarmo MA (2013) Highly porous carbon materials from biomass by chemical and carbonization method: a comparison study. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/620346
Demirbas E, Dizge N, Sulak MT, Kobya M (2009) Adsorption kinetics and equilibrium of copper from aqueous solutions using hazelnut shell activated carbon. Chem Eng J 148(2–3):480–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.09.027
Rao MM, Ramesh A, Rao GPC, Seshaiah K (2006) Removal of copper and cadmium from the aqueous solutions by activated carbon derived from Ceiba pentandra hulls. J Hazard Mater 129(1–3):123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.018
Khenniche L, Benissad-Aissani F (2010) Adsorptive removal of phenol by coffee residue activated carbon and commercial activated carbon: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics. J Chem Eng Data 55(11):4677–4686. https://doi.org/10.1021/je100302e
Rodrigues LA, da Silva MLCP, Alvarez-Mendes MO, dos Reis Coutinho A, Thim GP (2011) Phenol removal from aqueous solution by activated carbon produced from avocado kernel seeds. Chem Eng J 174(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.027
Sivakumar B, Kannan C, Karthikeyan S (2012) Preparation and characterization of activated carbon prepared from balsamodendron caudatum wood waste through various activation processes. Rasayan J Chem 5:321–327
van den Berg T, Ulbricht M (2020) Polymer nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes: the influence of polymeric additive, dispersion quality and particle modification on the integration of zinc oxide nanoparticles into polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Membranes 10(9):197
Nada AA, Abdellatif FHH, Soliman AA, Shen J, Hudson SM, Abou-Zeid NY (2019) Fabrication and bioevaluation of a medicated electrospun mat based on azido-cellulose acetate via click chemistry. Cellulose 26(18):9721–9736
Bagheripour E, Moghadassi AR, Hosseini SM, Ray MB, Parvizian F, Van der Bruggen B (2018) Highly hydrophilic and antifouling nanofiltration membrane incorporated with water-dispersible composite activated carbon/chitosan nanoparticles. Chem Eng Res Des 132:812–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2018.02.027
Hong CH, Ki SJ, Jeon JH, Che HL, Park IK, Kee CD, Oh IK (2013) Electroactive bio-composite actuators based on cellulose acetate nanofibers with specially chopped polyaniline nanoparticles through electrospinning. Compos Sci Technol 87:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.08.006
Hassan M, Berglund L, Abou-Zeid R, Hassan E, Abou-Elseoud W, Oksman K (2019) Nanocomposite film based on cellulose acetate and lignin-rich rice straw nanofibers. Materials 12(4):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12040595
Han B, Zhang D, Shao Z, Kong L, Lv S (2013) Preparation and characterization of cellulose acetate/carboxymethyl cellulose acetate blend ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 311:80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.11.002
Zinadini S, Zinatizadeh AA, Rahimi M, Vatanpour V, Zangeneh H (2014) Preparation of a novel antifouling mixed matrix PES membrane by embedding graphene oxide nanoplates. J Membr Sci 453:292–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.10.070
Arif Z, Sethy NK, Kumari L, Mishra PK, Verma B (2019) Antifouling behaviour of PVDF/TiO2 composite membrane: a quantitative and qualitative assessment. Iran Polym J 28(4):301–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-019-00700-y
Arthanareeswaran G, Devi TS, Raajenthiren M (2008) Effect of silica particles on cellulose acetate blend ultrafiltration membranes: Part I. Sep Purif Technol 64(1):38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2008.08.010
Yan L, Li YS, Xiang CB (2005) Preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) ultrafiltration membrane modified by nano-sized alumina (Al2O3) and its antifouling research. Polymer 46:7701–7706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2005.05.155
Jusoh N, Keong LK, Mohd Shariff A (2014) Preparation and characterization of polysulfone membrane for gas separation. Adv Mater Res 917:307–316
Huang J, Zhang K, Wang K, Xie Z, Ladewig B, Wang H (2012) Fabrication of polyethersulfone–mesoporous silica nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes with antifouling properties. J Membr Sci 423:362–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.08.029
Setiawan WK, Chiang KY (2019) Silica applied as mixed matrix membrane inorganic filler for gas separation: a review. Sustain Environ Res 29(1):1–21
Hong SK, Bae S, Jeon H, Kim M, Cho SJ, Lim G (2018) An underwater superoleophobic nanofibrous cellulosic membrane for oil/water separation with high separation flux and high chemical stability. Nanoscale 10(6):3037–3045
Li HJ, Cao YM, Qin JJ, Jie XM, Wang TH, Liu JH, Yuan Q (2006) Development and characterization of anti-fouling cellulose hollow fiber UF membranes for oil–water separation. J Membr Sci 279(1–2):328–335
Chakrabarty B, Ghoshal AK, Purkait MK (2008) Ultrafiltration of stable oil-in-water emulsion by polysulfone membrane. J Membr Sci 325(1):427–437
Salahi A, Gheshlaghi A, Mohammadi T, Madaeni SS (2010) Experimental performance evaluation of polymeric membranes for treatment of an industrial oily wastewater. Desalination 262(1–3):235–242
Fang J, Qin G, Wei W, Zhao X, Jiang L (2013) Elaboration of new ceramic membrane from spherical fly ash for microfiltration of rigid particle suspension and oil-in-water emulsion. Desalination 311:113–126
Suresh K, Srinu T, Ghoshal AK, Pugazhenthi G (2016) Preparation and characterization of TiO2 and γ-Al2O3 composite membranes for the separation of oil-in-water emulsions. RSC Adv 6(6):4877–4888
Li J, Xu C, Tian H, Zha F, Qi W, Wang Q (2018) Blend-electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride)/stearic acid membranes for efficient separation of water-in-oil emulsions. Colloids Surf A 538:494–499
Hong X, Zhang B, Zhang X, Wu Y, Wang T, Qiu J (2019) Tailoring the structure and property of microfiltration carbon membranes by polyacrylonitrile-based microspheres for oil–water emulsion separation. J Water Process Eng 32:100973
Zioui D, Salazar H, Aoudjit L, Martins PM, Lanceros-Méndez S (2020) Polymer-based membranes for oily wastewater remediation. Polymers 12(1):42
Arthanareeswaran G, Thanikaivelan P (2010) Fabrication of cellulose acetate–zirconia hybrid membranes for ultrafiltration applications: performance, structure and fouling analysis. Sep Purif Technol 74(2):230–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2010.06.010
Yin J, Fan H, Zhou J (2016) Cellulose acetate/poly (vinyl alcohol) and cellulose acetate/crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) blend membranes: preparation, characterization, and antifouling properties. Desalin Water Treat 57(23):10572–10584
Acknowledgements
We would like to show our gratitude to the Centre of Excellence for Environmental Studies, Government College of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India for providing facilities required for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shoba, B., Jeyanthi, J. Performance Analysis of Rubber Seed Shell Activated Carbon Incorporated Polymeric Membrane for the Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsion. J Polym Environ 30, 1055–1071 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02261-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02261-9