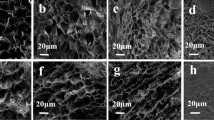
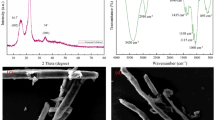
Abstract
Bacterial cellulose (BC) aerogel has great potential in treating oil spill and organic pollutant. However, its inherent hydrophilicity and poor rigidity limit its practical application and recyclability. In this study, elastically compressible and high oil-absorbing aerogels were developed by freeze-drying aqueous suspensions with appropriate BC concentrations, followed by a chemical vapor deposition of methyltrimethoxysilane with ammonia as catalyst. The modified aerogel shows high water contact angle of 142° and enhanced compression resistance. The effect of BC concentration on the absorption capacity and recyclability of aerogel has been investigated. The results show that the aerogel prepared with 0.3 wt% BC exhibits simultaneously high absorption capacity (121.8–284.1 g/g) and excellent recyclability. Futhermore, the aerogel could also separate chloroform-water mixture by gravity-driven filtration, giving the separation efficiency of 96.7%. Therefore, this economical green aerogel provides a feasible strategy for solving oil leakage in industry.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Meng Z, Liu J, Schlaich C, Yu Z, Deng X (2017) Breath figure lithography for the construction of a hierarchical structure in sponges and their applications to oil/water separation. J Mater Chem A 5(31):16369–16375. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA02751F
Wang Y, He Y, Fan Y, Li H, Yu H, Yu J et al (2021) A robust anti-fouling multifunctional aerogel inspired by seaweed for efficient water purification. Sep Purif Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118153
Viswanathan K, Wang S (2021) Experimental investigation on the application of preheated fish oil ethyl ester as a fuel in diesel engine. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119244
Li J, Xu C, Guo C, Tian H, Zha F, Guo L (2018) Underoil superhydrophilic desert sand layer for efficient gravity-directed water-in-oil emulsions separation with high flux. J Mater Chem A 6(1):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta08076j
Wang FP, Zhao XJ, Wahid F, Zhao XQ, Qin XT, Bai H et al (2021) Sustainable, superhydrophobic membranes based on bacterial cellulose for gravity-driven oil/water separation. Carbohydr Polym 253:117220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117220
Oshima T, Sakamoto T, Ohe K, Baba Y (2014) Cellulose aerogel regenerated from ionic liquid solution for immobilized metal affinity adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 103:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.12.021
Long S, Feng Y, Liu Y, Zheng L, Gan L, Liu J et al (2021) Renewable and robust biomass carbon aerogel derived from deep eutectic solvents modified cellulose nanofiber under a low carbonization temperature for oil-water separation. Sep Purif Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117577
Jiang J, Zhang Q, Zhan X, Chen F (2019) A multifunctional gelatin-based aerogel with superior pollutants adsorption, oil/water separation and photocatalytic properties. Chem Eng J 358:1539–1551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.144
Zhan C, Jana SC (2020) Shrinkage reduced polyimide-graphene oxide composite aerogel for oil absorption. Micropor Mesopor Mat. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110501
Zhang X, Zhang T, Yi Z, Yan L, Liu S, Yao X et al (2020) Multiscale mullite fiber/whisker reinforced silica aerogel nanocomposites with enhanced compressive strength and thermal insulation performance. Ceram Int 46(18):28561–28568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.013
Lu Y, Niu Z, Yuan W (2019) Multifunctional magnetic superhydrophobic carbonaceous aerogel with micro/nano-scale hierarchical structures for environmental remediation and energy storage. Appl Surf Sci 480:851–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.060
Karzar Jeddi M, Laitinen O, Liimatainen H (2019) Magnetic superabsorbents based on nanocellulose aerobeads for selective removal of oils and organic solvents. Mater Design. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108115
Yang J, Xia Y, Xu P, Chen B (2018) Super-elastic and highly hydrophobic/superoleophilic sodium alginate/cellulose aerogel for oil/water separation. Cellulose 25(6):3533–3544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1801-8
Hu J, Zhu J, Ge S, Jiang C, Guo T, Peng T et al (2020) Biocompatible, hydrophobic and resilience graphene/chitosan composite aerogel for efficient oil−water separation. Surf Coat Tech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125361
Yang H, Zhang S, Yan J (2020) Chitosan-reinforced MFC/NFC aerogel and antibacterial property. Adv Polym Tech 2020:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7890215
Cheng Z, Li J, Wang B, Zeng J, Xu J, Gao W et al (2020) Scalable and robust bacterial cellulose carbon aerogels as reusable absorbents for high-efficiency oil/water separation. ACS Appl Bio Mater 3(11):7483–7491. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c00708
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsen J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40(7):3941–3994. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00108b
Klemm D, Kramer F, Moritz S, Lindstrom T, Ankerfors M, Gray D et al (2011) Nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50(24):5438–5466. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201001273
Hou G-Y, Lyu Z-Y, Tang Y-P, Cao H-Z, Zheng G-Q (2020) Preparation of flexible composite electrode with bacterial cellulose (BC)-derived carbon aerogel supported low loaded NiS for methanol electrocatalytic oxidation. Int J Hydrogen Energ 45(32):16049–16059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.04.005
Zhang X, Zhao X, Xue T, Yang F, Fan W, Liu T (2020) Bidirectional anisotropic polyimide/bacterial cellulose aerogels by freeze-drying for super-thermal insulation. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123963
Wu ZY, Li C, Liang HW, Chen JF, Yu SH (2013) Ultralight, flexible, and fire-resistant carbon nanofiber aerogels from bacterial cellulose. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52(10):2925–2929. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201209676
Zhu W, Yao Y, Zhang Y, Jiang H, Wang Z, Chen W et al (2020) Preparation of an amine-modified cellulose nanocrystal aerogel by chemical vapor deposition and its application in CO2 capture. Ind Eng Chem Res 59(38):16660–16668. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c02687
Wang J, Liu S (2019) Remodeling of raw cotton fiber into flexible, squeezing-resistant macroporous cellulose aerogel with high oil retention capability for oil/water separation. Sep Purif Technol 221:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.03.097
Yi L, Xia Y, Tan Z, Fang X, Zhao L, Wu H et al (2020) Design of tubelike aerogels with macropores from bamboo fungus for fast oil/water separation. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121558
Wang Q, Tian D, Hu J, Huang M, Shen F, Zeng Y et al (2020) Harvesting bacterial cellulose from kitchen waste to prepare superhydrophobic aerogel for recovering waste cooking oil toward a closed-loop biorefinery. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(35):13400–13407. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04212
Sai H, Fu R, Xing L, Xiang J, Li Z, Li F et al (2015) Surface modification of bacterial cellulose aerogels’ web-like skeleton for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(13):7373–7381. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b00846
He J, Zhao H, Li X, Su D, Zhang F, Ji H et al (2018) Superelastic and superhydrophobic bacterial cellulose/silica aerogels with hierarchical cellular structure for oil absorption and recovery. J Hazard Mater 346:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.12.045
Liu H, Geng B, Chen Y, Wang H (2016) Review on the aerogel-type oil sorbents derived from nanocellulose. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(1):49–66. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02301
Wang J, Zhang W, Zhang C (2019) Versatile fabrication of anisotropic and superhydrophobic aerogels for highly selective oil absorption. Carbon 155:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.08.049
Jiménez-Saelices C, Seantier B, Cathala B, Grohens Y (2017) Effect of freeze-drying parameters on the microstructure and thermal insulating properties of nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn 84(3):475–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4451-7
Azimi Yancheshme A, Momen G, Jafari Aminabadi R (2020) Mechanisms of ice formation and propagation on superhydrophobic surfaces: A review. Adv Colloid Interfac 279:102155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102155
Dilamian M, Noroozi B (2021) Rice straw agri-waste for water pollutant adsorption: Relevant mesoporous super hydrophobic cellulose aerogel. Carbohydr Polym 251:117016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117016
Li L, Hu T, Sun H, Zhang J, Wang A (2017) Pressure-sensitive and conductive carbon aerogels from poplars catkins for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(21):18001–18007. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b04687
Lu J, Xu D, Wei J, Yan S, Xiao R (2017) Superoleophilic and flexible thermoplastic polymer nanofiber aerogels for removal of oils and organic solvents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(30):25533–25541. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b07004
Wang NN, Wang H, Wang YY, Wei YH, Si JY, Yuen ACY et al (2019) Robust, lightweight, hydrophobic, and fire-retarded Polyimide/MXene Aerogels for effective oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(43):40512–40523. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b14265
Xiao J, Lv W, Song Y, Zheng Q (2018) Graphene/nanofiber aerogels: Performance regulation towards multiple applications in dye adsorption and oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 338:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.156
Li Z, Zhong L, Zhang T, Qiu F, Yue X, Yang D (2019) Sustainable, flexible, and superhydrophobic functionalized cellulose aerogel for selective and versatile oil/water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(11):9984–9994. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b01122
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by Fujian Provincial Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant 2018J01755).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhuofeng Yan: Conceptualization, Verification, Writing manuscript. Qian Liu: Resources, Investigation, Software. Kaixiao Zhu: Resources. Xiangqi Li: Supervision, Writing—review. Xiao Wu: Reviewing & editing manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Z., Zhu, K., Li, X. et al. Recyclable Bacterial Cellulose Aerogel for Oil and Water Separation. J Polym Environ 30, 2774–2784 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02369-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02369-y